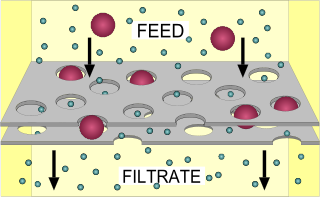
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

A Büchner funnel is a piece of laboratory equipment used in filtration. It is traditionally made of porcelain, but glass and plastic funnels are also available. On top of the funnel-shaped part there is a cylinder with a fritted glass disc/perforated plate separating it from the funnel. The Hirsch funnel has a similar design; it is used similarly, but for smaller quantities of material. The main difference is that the plate of a Hirsch funnel is much smaller, and the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical.

Crystallization is the process by which solids form, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation.
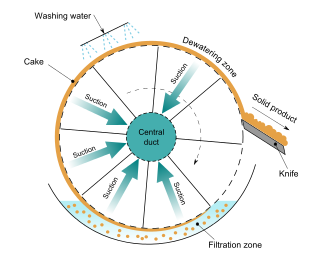
A Rotary Vacuum Filter Drum consists of a cylindrical filter membrane that is partly sub-merged in a slurry to be filtered. The inside of the drum is held lower than the ambient pressure. As the drum rotates through the slurry, the liquid is sucked through the membrane, leaving solids to cake on the membrane surface while the drum is submerged. A knife or blade is positioned to scrape the product from the surface.

The Schlenk line is a commonly used chemistry apparatus developed by Wilhelm Schlenk. It consists of a dual manifold with several ports. One manifold is connected to a source of purified inert gas, while the other is connected to a vacuum pump. The inert-gas line is vented through an oil bubbler, while solvent vapors and gaseous reaction products are prevented from contaminating the vacuum pump by a liquid-nitrogen or dry-ice/acetone cold trap. Special stopcocks or Teflon taps allow vacuum or inert gas to be selected without the need for placing the sample on a separate line.

In chemical engineering, biochemical engineering and protein purification, cross-flow filtration is a type of filtration. Cross-flow filtration is different from dead-end filtration in which the feed is passed through a membrane or bed, the solids being trapped in the filter and the filtrate being released at the other end. Cross-flow filtration gets its name because the majority of the feed flow travels tangentially across the surface of the filter, rather than into the filter. The principal advantage of this is that the filter cake is substantially washed away during the filtration process, increasing the length of time that a filter unit can be operational. It can be a continuous process, unlike batch-wise dead-end filtration.
Ceramic foam is a tough foam made from ceramics. Manufacturing techniques include impregnating open-cell polymer foams internally with ceramic slurry and then firing in a kiln, leaving only ceramic material. The foams may consist of several ceramic materials such as aluminium oxide, a common high-temperature ceramic, and gets insulating properties from the many tiny air-filled voids within the material.

An industrial filter press is a tool used in separation processes, specifically to separate solids and liquids. The machine stacks many filter elements and allows the filter to be easily opened to remove the filtered solids, and allows easy cleaning or replacement of the filter media.
A vacuum ceramic filter is designed to separate liquids from solids for dewatering of ore concentrates purposes. The device consists of a rotator, slurry tank, ceramic filter plate, distributor, discharge scraper, cleaning device, frame, agitating device, pipe system, vacuum system, automatic acid dosing system, automatic lubricating system, valve and discharge chute. The operation and construction principle of vacuum ceramic filter resemble those of a conventional disc filter, but the filter medium is replaced by a finely porous ceramic disc. The disc material is inert, has a long operational life and is resistant to almost all chemicals. Performance can be optimized by taking into account all those factors which affect the overall efficiency of the separation process. Some of the variables affecting the performance of a vacuum ceramic filter include the solid concentration, speed rotation of the disc, slurry level in the feed basin, temperature of the feed slurry, and the pressure during dewatering stages and filter cake formation.
Electrofiltration is a method that combines membrane filtration and electrophoresis in a dead-end process.
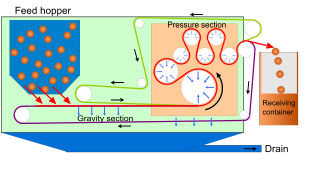
The belt filter is an industrial machine, used for solid/liquid separation processes, particularly the dewatering of sludges in the chemical industry, mining and water treatment. Belt filter presses are also used in the production of apple juice, cider and winemaking. The process of filtration is primarily obtained by passing a pair of filtering cloths and belts through a system of rollers. The system takes a sludge or slurry as a feed, and separates it into a filtrate and a solid cake.

