| Italiot Greek | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Italy |
| Region | Salento, Calabria |
| Ethnicity | Griko people |
| Greek alphabet, Latin alphabet | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | apul1236 Apulia-Calabrian Greek |
| IETF | el-IT |
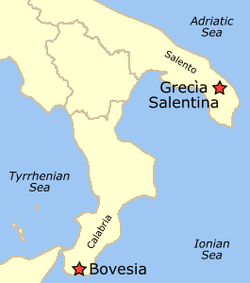 Location map of the Italiot-speaking areas in Salento and Calabria | |
Italiot Greek, also known as Italic-Greek, Salentino-Calabrian Greek or Apulia-Calabrian Greek, is a pair of varieties of Modern Greek spoken in Italy by the Griko people.
The Italiot Greek varieties are spoken in areas of southern Italy, a historical remnant of Magna Graecia. There are two small Griko-speaking communities known as the Griko people who live in the Italian regions of Calabria, the southern tip of the Italian peninsula, and in Apulia, its southeasternmost corner. These varieties too are thought to have developed on the basis of an originally Doric ancient dialect, and have preserved some elements of it, though to a lesser extent than Tsakonian. They subsequently adopted influences from ancient Koiné, but became isolated from the rest of the Greek-speaking world after the decline of Byzantine rule in Italy during the Middle Ages. [1] Among their linguistic peculiarities, besides influences from local Romance languages, is the preservation of the infinitive, which was lost in the modern Greek of the Balkans. Like Greek dialects in Asia Minor, the adjectival syntax of demonstratives is being lost in Italiot Greek. [2]
The dialects are:
- Griko, spoken in Salento
- Calabrian Greek, spoken in southern Calabria, also known as Bovese [3]