| Slavic | |
|---|---|
| Slavonic | |
| Geographic distribution | Throughout Central Europe, Eastern Europe, and Southeast Europe, plus Central Asia and North Asia (Siberia) |
| Ethnicity | Slavs |
Native speakers | c. 315 million (2001) [1] |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Slavic |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | sla |
| Linguasphere | 53 (phylozone) |
| Glottolog | slav1255 |
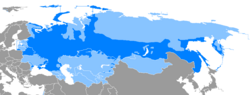
 Political map of Europe with countries where a Slavic language is a national language East Slavic languages South Slavic languages West Slavic languages | |
The Slavic languages, also known as the Slavonic languages, are Indo-European languages spoken primarily by the Slavic peoples and their descendants. They are thought to descend from a proto-language called Proto-Slavic, spoken during the Early Middle Ages, which in turn is thought to have descended from the earlier Proto-Balto-Slavic language, linking the Slavic languages to the Baltic languages in a Balto-Slavic group within the Indo-European family.
Contents
- Branches
- History
- Common roots and ancestry
- Differentiation
- Linguistic history
- Features
- Consonants
- Vowels
- Length, accent, and tone
- Grammar
- Selected cognates
- Influence on neighboring languages
- Germanic languages
- Finno-Ugric languages
- Other
- Detailed list
- See also
- Notes
- Citations
- References
- General references
- External links
The current geographical distribution of natively spoken Slavic languages includes the Balkans, Central and Eastern Europe, and all the way from Western Siberia to the Russian Far East. Furthermore, the diasporas of many Slavic peoples have established isolated minorities of speakers of their languages all over the world. The number of speakers of all Slavic languages together was estimated to be 315 million at the turn of the twenty-first century. [1] It is the largest and most diverse ethno-linguistic group in Europe. [2] [3]
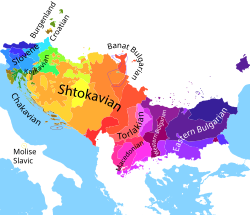
The Slavic languages are conventionally (that is, also on the basis of extralinguistic features, such as geography) divided into three subgroups: East, South, and West, which together constitute more than 20 languages. Of these, 10 have at least one million speakers and official status as the national languages of the countries in which they are predominantly spoken: Russian, Belarusian and Ukrainian (of the East group), Polish, Czech and Slovak (of the West group), Bulgarian and Macedonian (eastern members of the South group), and Serbo-Croatian and Slovene (western members of the South group). In addition, Aleksandr Dulichenko recognizes a number of Slavic microlanguages: both isolated ethnolects and peripheral dialects of more well-established Slavic languages. [4] [5] [ page needed ] [6]
All Slavic languages have fusional morphology and, with a partial exception of Bulgarian and Macedonian, they have fully developed inflection-based conjugation and declension. In their relational synthesis Slavic languages distinguish between lexical and inflectional suffixes. In all cases, the lexical suffix precedes the inflectional in an agglutination mode. The fusional categorization of Slavic languages is based on grammatic inflectional suffixes alone.
Prefixes are also used, particularly for lexical modification of verbs. For example, the equivalent of English "came out" in Russian is "vyshel", where the prefix "vy-" means "out", the reduced root "-sh" means "come", and the suffix "-el" denotes past tense of masculine gender. The equivalent phrase for a feminine subject is "vyshla". The gender conjugation of verbs, as in the preceding example, is another feature of some Slavic languages rarely found in other language groups.
The well-developed fusional grammar allows Slavic languages to have a somewhat unusual feature of virtually free word order in a sentence clause, although subject–verb–object and adjective-before-noun is the preferred order in the neutral style of speech. [7]
Modern Bulgarian differs from other Slavic languages, because it almost completely lost declension, it developed definite articles from demonstrative pronouns (similar to "the" from "this" in English), and it formed indicative and renarrative tenses for verbs. [8]