
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data, combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations.

In psychology, decision-making is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either rational or irrational. The decision-making process is a reasoning process based on assumptions of values, preferences and beliefs of the decision-maker. Every decision-making process produces a final choice, which may or may not prompt action.
Cost–benefit analysis (CBA), sometimes also called benefit–cost analysis, is a systematic approach to estimating the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives. It is used to determine options which provide the best approach to achieving benefits while preserving savings in, for example, transactions, activities, and functional business requirements. A CBA may be used to compare completed or potential courses of action, and to estimate or evaluate the value against the cost of a decision, project, or policy. It is commonly used to evaluate business or policy decisions, commercial transactions, and project investments. For example, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission must conduct cost-benefit analyses before instituting regulations or deregulations.
Managerial economics is a branch of economics involving the application of economic methods in the managerial decision-making process. Economics is the study of the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services. Managerial economics involves the use of economic theories and principles to make decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life-cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The systems development life cycle concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.

Life cycle assessment or LCA is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufactured product, environmental impacts are assessed from raw material extraction and processing (cradle), through the product's manufacture, distribution and use, to the recycling or final disposal of the materials composing it (grave).
Sensitivity analysis is the study of how the uncertainty in the output of a mathematical model or system can be divided and allocated to different sources of uncertainty in its inputs. A related practice is uncertainty analysis, which has a greater focus on uncertainty quantification and propagation of uncertainty; ideally, uncertainty and sensitivity analysis should be run in tandem.
A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM), also known as RACI matrix or linear responsibility chart (LRC), describes the participation by various roles in completing tasks or deliverables for a project or business process. RACI is an acronym derived from the four key responsibilities most typically used: responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed. It is used for clarifying and defining roles and responsibilities in cross-functional or departmental projects and processes. There are a number of alternatives to the RACI model.
Decision analysis (DA) is the discipline comprising the philosophy, methodology, and professional practice necessary to address important decisions in a formal manner. Decision analysis includes many procedures, methods, and tools for identifying, clearly representing, and formally assessing important aspects of a decision; for prescribing a recommended course of action by applying the maximum expected-utility axiom to a well-formed representation of the decision; and for translating the formal representation of a decision and its corresponding recommendation into insight for the decision maker, and other corporate and non-corporate stakeholders.
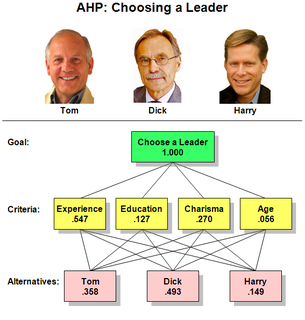
In the theory of decision making, the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), also analytical hierarchy process, is a structured technique for organizing and analyzing complex decisions, based on mathematics and psychology. It was developed by Thomas L. Saaty in the 1970s; Saaty partnered with Ernest Forman to develop Expert Choice software in 1983, and AHP has been extensively studied and refined since then. It represents an accurate approach to quantifying the weights of decision criteria. Individual experts’ experiences are utilized to estimate the relative magnitudes of factors through pair-wise comparisons. Each of the respondents compares the relative importance each pair of items using a specially designed questionnaire.
The Information Services Procurement Library (ISPL) is a best practice library for the management of Information Technology related acquisition processes. It helps both the customer and supplier organization to achieve the desired quality using the corresponded amount of time and money by providing methods and best practices for risk management, contract management, and planning. ISPL focuses on the relationship between the customer and supplier organization: It helps constructing the request for proposal, it helps constructing the contract and delivery plan according to the project situation and risks, and it helps monitoring the delivery phase. ISPL is a unique Information Technology method because where most other Information Technology methods and frameworks focus on development, ISPL focuses purely on the procurement of information services. The target audience for ISPL consists of procurement managers, acquisition managers, programme managers, contract managers, facilities managers, service level managers, and project managers in the IT area. Because of ISPL's focus on procurement it is very suitable to be used with ITIL and PRINCE2.

The Wisdom of Crowds: Why the Many Are Smarter Than the Few and How Collective Wisdom Shapes Business, Economies, Societies and Nations, published in 2004, is a book written by James Surowiecki about the aggregation of information in groups, resulting in decisions that, he argues, are often better than could have been made by any single member of the group. The book presents numerous case studies and anecdotes to illustrate its argument, and touches on several fields, primarily economics and psychology.
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the user experience. In computer or software design, user interface (UI) design is the process of building interfaces that are aesthetically pleasing. Designers aim to build interfaces that are easy and pleasant to use. UI design refers to graphical user interfaces and other forms of interface design. The goal of user interface design is to make the user's interaction as simple and efficient as possible, in terms of accomplishing user goals.
The engineering design process is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative - parts of the process often need to be repeated many times before another can be entered - though the part(s) that get iterated and the number of such cycles in any given project may vary.
For the application of engineering economics in the practice of civil engineering see Engineering economics.
A phase-gate process is a project management technique in which an initiative or project is divided into distinct stages or phases, separated by decision points.
Decision-making software is software for computer applications that help individuals and organisations make choices and take decisions, typically by ranking, prioritizing or choosing from a number of options.
Robust decision-making (RDM) is an iterative decision analytic framework that aims to help identify potential robust strategies, characterize the vulnerabilities of such strategies, and evaluate the tradeoffs among them. RDM focuses on informing decisions under conditions of what is called "deep uncertainty", that is, conditions where the parties to a decision do not know or do not agree on the system model(s) relating actions to consequences or the prior probability distributions for the key input parameters to those model(s).
Decision quality (DQ) is the quality of a decision at the moment the decision is made, regardless of its outcome. Decision quality concepts permit the assurance of both effectiveness and efficiency in analyzing decision problems. In that sense, decision quality can be seen as an extension to decision analysis. Decision quality also describes the process that leads to a high-quality decision. Properly implemented, the DQ process enables capturing maximum value in uncertain and complex scenarios.

Value tree analysis is a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) implement by which the decision-making attributes for each choice to come out with a preference for the decision makes are weighted. Usually, choices' attribute-specific values are aggregated into a complete method. Decision analysts (DAs) distinguished two types of utility. The preferences of value are made among alternatives when there is no uncertainty. Risk preferences solves the attitude of DM to risk taking under uncertainty. This learning package focuses on deterministic choices, namely value theory, and in particular a decision analysis tool called a value tree.








