Related Research Articles
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes.
The Suzuki reaction is an organic reaction, classified as a cross-coupling reaction, where the coupling partners are a boronic acid and an organohalide and the catalyst is a palladium(0) complex. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of palladium-catalyzed cross-couplings in organic synthesis. This reaction is also known as the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction or simply as the Suzuki coupling. It is widely used to synthesize polyolefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. Several reviews have been published describing advancements and the development of the Suzuki reaction. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon-carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base.
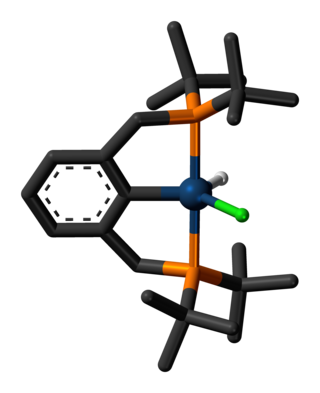
In chemistry, a transition metal pincer complex is a type of coordination complex with a pincer ligand. Pincer ligands are chelating agents that binds tightly to three adjacent coplanar sites in a meridional configuration. The inflexibility of the pincer-metal interaction confers high thermal stability to the resulting complexes. This stability is in part ascribed to the constrained geometry of the pincer, which inhibits cyclometallation of the organic substituents on the donor sites at each end. In the absence of this effect, cyclometallation is often a significant deactivation process for complexes, in particular limiting their ability to effect C-H bond activation. The organic substituents also define a hydrophobic pocket around the reactive coordination site. Stoichiometric and catalytic applications of pincer complexes have been studied at an accelerating pace since the mid-1970s. Most pincer ligands contain phosphines. Reactions of metal-pincer complexes are localized at three sites perpendicular to the plane of the pincer ligand, although in some cases one arm is hemi-labile and an additional coordination site is generated transiently. Early examples of pincer ligands were anionic with a carbanion as the central donor site and flanking phosphine donors; these compounds are referred to as PCP pincers.
In organic chemistry, the Kumada coupling is a type of cross coupling reaction, useful for generating carbon–carbon bonds by the reaction of a Grignard reagent and an organic halide. The procedure uses transition metal catalysts, typically nickel or palladium, to couple a combination of two alkyl, aryl or vinyl groups. The groups of Robert Corriu and Makoto Kumada reported the reaction independently in 1972.

Richard Frederick Heck was an American chemist noted for the discovery and development of the Heck reaction, which uses palladium to catalyze organic chemical reactions that couple aryl halides with alkenes. The analgesic naproxen is an example of a compound that is prepared industrially using the Heck reaction.
Bruce H. Lipshutz is an American chemist. He is a professor at the University of California, Santa Barbara.
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this:

CataCXium F sulf is a water-soluble organophosphorus compound derived from fluorene. The palladium complexes of the respective phosphine show an excellent activity in various palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, including Suzuki reactions, Sonogashira couplings and Buchwald–Hartwig reactions.

Akira Suzuki is a Japanese chemist and Nobel Prize Laureate (2010), who first published the Suzuki reaction, the organic reaction of an aryl- or vinyl-boronic acid with an aryl- or vinyl-halide catalyzed by a palladium(0) complex, in 1979.

PEPPSI is an abbreviation for pyridine-enhanced precatalyst preparation stabilization and initiation. It refers to a family of commercially available palladium catalysts developed around 2005 by Prof. Michael G. Organ and co-workers at York University, which can accelerate various carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bond forming cross-coupling reactions. In comparison to many alternative palladium catalysts, Pd-PEPPSI-type complexes are stable to air and moisture and are relatively easy to synthesize and handle.
Marcetta York Darensbourg is an American inorganic chemist. She is a Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at Texas A&M University. Her current work focuses on iron hydrogenases and iron nitrosyl complexes.
Melanie Sarah Sanford is an American chemist, currently the Moses Gomberg Distinguished University Professor of Chemistry and Arthur F. Thurnau Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan. She is a Fellow for the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2016. She has served as an executive editor of the Journal of the American Chemical Society since 2021, having been an associate editor of the since 2014.
Guy Charles Lloyd-Jones FRS FRSE is a British chemist. He is the Forbes Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Edinburgh in the United Kingdom. His research is largely concerned with the determination of organometallic reaction mechanisms, especially those of palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions such as Suzuki-Miyaura coupling.

