
A vacuum cleaner, also known simply as a vacuum, is a device that uses suction, and often agitation, in order to remove dirt and other debris from carpets and hard floors.

A nephelometer or aerosol photometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam and a light detector set to one side of the source beam. Particle density is then a function of the light reflected into the detector from the particles. To some extent, how much light reflects for a given density of particles is dependent upon properties of the particles such as their shape, color, and reflectivity. Nephelometers are calibrated to a known particulate, then use environmental factors (k-factors) to compensate lighter or darker colored dusts accordingly. K-factor is determined by the user by running the nephelometer next to an air sampling pump and comparing results. There are a wide variety of research-grade nephelometers on the market as well as open source varieties.

A diving air compressor is a breathing air compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a hyperbaric breathing gas. A low pressure diving air compressor usually has a delivery pressure of up to 30 bar, which is regulated to suit the depth of the dive. A high pressure diving compressor has a delivery pressure which is usually over 150 bar, and is commonly between 200 and 300 bar. The pressure is limited by an overpressure valve which may be adjustable.
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect.

Flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) is a set of technologies used to remove sulfur dioxide from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants, and from the emissions of other sulfur oxide emitting processes such as waste incineration, petroleum refineries, cement and lime kilns.

An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a filterless device that removes fine particles, such as dust and smoke, from a flowing gas using the force of an induced electrostatic charge minimally impeding the flow of gases through the unit.

A diesel particulate filter (DPF) is a device designed to remove diesel particulate matter or soot from the exhaust gas of a diesel engine.

A dust collector is a system used to enhance the quality of air released from industrial and commercial processes by collecting dust and other impurities from air or gas. Designed to handle high-volume dust loads, a dust collector system consists of a blower, dust filter, a filter-cleaning system, and a dust receptacle or dust removal system. It is distinguished from air purifiers, which use disposable filters to remove dust.

Acoustic cleaning is a maintenance method used in material-handling and storage systems that handle bulk granular or particulate materials, such as grain elevators, to remove the buildup of material on surfaces. An acoustic cleaning apparatus, usually built into the material-handling equipment, works by generating powerful sound waves which shake particulates loose from surfaces, reducing the need for manual cleaning.
A particle counter is used for monitoring and diagnosing particle contamination within specific clean media, including air, water and chemicals. Particle counters are used in a variety of applications in support of clean manufacturing practices, industries include: electronic components and assemblies, pharmaceutical drug products and medical devices, and industrial technologies such as oil and gas.

Air showers are specialized enclosed antechambers which are incorporated as entryways of cleanrooms and other controlled environments to reduce particle contamination. Air showers utilize high-pressure, HEPA- or ULPA-filtered air to remove dust, fibrous lint and other contaminants from personnel or object surfaces. The forceful "cleansing" of surfaces before entering clean environments reduces the number of airborne particulates introduced.
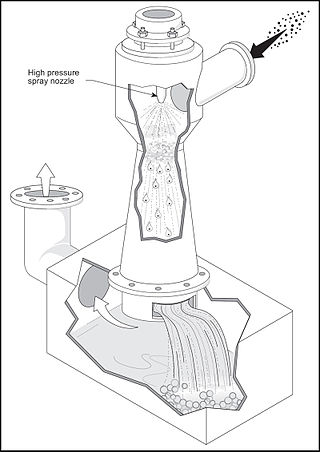
A venturi scrubber is designed to effectively use the energy from a high-velocity inlet gas stream to atomize the liquid being used to scrub the gas stream. This type of technology is a part of the group of air pollution controls collectively referred to as wet scrubbers.
The term wet scrubber describes a variety of devices that remove pollutants from a furnace flue gas or from other gas streams. In a wet scrubber, the polluted gas stream is brought into contact with the scrubbing liquid, by spraying it with the liquid, by forcing it through a pool of liquid, or by some other contact method, so as to remove the pollutants.

Industrial fans and blowers are machines whose primary function is to provide and accommodate a large flow of air or gas to various parts of a building or other structures. This is achieved by rotating a number of blades, connected to a hub and shaft, and driven by a motor or turbine. The flow rates of these mechanical fans range from approximately 200 cubic feet (5.7 m3) to 2,000,000 cubic feet (57,000 m3) per minute. A blower is another name for a fan that operates where the resistance to the flow is primarily on the downstream side of the fan.

A central vacuum cleaner is a type of vacuum cleaner appliance installed into a building as a semi-permanent fixture. Central vacuum systems are designed to remove dirt and debris from homes and buildings by sending dirt particles through piping installed inside the walls to a collection container inside a remote utility space. The power unit is a permanent fixture, usually installed in a basement, garage, or storage room, along with the collection container. Inlets are installed in walls throughout the building that attach to power hoses and other central vacuum accessories to remove dust, particles, and small debris from interior rooms. Most power hoses have a power switch located on the handle.

Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.

A biosafety cabinet (BSC)—also called a biological safety cabinet or microbiological safety cabinet—is an enclosed, ventilated laboratory workspace for safely working with materials contaminated with pathogens requiring a defined biosafety level. Several different types of BSC exist, differentiated by the degree of biocontainment they provide. BSCs first became commercially available in 1950.
A baghouse, also known as a baghouse filter, bag filter, or fabric filter is an air pollution control device and dust collector that removes particulates or gas released from commercial processes out of the air. Power plants, steel mills, pharmaceutical producers, food manufacturers, chemical producers and other industrial companies often use baghouses to control emission of air pollutants. Baghouses came into widespread use in the late 1970s after the invention of high-temperature fabrics capable of withstanding temperatures over 350 °F (177 °C).
Compressed air dryers are special types of filter systems that are specifically designed to remove the water that is inherent in compressed air. The compression of air raises its temperature and concentrates atmospheric contaminants, primarily water vapor, as resulting in air with elevated temperature and 100% relative humidity. As the compressed air cools down, water vapor condenses into the tank(s), pipes, hoses and tools connected downstream from the compressor which may be damaging. Therefore water vapor is removed from compressed air to prevent condensation from occurring and to prevent moisture from interfering in sensitive industrial processes.
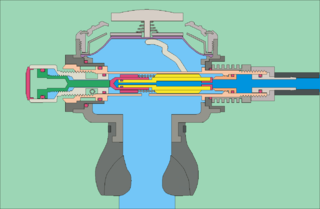
The mechanism of diving regulators is the arrangement of components and function of gas pressure regulators used in the systems which supply breathing gases for underwater diving. Both free-flow and demand regulators use mechanical feedback of the downstream pressure to control the opening of a valve which controls gas flow from the upstream, high-pressure side, to the downstream, low-pressure side of each stage. Flow capacity must be sufficient to allow the downstream pressure to be maintained at maximum demand, and sensitivity must be appropriate to deliver maximum required flow rate with a small variation in downstream pressure, and for a large variation in supply pressure, without instability of flow. Open circuit scuba regulators must also deliver against a variable ambient pressure. They must be robust and reliable, as they are life-support equipment which must function in the relatively hostile seawater environment, and the human interface must be comfortable over periods of several hours.
















