A request that this article title be changed to Tocharian B is under discussion . Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (May 2025)Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Kuchean | |
|---|---|
| Tocharian B | |
| Kuśiññe | |
 Tocharian inscription "This Buddha was painted by the hand of Sanketava" | |
| Native to | Kucha |
| Region | Tarim Basin |
| Ethnicity | Tocharians |
| Extinct | 9th century AD |
Indo-European
| |
Early form | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | txb |
xtb Tocharian B | |
| Glottolog | tokh1243 |
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
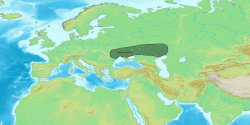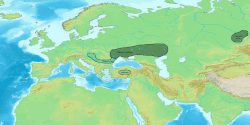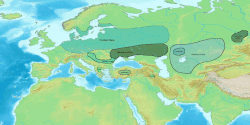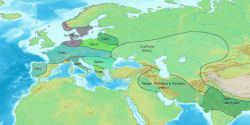 |
Kuchean (also known as Tocharian B or West Tocharian) was a Western member of the Tocharian branch of Indo-European languages, extinct from the ninth century. Once spoken in the Tarim Basin in Central Asia, Tocharian B shows an internal chronological development; three linguistic stages have been detected. [1] The oldest stage is attested only in Kucha. There is also the middle ('classicalʼ), and the late stage. [2]