John Perry Wolfe is an American chemist and a professor of chemistry at the University of Michigan. He is best known for palladium-catalyzed C-C and C-N bond formation reactions. He was also one of the key scientists in the development of Buchwald ligands, one of which is appropriately named "JohnPhos" after him. Wolfe has taught at the University of Michigan since 2002.

In organometallic chemistry, palladium-NHC complexes are a family of organopalladium compounds in which palladium forms a coordination complex with N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). They have been investigated for applications in homogeneous catalysis, particularly cross-coupling reactions.
Dialkylbiaryl phosphine ligands are phosphine ligands that are used in homogeneous catalysis. They have proved useful in Buchwald-Hartwig amination and etherification reactions as well as Negishi cross-coupling, Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling, and related reactions. In addition to these Pd-based processes, their use has also been extended to transformations catalyzed by nickel, gold, silver, copper, rhodium, and ruthenium, among other transition metals.

The Mizoroki−Heck coupling of aryl halides and alkenes to form C(sp2)–C(sp2) bonds has become a staple transformation in organic synthesis, owing to its broad functional group compatibility and varied scope. In stark contrast, the palladium-catalyzed reductive Heck reaction has received considerably less attention, despite the fact that early reports of this reaction date back almost half a century. From the perspective of retrosynthetic logic, this transformation is highly enabling because it can forge alkyl–aryl linkages from widely available alkenes, rather than from the less accessible and/or more expensive alkyl halide or organometallic C(sp3) synthons that are needed in a classical aryl/alkyl cross-coupling.
Miyaura borylation, also known as the Miyaura borylation reaction, is a named reaction in organic chemistry that allows for the generation of boronates from vinyl or aryl halides with the cross-coupling of bis(pinacolato)diboron in basic conditions with a catalyst such as PdCl2(dppf). The resulting borylated products can be used as coupling partners for the Suzuki reaction.
Heterogeneous metal catalyzed cross-coupling is a subset of metal catalyzed cross-coupling in which a heterogeneous metal catalyst is employed. Generally heterogeneous cross-coupling catalysts consist of a metal dispersed on an inorganic surface or bound to a polymeric support with ligands. Heterogeneous catalysts provide potential benefits over homogeneous catalysts in chemical processes in which cross-coupling is commonly employed—particularly in the fine chemical industry—including recyclability and lower metal contamination of reaction products. However, for cross-coupling reactions, heterogeneous metal catalysts can suffer from pitfalls such as poor turnover and poor substrate scope, which have limited their utility in cross-coupling reactions to date relative to homogeneous catalysts. Heterogeneous metal catalyzed cross-couplings, as with homogeneous metal catalyzed ones, most commonly use Pd as the cross-coupling metal.
Norio Miyaura was a Japanese organic chemist. He was a professor of graduate chemical engineering at Hokkaido University. His major accomplishments surrounded his work in cross-coupling reactions / conjugate addition reactions of organoboronic acids and addition / coupling reactions of diborons and boranes. He is also the co-author of Cross-Coupling Reactions: A Practical Guide with M. Nomura E. S.. Miyaura was a world-known and accomplished researcher by the time he retired and so, in 2007, he won the Japan Chemical Society Award.
References
- ↑ "Professor (Emeritus)". Department of Chemistry. Indian Institute of Technology Delhi. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ Kumar, Arun; Rao, Gyandshwar Kumar; Kumar, Satyendra; Singh, Ajai K. (16 October 2013). "Formation and Role of Palladium Chalcogenide and Other Species in Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck C–C Coupling Reactions Catalyzed with Palladium(II) Complexes of Organochalcogen Ligands: Realities and Speculations". Organometallics. 33 (12): 2921–2943. doi:10.1021/om4007196.
- ↑ Rao, Gyandshwar Kumar; Kumar, Arun; Ahmed, Jahangeer; Singh, Ajai Kumar (2010). "Palladacycle containing nitrogen and selenium: Highly active pre-catalyst for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction and unprecedented conversion into nano-sized Pd17Se15". Chemical Communications. 46 (32): 5954–6. doi:10.1039/C0CC01075H. PMID 20625588.
- ↑ Kumar, Arun; Kumar Rao, Gyandshwar; k Singh, Ajai (2012). "Organochalcogen ligands and their palladium(ii) complexes: Synthesis to catalytic activity for Heck coupling". RSC Advances. 2 (33): 12552. doi:10.1039/C2RA20508D.
- ↑ "Ajai Kumar Singh's profile on Publons".