Laboratory funnels are funnels that have been made for use in the chemical laboratory. There are many different kinds of funnels that have been adapted for these specialized applications. Filter funnels, thistle funnels, and dropping funnels have stopcocks which allow the fluids to be added to a flask slowly. For solids, a powder funnel with a short and wide neck/stem is more appropriate as it prevents clogging.
Membrane technology encompasses the scientific processes used in the construction and application of membranes. Membranes are used to facilitate the transport or rejection of substances between mediums, and the mechanical separation of gas and liquid streams. In the simplest case, filtration is achieved when the pores of the membrane are smaller than the diameter of the undesired substance, such as a harmful microorganism. Membrane technology is commonly used in industries such as water treatment, chemical and metal processing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, the food industry, as well as the removal of environmental pollutants.

A filter drier is a piece of process equipment used during the filtration and drying phase of a pharmaceutical, bio pharmaceutical or chemical process for an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or other compounds production. Filter dryers are designed for washing and isolating solids with or without integrated containment systems.

A pusher centrifuge is a type of filtration technique that offers continuous operation to de-water and wash materials such as relatively in-compressible feed solids, free-draining crystalline, polymers and fibrous substances. It consists of a constant speed rotor and is fixed to one of several baskets. This assembly is applied with centrifugal force that is generated mechanically for smaller units and hydraulically for larger units to enable separation.
The peeler centrifuge is a device that performs by rotating filtration basket in an axis. A centrifuge follows on the principle of centrifugal force to separate solids from liquids by density difference. High rotation speed provides high centrifugal force that allows the suspended solid in feed to settle on the inner surface of basket. There are three kinds of centrifuge, horizontal, vertical peeler centrifuge and siphon peeler centrifuge. These classes of instrument apply to various areas such as fertilisers, pharmaceutical, plastics and food including artificial sweetener and modified starch.

A solid bowl centrifuge is a type of centrifuge that uses the principle of sedimentation. A centrifuge is used to separate a mixture that consists of two substances with different densities by using the centrifugal force resulting from continuous rotation. It is normally used to separate solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, and solid-solid mixtures. Solid bowl centrifuges are widely used in various industrial applications, such as wastewater treatment, coal manufacturing, and polymer manufacturing. One advantage of solid bowl centrifuges for industrial uses is the simplicity of installation compared to other types of centrifuge. There are three design types of solid bowl centrifuge, which are conical, cylindrical, and conical-cylindrical.
A conical plate centrifuge is a type of centrifuge that has a series of conical discs which provides a parallel configuration of centrifugation spaces.
Screen/Scroll centrifuge is a filtering or screen centrifuge which is also known as worm screen or conveyor discharge centrifuge. This centrifuge was first introduced in the midst of 19th century. After developing new technologies over the decades, it is now one of the widely used processes in many industries for the separation of crystalline, granular or fibrous materials from a solid-liquid mixture. Also, this process is considered to dry the solid material. This process has been some of the most frequently seen within, especially, coal preparation industry. Moreover, it can be found in other industries such as chemical, environmental, food and other mining fields.
Pile Cloth Media Filtration is a mechanical process for the separation of organic and inorganic solids from liquids. It belongs to the processes of surface filtration and cake filtration where, in addition to the sieve effect, real filtration effects occur over the depth of the pile layer. Pile Cloth Media Filtration represents a branch of cloth filtration processes and is used for water and wastewater treatment in medium and large scale. In Pile Cloth Media Filtration, three-dimensional textile fabrics are used as filter media. During the filter cleaning of the pile layer the filtration process continues and is not interrupted.












