History
The earliest known mention of Albanian writings comes from a French Catholic church document from 1332. [13] [14] Written either by archbishop Guillaume Adam or the monk Brocardus Monacus the report notes that "Licet Albanenses aliam omnino linguam a latina habeant et diversam, tamen litteram latinam habent in usu et in omnibus suis libris" ('Though the Albanians have a language entirely their own and different from Latin, they nevertheless use Latin letters in all their books'). [13] [14] Scholars warn that this could mean Albanians also wrote in the Latin language, not necessarily just Albanian with a Latin script. [15]
The history of the later Albanian alphabet is closely linked with the influence of religion among Albanians. The writers from the North of Albania used Latin letters under the influence of the Catholic Church, those from the South of Albania under the Greek Orthodox church used Greek letters, while others used Arabic letters under the influence of Islam. There were also attempts for an original Albanian alphabet in the period of 1750–1850. The current alphabet in use among Albanians is one of the two variants approved in the Congress of Manastir held by Albanian intellectuals from 14 to 22 November 1908, in Manastir (Bitola, North Macedonia).
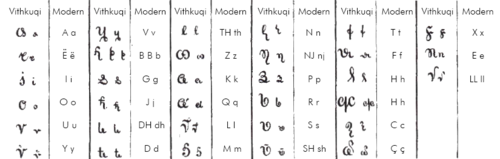
Alphabet used in early literature
The first certain document in Albanian is the Formula e pagëzimit (1462) (baptismal formula), issued by Pal Engjëlli (1417–1470); it was written in Latin characters. [16] It was a simple phrase that was supposed to be used by the relatives of a dying person if they could not make it to churches during the troubled times of the Ottoman invasion.
Also, the five Albanian writers of the 16th and 17th centuries (Gjon Buzuku, Lekë Matrënga, Pjetër Budi, Frang Bardhi and Pjetër Bogdani) who form the core of early Albanian literature, all used a Latin alphabet for their Albanian books; this alphabet remained in use by writers in northern Albania until the beginning of the 20th century.
The Greek intellectual Anastasios Michael, in his speech to the Berlin Academy (c. 1707) mentions an Albanian alphabet produced "recently" by Kosmas from Cyprus, bishop of Dyrrachium. It is assumed that this is the alphabet used later for the "Gospel of Elbasan". Anastasios calls Kosmas the "Cadmus of Albania". [17]
National awakening 19th-century endeavours

In 1857 Kostandin Kristoforidhi, an Albanian scholar and translator, drafted in Istanbul, Ottoman Empire, a Memorandum for the Albanian language. He then went to Malta, where he stayed until 1860 in a Protestant seminary, finishing the translation of The New Testament in the Tosk and Gheg dialects. He was helped by Nikolla Serreqi from Shkodër with the Gheg version of the New Testament. Nikolla Serreqi was also the propulsor for the use of the Latin script for the translation of the New Testament, which had already been used by the early writers of the Albanian literature; Kristoforidhi enthusiastically embraced the idea of a Latin alphabet. [18]
In November 1869, a Commission for the Alphabet of the Albanian Language was gathered in Istanbul. One of its members was Kostandin Kristoforidhi and the main purpose of the commission was the creation of a unique alphabet for all the Albanians. In January 1870 the commission ended its work of the standardisation of the alphabet, which was mainly in Latin letters. A plan on the creation of textbooks and spread of Albanian schools was drafted. However this plan was not realized, because the Ottoman government would not finance the expenses for the establishment of such schools. [19]
Although this commission had gathered and delivered an alphabet in 1870, the writers from the North still used the Latin-based alphabet, whereas in southern Albania writers used mostly the Greek letters. In southern Albania, the main activity of Albanian writers consisted in translating Greek Orthodox religious texts, and not in forming any kind of literature which could form a strong tradition for the use of Greek letters. As the albanologist Robert Elsie has written: [20]
The predominance of Greek as the language of Christian education and culture in southern Albania and the often hostile attitude of the Orthodox church to the spread of writing in Albanian made it impossible for an Albanian literature in Greek script to evolve. The Orthodox church, as the main vehicle of culture in the southern Balkans, while intent on spreading Christian education and values, was never convinced of the utility of writing in the vernacular as a means of converting the masses, as the Catholic church in northern Albania had been, to a certain extent, during the Counter-Reformation. Nor, with the exception of the ephemeral printing press in Voskopoja, did the southern Albanians ever have at their disposal publishing facilities like those available to the clerics and scholars of Catholic Albania in Venice and Dalmatia. As such, the Orthodox tradition in Albanian writing, a strong cultural heritage of scholarship and erudition, though one limited primarily to translations of religious texts and to the compilation of dictionaries, was to remain a flower which never really blossomed.
