Agesilaus II was king of Sparta from c. 400 to c. 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War. Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC.

The Second Peloponnesian War, often called simply the Peloponnesian War, was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.
Year 404 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Volusus, Cossus, Fidenas, Ambustus, Maluginensis and Rutilus. The denomination 404 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

This article concerns the period 409 BC – 400 BC.

Lysander was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus.
Year 403 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Mamercinus, Varus, Potitus, Iullus, Crassus and Fusus. The denomination 403 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Thrasybulus was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the ultimately successful democratic resistance to the coup. As general, he was responsible for recalling the controversial nobleman Alcibiades from exile, and the two worked together extensively over the next several years. In 411 and 410, Thrasybulus was in command along with Alcibiades and others at several critical Athenian naval victories.

Conon was an Athenian general at the end of the Peloponnesian War, who led the Athenian naval forces when they were defeated by a Peloponnesian fleet in the crucial Battle of Aegospotami; later he contributed significantly to the restoration of Athens' political and military power.

Theramenes was an Athenian military leader and statesman, prominent in the final decade of the Peloponnesian War. He was active during the two periods of oligarchic government at Athens, the 400 and later the Thirty Tyrants, as well as in the trial of the generals who had commanded at Arginusae in 406 BC. A moderate oligarch, he often found himself caught between the democrats on the one hand and the extremist oligarchs on the other. Successful in replacing a narrow oligarchy with a broader one in 411 BC, he failed to achieve the same end in 404 BC, and was executed by the extremists whose policies he had opposed.
Spartan hegemony refers to the period of dominance by Sparta in Greek affairs from 404 to 371 BC. Even before this period the polis of Sparta was the greatest military land power of classical Greek antiquity and governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. The defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431–404 BC resulted in a short-lived Spartan dominance of the southern Greek world from 404 to 371 BC. Due to their mistrust of others, Spartans discouraged the creation of records about their internal affairs. The only histories of Sparta are from the writings of Xenophon, Thucydides, Herodotus and Plutarch, none of whom were Spartans. Plutarch was writing several centuries after the period of Spartan hegemony had ceased. This creates difficulties in understanding the Spartan political system, which was distinctly different from any other Greek polis.
The Battle of Aegospotami was a naval confrontation that took place in 405 BC and was the last major battle of the Peloponnesian War. In the battle, a Spartan fleet under Lysander destroyed the Athenian navy. This effectively ended the war, since Athens could not import grain or communicate with its empire without control of the sea.
The Thirty Tyrants were an oligarchy that briefly ruled Athens from 404 BC to 403 BC. Installed into power by the Spartans after the Athenian surrender in the Peloponnesian War, the Thirty became known for their tyrannical rule, first being called "The Thirty Tyrants" by Polycrates. Although they maintained power for only eight months, their reign resulted in the killing of 5% of the Athenian population, the confiscation of citizens' property, and the exile of other democratic supporters.
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs.
Agis II was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.
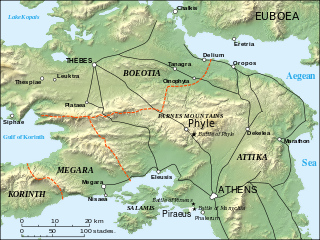
The Battle of Phyle was fought between Athenian exiles who were seeking to restore democracy to Athens and a Spartan garrison trying to protect the oligarchic Thirty Tyrants. In the battle, 700 Athenian exiles under Thrasybulus decisively defeated Spartans and their Athenian cavalry in a dawn ambush.

The Battle of Munychia was fought between Athenians exiled by the oligarchic government of the Thirty Tyrants and the forces of that government, supported by a Spartan garrison. In the battle, a substantially superior force composed of the Spartan garrison of Athens and the army of the oligarchic government attacked a hill in Piraeus which had been seized by 1,000 exiles under Thrasybulus, but was defeated. After this defeat, the Thirty Tyrants were forced to flee to Eleusis.

The Battle of Piraeus was fought in 403 BC between Athenian exiles who had defeated the government of the Thirty Tyrants and occupied Piraeus and a Spartan force sent to combat them. In the battle, the Spartans narrowly defeated the exiles, with both sides suffering appreciable casualties. After the battle, Pausanias arranged a settlement between the two parties which allowed the reestablishment of democratic government in Athens.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining mathematics, science, artistic thought, theatre, literature, philosophy, and politics of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.

The history of Sparta describes the history of the ancient Doric Greek city-state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, as Allied State, in 146 BC, a period of roughly 1000 years. Since the Dorians were not the first to settle the valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnesus of Greece, the preceding Mycenaean and Stone Age periods are described as well. Sparta went on to become a district of modern Greece. Brief mention is made of events in the post-classical periods.

Pausanias was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander.










