Related Research Articles

The Stolen Generations were the children of Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander descent who were removed from their families by the Australian federal and state government agencies and church missions, under acts of their respective parliaments. The removals of those referred to as "half-caste" children were conducted in the period between approximately 1905 and 1967, although in some places mixed-race children were still being taken into the 1970s.
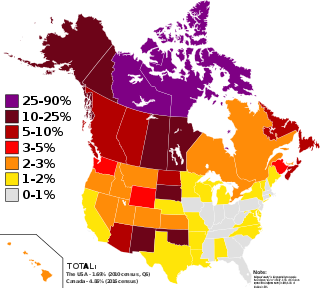
In Canada, Indigenous peoples comprise the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis. Although Indian is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors Indian and Eskimo have fallen into disuse in Canada, and many consider them to be pejorative. Aboriginal peoples as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, though in most Indigenous circles Aboriginal has also fallen into disfavour.
First Nations is a term used to identify Indigenous peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia.
Indigenous or Aboriginal rock is a style of music which mixes rock music with the instrumentation and singing styles of Indigenous peoples. Two countries with prominent Aboriginal rock scenes are Australia and Canada.

Koori is a demonym for Aboriginal Australians from a region that approximately corresponds to southern New South Wales and Victoria. The word derives from the Indigenous language Awabakal. For some people and groups, it has been described as a reclaiming of Indigenous language and culture, as opposed to relying on European titles such as "Aboriginal". The term is also used with reference to institutions involving Koori communities and individuals, such as the Koori Court, Koori Radio and Koori Knockout.

The Aboriginal Tent Embassy is a permanent protest occupation site as a focus for representing the political rights of Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islander people. Established on 26 January 1972, and celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2022, it is the longest continuous protest for Indigenous land rights in the world.

The Australian Aboriginal flag is the official flag of Aboriginal Australians. It was granted official status in 1995 under the Flags Act 1953, together with the Torres Strait Islander flag, in recognition of their status as Indigenous peoples of Australia. The two flags are often flown together with the Australian national flag.

Indigenous music of Australia comprises the music of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia, intersecting with their cultural and ceremonial observances, through the millennia of their individual and collective histories to the present day. The traditional forms include many aspects of performance and musical instrumentation that are unique to particular regions or Aboriginal Australian groups; and some elements of musical tradition are common or widespread through much of the Australian continent, and even beyond. The music of the Torres Strait Islanders is related to that of adjacent parts of New Guinea. Music is a vital part of Indigenous Australians' cultural maintenance.

Lowitja O'Donoghue, also known as Lois O'Donoghue and Lois Smart, was an Australian public administrator and Indigenous rights advocate. She was the inaugural chairperson of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission (ATSIC) from 1990 to 1996. She is known for her work in improving the health and welfare of Indigenous Australians, and also for the part she played in the drafting of the Native Title Act 1993, which established native title in Australia.
Reconciliation Australia is a non-government, not-for-profit foundation established in January 2001 to promote a continuing national focus for reconciliation between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. It was established by the Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation, which was established to create a framework for furthering a government policy of reconciliation in Australia.
NAIDOC Week is an Australian observance lasting from the first Sunday in July until the following Sunday. The acronym NAIDOC stands for National Aborigines' and Islanders' Day Observance Committee. NAIDOC Week has its roots in the 1938 Day of Mourning, becoming a week-long event in 1975.

Creative Australia, formerly known as the Australia Council for the Arts and the Australia Council, is the country's official arts council, serving as an arts funding and advisory body for the Government of Australia.

