
Sweden established colonies in the Americas in the mid-17th century, including the colony of New Sweden (1638–1655) on the Delaware River in what is now Delaware, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Maryland, as well as two possessions in the Caribbean during the 18th and 19th centuries.
Gallitzin is a borough in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is bordered by Gallitzin Township and Tunnelhill, all of which sit astride the Eastern continental divide. Tunnel Hill and Gallitzin both are pierced by railroad tunnels shortening the necessary ascent for rails crossing the Allegheny Front onto the Allegheny Plateau which encompasses the towns' terrains. Topping the gaps of the Allegheny, the area is one of only five major breaks in the Appalachians allowing east–west transportation corridors before the advent of 20th century technologies.

Lehighton is a borough in Carbon County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is part of Northeastern Pennsylvania. Lehighton is located 28.9 miles (46.5 km) northwest of Allentown and 77.5 miles (124.7 km) northwest of Philadelphia.

Manor Township is a second-class township in west-central Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 21,920.

Duryea is a borough in the Greater Pittston area of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, United States, 9 miles (14 km) south of Scranton. The Susquehanna River marks Duryea's western boundary and the Lackawanna River flows through Duryea. It was incorporated as a borough in 1901, and had a notable switching rail yard, the Duryea yard, connecting the central Wyoming Valley to destinations in lower New York and down-state Pennsylvania. Coal mining and silk manufacturing were the chief industries in Duryea's early years. The population was 5,032 at the 2020 census.

Danville is a borough in and the county seat of Montour County, Pennsylvania, United States, along the North Branch of the Susquehanna River. The population was 4,221 at the 2020 census. Danville is part of the Bloomsburg-Berwick micropolitan area.

The Beaver Wars, also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies. As a result of this conflict, the Iroquois destroyed several confederacies and tribes through warfare: the Hurons or Wendat, Erie, Neutral, Wenro, Petun, Susquehannock, Mohican and northern Algonquins whom they defeated and dispersed, some fleeing to neighboring peoples and others assimilated, routed, or killed.

The Susquehannock, also known as the Conestoga, Minquas, and Andaste, were an Iroquoian people who lived in the lower Susquehanna River watershed in what is now Pennsylvania. Their name means “people of the muddy river.”
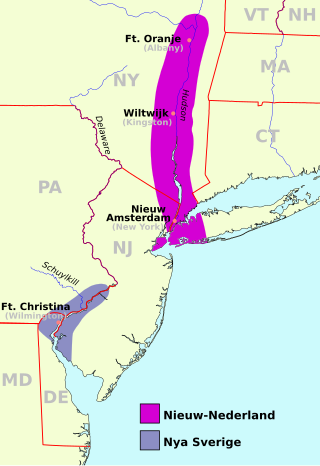
The Peach Tree War, also known as the Peach War, was a large-scale attack on September 15, 1655 by the Susquehannock Indians and allied tribes on several New Netherland settlements along the North River.
According to historian Kevin Kenny, the Paxton Boys were Pennsylvania's most aggressive colonists. This group of vigilantes from Lancaster and Cumberland counties formed in 1763 to defend themselves from attacks by the Lenape and Shawnee during Pontiac's War. They are infamous for the murder of twenty Susquehannock in December 1763 during the events known as the Conestoga Massacre. In February 1764, the Paxton Boys marched on Philadelphia with the intent of murdering the Moravian Lenape and Mohican who had been moved there for their protection. They dispersed at Germantown after meeting with a delegation headed by Benjamin Franklin. Members of the group led by Lazarus Stewart later supported settlers from Connecticut in the Wyoming Valley during the Pennamite-Yankee Wars and Revolutionary War.

The Conestoga River, also referred to as Conestoga Creek, is a 61.6-mile-long (99.1 km) tributary of the Susquehanna River flowing through the center of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, United States.
Protohistory is a period between prehistory and written history during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures have already noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. For example, in Europe, the Celts and the Germanic tribes are considered to have been protohistoric when they began appearing in Greek and Roman sources.

Susquehannock State Forest is a Pennsylvania state forest in Pennsylvania Bureau of Forestry District #15. The main office is located in Coudersport in Potter County, Pennsylvania in the United States.

Susquehannock, also known as Conestoga, is an Iroquoian language spoken by the Native American people variously known as the Susquehannock or Conestoga.

Susquehannock State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 224 acres (91 ha) in Drumore Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is on a scenic plateau overlooking the Susquehanna River and Conowingo Reservoir. The park is named for the Susquehannock people, who lived in the area. Susquehannock State Park is located on small roads a few miles south of Pennsylvania Route 372 and west of Pennsylvania Route 272. The nearest city is Quarryville, Pennsylvania, about 12 miles (19 km) East.

Prouty Place State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 5 acres (2 ha) in Summit Township, Potter County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Pennsylvania Route 44, along Prouty Road near the junction with Long Toe Road, near Sweden Valley. The park provides access points for hiking, hunting and fishing in the Susquehannock State Forest. It is a small rest area for hikers and other travellers to the wilds of Potter County.

The Forbes Expedition was a British military expedition to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the now historic trail, the Forbes Road. The Treaty of Easton served to cause a loss of Native American support for the French, resulting in the French destroying the fort before the expedition could arrive on November 24.

The Susquehannock Trail System (STS) is an 83.4-mile (134.2 km) loop hiking trail in Susquehannock State Forest in Potter County in north-central Pennsylvania, United States. The trail walks through two state parks and passes near three more state parks. It also traverses Hammersley Wild Area, the largest area in Pennsylvania without a road. The loop is supplemented by two cross-connector trails, several short access trails, a shared path with the Donut Hole Trail, and two connectors to the Black Forest Trail. The STS is the oldest backpacking trail in Pennsylvania, and has been noted for its solitude while traversing remote areas with few signs of civilization. The STS also includes several overnight shelters.

Hammersley Wild Area is a 30,253-acre (12,243 ha) wild area in the Susquehannock State Forest in Potter and Clinton counties in north-central Pennsylvania in the United States. It is the largest area without a road in Pennsylvania and the state's second largest wild area. The wild area is named for Hammersley Fork, a tributary of Kettle Creek, which flows through the area. The wild area includes 10.78 miles (17.35 km) of the Susquehannock Trail System, an 83.4-mile (134.2 km) loop hiking trail almost entirely on state forest land.
The history of Native Americans in Baltimore and what is now Baltimore dates back at least 12,000 years. As of 2014, Baltimore is home to a small Native American population, centered in East Baltimore. The majority of Native Americans now living in Baltimore belong to the Lumbee, Piscataway, and Cherokee tribes. The Piscataway people live in Southern Maryland and are recognized by the state of Maryland. The Lumbee and Cherokee are Indigenous to North Carolina and neighboring states of the Southeastern United States. Many of the Lumbee and Cherokee migrated to Baltimore during the mid-20th century along with other migrants from the Southern United States, such as African-Americans and white Appalachians. The Lumbee are state recognized in North Carolina as the Lumbee Tribe of North Carolina, but have no state recognition in Maryland. The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians in North Carolina are a federally recognized tribe. There are three state recognized tribes in Maryland; the Piscataway-Conoy Tribe of Maryland, the Piscataway Indian Nation and Tayac Territory, and the Accohannock Indian Tribe. Maryland has no federally recognized tribes.














