
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the claimant while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the verifier. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity.
An authenticator is a means used to confirm a user's identity, that is, to perform digital authentication. A person authenticates to a computer system or application by demonstrating that he or she has possession and control of an authenticator. In the simplest case, the authenticator is a common password.

Authentication is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. It might involve validating personal identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product or document is not counterfeit.
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance.
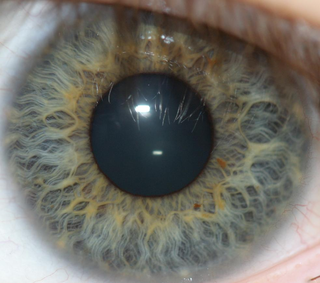
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.
Speaker recognition is the identification of a person from characteristics of voices. It is used to answer the question "Who is speaking?" The term voice recognition can refer to speaker recognition or speech recognition. Speaker verification contrasts with identification, and speaker recognition differs from speaker diarisation.
Self-service password reset (SSPR) is defined as any process or technology that allows users who have either forgotten their password or triggered an intruder lockout to authenticate with an alternate factor, and repair their own problem, without calling the help desk. It is a common feature in identity management software and often bundled in the same software package as a password synchronization capability.
Living in the intersection of cryptography and psychology, password psychology is the study of what makes passwords or cryptographic keys easy to remember or guess.
In computer security, shoulder surfing is a type of social engineering technique used to obtain information such as personal identification numbers (PINs), passwords and other confidential data by looking over the victim's shoulder. Unauthorized users watch the keystrokes inputted on a device or listen to sensitive information being spoken, which is also known as eavesdropping.
Electronic authentication is the process of establishing confidence in user identities electronically presented to an information system. Digital authentication, or e-authentication, may be used synonymously when referring to the authentication process that confirms or certifies a person's identity and works. When used in conjunction with an electronic signature, it can provide evidence of whether data received has been tampered with after being signed by its original sender. Electronic authentication can reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft by verifying that a person is who they say they are when performing transactions online.
PerSay was an Israeli start-up company specializing in Voice Biometrics technology. Founded in 2000, its voice biometrics systems are used in the banking, insurance, governments, and telecommunications industries worldwide.
Daon is an international biometrics and identity assurance software company founded in 1999 by Irish entrepreneur Dermot Desmond. The name, Daon, was chosen because it stems from the Celtic word for human being, duine daonna. Daon is headquartered just miles outside of Washington, DC in Fairfax, VA. Daon also has major operations in Dublin, located in the International Financial Services Center (IFSC). It has an additional offices in Belgrade, Serbia and Canberra, Australia.
Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.

Vein matching, also called vascular technology, is a technique of biometric identification through the analysis of the patterns of blood vessels visible from the surface of the skin. Though used by the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Central Intelligence Agency, this method of identification is still in development and has not yet been universally adopted by crime labs as it is not considered as reliable as more established techniques, such as fingerprinting. However, it can be used in conjunction with existing forensic data in support of a conclusion.
A whole new range of techniques has been developed to identify people since the 1960s from the measurement and analysis of parts of their bodies to DNA profiles. Forms of identification are used to ensure that citizens are eligible for rights to benefits and to vote without fear of impersonation while private individuals have used seals and signatures for centuries to lay claim to real and personal estate. Generally, the amount of proof of identity that is required to gain access to something is proportionate to the value of what is being sought. It is estimated that only 4% of online transactions use methods other than simple passwords. Security of systems resources generally follows a three-step process of identification, authentication and authorization. Today, a high level of trust is as critical to eCommerce transactions as it is to traditional face-to-face transactions.
Eye vein verification is a method of biometric authentication that applies pattern-recognition techniques to video images of the veins in a user's eyes. The complex and random patterns are unique, and modern hardware and software can detect and differentiate those patterns at some distance from the eyes.
Identity-based security is a type of security that focuses on access to digital information or services based on the authenticated identity of an entity. It ensures that the users and services of these digital resources are entitled to what they receive. The most common form of identity-based security involves the login of an account with a username and password. However, recent technology has evolved into fingerprinting or facial recognition.
EyeVerify, Inc. is a biometric security technology company based in Kansas City, Missouri owned by Ant Group. Its chief product, Eyeprint ID, provides verification using eye veins and other micro-features in and around the eye. Images of the human eye are used to authenticate mobile device users. EyeVerify licenses its software for use in mobile banking applications, such as those offered by Tangerine Bank, NCR/Digital Insight and Wells Fargo.

A biometric device is a security identification and authentication device. Such devices use automated methods of verifying or recognising the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial images, iris and voice recognition.
Passwordless authentication is an authentication method in which a user can log in to a computer system without the entering a password or any other knowledge-based secret. In most common implementations users are asked to enter their public identifier and then complete the authentication process by providing a secure proof of identity through a registered device or token.