The Encyclopaedia of Aboriginal Australia: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander history, society and culture, edited by David Horton, is an encyclopaedia published by the Aboriginal Studies Press at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS) in 1994 and available in two volumes or on CD-ROM covering all aspects of Indigenous Australians lives and world. There are 2000 entries and 1000 photographs, with the CD-ROM having 250 sound items and 40 videos.
Australian Aboriginal culture includes a number of practices and ceremonies centered on a belief in the Dreamtime and other mythology. Reverence and respect for the land and oral traditions are emphasised. Over 300 languages and other groupings have developed a wide range of individual cultures. Due the colonization of Australia under terra nullius concept these cultures were treated as one monoculture. Australian Aboriginal art has existed for thousands of years and ranges from ancient rock art to modern watercolour landscapes. Aboriginal music has developed a number of unique instruments. Contemporary Australian Aboriginal music spans many genres. Aboriginal peoples did not develop a system of writing before colonisation, but there was a huge variety of languages, including sign languages.

National Indigenous Television (NITV) is an Australian free-to-air television channel that broadcasts programming produced and presented largely by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. It includes the six-day-a-week NITV News Update, with programming including other news and current affairs programmes, sports coverage, entertainment for children and adults, films and documentaries covering a range of topics. Its primary audience is Indigenous Australians, but many non-Indigenous people tune in to learn more about the history of and issues affecting the country's First Nations peoples.
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, and/or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of present day Australia prior to British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups, which includes many ethnic groups: the Aboriginal Australians of the mainland and many islands, including Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islanders of the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea, located in Melanesia. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the terms First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common; 812,728 people self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these Indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal; 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander; while 4.4% identified with both groups. Since 1995, the Australian Aboriginal flag and the Torres Strait Islander flag have been official flags of Australia.
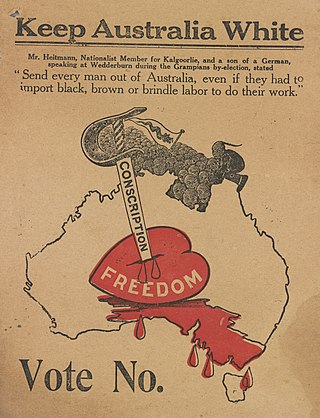
Racism in Australia comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are held by various people and groups in Australia, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions at various times in the history of Australia against racial or ethnic groups.
Indigenous Australians are both convicted of crimes and imprisoned at a disproportionately higher rate in Australia, as well as being over-represented as victims of crime. As of September 2019, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander prisoners represented 28% of the total adult prisoner population, while accounting for 2% of the general adult population. Various explanations have been given for this over-representation, both historical and more recent. Federal and state governments and Indigenous groups have responded with various analyses, programs and measures.
Indigenous treaties in Australia are proposed binding legal agreements between Australian governments and Australian First Nations. A treaty could recognise First Nations as distinct political communities, acknowledge Indigenous Sovereignty, set out mutually recognised rights and responsibilities or provide for some degree of self-government. As of 2023, no such treaties are in force, however the Commonwealth and all states except Western Australia have expressed support previously for a treaty process. However, the defeat of the Voice referendum has led to a reversal by several state liberal and national parties in their support for treaty and a much more ambigious expressed position by state Labor parties and governments.

Reconciliation in Australia is a process which officially began in 1991, focused on the improvement of relations between the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples of Australia and the rest of the population. The Council for Aboriginal Reconciliation (CAR), created by the government for a term of ten years, laid the foundations for the process, and created the peak body for implementation of reconciliation as a government policy, Reconciliation Australia, in 2001.
References
- ↑ Popular Music & Society, Volume 24, Issue 2, 1 July 2000, "Singing about nations within nations: Geopolitics and identity in Australian indigenous rock music" by Peter Dunbar-Hall and Chris Gibson
- ↑ The Age, 6 January 2000, "Yo, Snoop Doggy Dingo!" by Brian Courtis
- ↑ The Australian, 25 July 1997, "Big-time dreamers on track." by Katrina Strickland
- ↑ Daily Telegraph, 25 September 1997, "Aim right on target" by Jane Albert
- ↑ The West Australian, 6 January 2000, "Aboriginal Youth Take The Rap" by Mark Naglazas