The turning point was the aftermath of the League of Prizren (1878) events when in 1879 Sami Frashëri and Naim Frashëri formed the Society for the Publication of Albanian Writings. Sami Frashëri, Koto Hoxhi, Pashko Vasa and Jani Vreto created an alphabet.[ citation needed ] This was based on the principle of "one sound one letter" (although the revision of 1908 replaced the letter ρ with the rr digraph to avoid confusion with p). This was called the "Istanbul alphabet" (also "Frashëri alphabet"). In 1905 this alphabet was in widespread use in all Albanian territory, North and South, including Catholic, Muslim and Orthodox areas.
One year earlier, in 1904 had been published the Albanian dictionary (Albanian : Fjalori i Gjuhës Shqipe) of Kostandin Kristoforidhi, after the author's death. The dictionary had been drafted 25 years before its publication and was written in the Greek alphabet. [21]
The so-called Bashkimi alphabet was designed by the Society for the Unity of the Albanian Language for being written on a French typewriter and includes no diacritics other than é (compared to ten graphemes of the Istanbul alphabet which were either non-Latin or had diacritics).
Congress of Manastir

In 1908, the Congress of Manastir was held by Albanian intellectuals in Bitola, in what is now the Republic of North Macedonia. The Congress was hosted by the Bashkimi ("unity") club, and prominent delegates included Gjergj Fishta, Ndre Mjeda, Mit'hat Frashëri, Sotir Peçi, Shahin Kolonja, and Gjergj D. Qiriazi. There was much debate and the contending alphabets were Istanbul, Bashkimi and Agimi. However, the Congress was unable to make a clear decision and opted for a compromise solution of using both the widely used Istanbul, with minor changes, and a modified version of the Bashkimi alphabet. Usage of the alphabet of Istanbul declined rapidly and it was essentially extinct over the following decades, due largely to its inconvenience in requiring new custom-made glyphs that Bashkimi did not.
During 1909 and 1910 there were movements by members of the Young Turks to adopt an Arabic alphabet, as they considered the Latin script to be un-Islamic. In Korçë and Gjirokastër, demonstrations took place favoring the Latin script, and in Elbasan, Muslim clerics led a demonstration for the Arabic script, telling their congregations that using the Latin script would make them infidels. In 1911, the Young Turks dropped their opposition to the Latin script; finally, the Latin Bashkimi alphabet was adopted, and is still in use today.
The modifications to the Bashkimi alphabet were made to include characters used in the Istanbul and Agimi alphabets. Ç was chosen over ch since c with cedilla could be found on every typewriter, given its use in French. Other changes were more esthetic and as a way to combine the three scripts.
| Alphabetical order: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 |
| IPA: | [a ɑ ɒ] | [b] | [ts] | [tʃ] | [d] | [ð] | [e ɛ] | [ə] | [f] | [ɡ] | [ɟ] | [h ħ] | [i] | [j] | [k q] | [l] | [ɫ] | [m] | [n] | [ɲ] | [o ɔ] | [p] | [c tɕ] | [ɹ] | [r] | [s] | [ʃ] | [t] | [θ] | [u] | [v] | [dz] | [dʒ] | [y] | [z] | [ʒ] |
| Old Bashkimi alphabet: | A a | B b | Ts ts | Ch ch | D d | Dh dh | É é | E e | F f | G g | Gh gh | H h | I i | J j | K k | L l | Ll ll | M m | N n | Gn gn | O o | P p | C c | R r | Rr rr | S s | Sh sh | T t | Th th | U u | V v | Z z | Zh zh | Y y | X x | Xh xh |
| Manastir alphabet (modified Bashkimi, current alphabet): | C c | Ç ç | E e | Ë ë | Gj gj | Nj nj | Q q | X x | Xh xh | Z z | Zh zh |
A second congress at Manastir (Bitola) was held in April 1910, which confirmed the decision taken in the first congress of Manastir. After Albanian independence in 1912, there were two alphabets in use. Following the events of the Balkan wars and World War I, the Bashkimi variant dominated. The Bashkimi alphabet is at the origin of the official alphabet of the Albanian language in use today. The digraphs of the Albanian alphabet are the letters Dh, Gj, Ll, Nj, Rr, Sh, Th, Xh, and Zh.