
Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper ores consists of a series of physical, chemical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.

Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower-grade ore than previously.

Heap leaching is an industrial mining process used to extract precious metals, copper, uranium, and other compounds from ore using a series of chemical reactions that absorb specific minerals and re-separate them after their division from other earth materials. Similar to in situ mining, heap leach mining differs in that it places ore on a liner, then adds the chemicals via drip systems to the ore, whereas in situ mining lacks these liners and pulls pregnant solution up to obtain the minerals. Heap leaching is widely used in modern large-scale mining operations as it produces the desired concentrates at a lower cost compared to conventional processing methods such as flotation, agitation, and vat leaching.

Mining in Western Australia, together with the petroleum industry in the state, accounted for 94% of the State's and 46% of Australia's income from total merchandise exports in 2019–20. The state of Western Australia hosted 123 predominantly higher value and export-oriented mining projects and hundreds of smaller quarries and mines. The principal projects produced more than 99 per cent of the industry's total sales value.

Antoine Marc Gaudin was a metallurgist who laid the foundation for understanding the scientific principles of the froth flotation process in the minerals industry. He was also a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and during World War II developed there the ore-processing techniques needed to extract uranium from its low grade ores for the Manhattan Project. He was a founding member of the National Academy of Engineering.
Mount Isa Mines Limited ("MIM") operates the Mount Isa copper, lead, zinc and silver mines near Mount Isa, Queensland, Australia as part of the Glencore group of companies. For a brief period in 1980, MIM was Australia's largest company. It has pioneered several significant mining industry innovations, including the Isa Process copper refining technology, the Isasmelt smelting technology, and the IsaMill fine grinding technology, and it also commercialized the Jameson Cell column flotation technology.

The Broken Hill Ore Deposit is located underneath Broken Hill in western New South Wales, Australia, and is the namesake for the town. It is arguably the world's richest and largest zinc-lead ore deposit.
The mineral industry of Kazakhstan is one of the most competitive and fastest growing sectors of the country. Kazakhstan ranks second to Russia among the countries of the CIS in its quantity of mineral production. It is endowed with large reserves of a wide range of metallic ores, industrial minerals, and fuels, and its metallurgical sector is a major producer of a large number of metals from domestic and imported raw materials. In 2005, its metal mining sector produced bauxite, chromite, copper, iron, lead, manganese, and zinc ores, and its metallurgical sector produced such metals as beryllium, bismuth, cadmium, copper, ferroalloys, lead, magnesium, rhenium, steel, titanium, and zinc. The country produced significant amounts of other nonferrous and industrial mineral products, such as alumina, arsenic, barite, gold, molybdenum, phosphate rock, and tungsten. The country was a large producer of mineral fuels, including coal, natural gas, oil, and uranium. The country's economy is heavily dependent on the production of minerals. Output from Kazakhstan's mineral and natural resources sector for 2004 accounted for 74.1% of the value of industrial production, of which 43.1% came from the oil and gas condensate extraction. In 2004, the mineral extraction sector accounted for 32% of the GDP, employed 191,000 employees, and accounted for 33.1% of capital investment and 64.5% of direct foreign investment, of which 63.5% was in the oil sector. Kazakhstan's mining industry is estimated at US$29.5 billion by 2017.
The second-largest mineral industry in the world is the mineral industry of Africa, which implies large quantities of resources due to Africa being the second largest continent, with 30.37 million square kilometres of land.With a population of 1.4 billion living there, mineral exploration and production constitute significant parts of their economies for many African countries and remain keys to economic growth. Africa is richly endowed with mineral reserves and ranks first in quantity of world reserves for bauxite, cobalt, industrial diamond, phosphate rock, platinum-group metals (PGM), vermiculite, and zirconium.

Mining is the biggest contributor to Namibia's economy in terms of revenue. It accounts for 25% of the country's income. Its contribution to the gross domestic product is also very important and makes it one of the largest economic sectors of the country. Namibia produces diamonds, uranium, copper, magnesium, zinc, silver, gold, lead, semi-precious stones and industrial minerals. The majority of revenue comes from diamond mining. In 2014, Namibia was the fourth-largest exporter of non-fuel minerals in Africa.
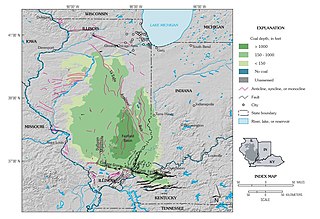
The Illinois Basin is a Paleozoic depositional and structural basin in the United States, centered in and underlying most of the state of Illinois, and extending into southwestern Indiana and western Kentucky. The basin is elongate, extending approximately 400 miles (640 km) northwest-southeast, and 200 miles (320 km) southwest-northeast.
The IsaMill is an energy-efficient mineral industry grinding mill that was jointly developed in the 1990s by Mount Isa Mines Limited and Netzsch Feinmahltechnik ("Netzsch"), a German manufacturer of bead mills. The IsaMill is primarily known for its ultrafine grinding applications in the mining industry, but is also being used as a more efficient means of coarse grinding. By the end of 2008, over 70% of the IsaMill’s installed capacity was for conventional regrinding or mainstream grinding applications, with target product sizes ranging from 25 to 60 µm.
Walter R. Hibbard Jr was an American metallurgist, a distinguished professor at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and the 11th director of the U.S. Bureau of Mines in President Johnson's administration.

The ISASMELT process is an energy-efficient smelting process that was jointly developed from the 1970s to the 1990s by Mount Isa Mines and the Government of Australia's CSIRO. It has relatively low capital and operating costs for a smelting process.
Mining in North Korea is important to the country's economy. North Korea is naturally abundant in metals such as magnesite, zinc, tungsten, and iron; with magnesite resources of 6 billion tonnes, particularly in the North and South Hamgyong Province and Chagang Province. However, often these cannot be mined due to the acute shortage of electricity in the country, as well as the lack of proper tools to mine these materials and an antiquated industrial base. Coal, iron ore, limestone, and magnesite deposits are larger than other mineral commodities. Mining joint ventures with other countries include China, Canada, Egypt, and South Korea.

The Jameson Cell is a high-intensity froth flotation cell that was invented by Laureate Professor Graeme Jameson of the University of Newcastle (Australia) and developed in conjunction with Mount Isa Mines Limited.

The mining industry of Morocco is important to the national economy. Morocco is the world's largest producer of phosphate, and contains about 75% of the world's estimated reserves. Mining contributed up to 35% of exports and 5% of GDP in 2011. Foreign investors have found the investment climate, the infrastructure, fiscal situation, and political stability very favorable to continue business in the country in this sector.
Louis-Édouard Rivot was a French metallurgist and mining engineer.
Alban Jude LynchAOHonFAusIMM was a mining engineer and academic who helped develop the mineral processing teaching experience for mining students in Australia.
Thomas Victor Falkie was an American mining engineer and educator. He served as the 14th director of the U.S. Bureau of Mines.











