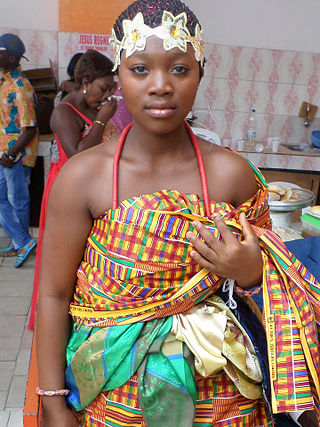A doll is a model typically of a human or humanoid character, often used as a toy for children. Dolls have also been used in traditional religious rituals throughout the world. Traditional dolls made of materials such as clay and wood are found in the Americas, Asia, Africa and Europe. The earliest documented dolls go back to the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, and Rome. They have been made as crude, rudimentary playthings as well as elaborate art. Modern doll manufacturing has its roots in Germany, from the 15th century. With industrialization and new materials such as porcelain and plastic, dolls were increasingly mass-produced. During the 20th century, dolls became increasingly popular as collectibles.

African art describes the modern and historical paintings, sculptures, installations, and other visual culture from native or indigenous Africans and the African continent. The definition may also include the art of the African diasporas, such as African-American, Caribbean or art in South American societies inspired by African traditions. Despite this diversity, there are unifying artistic themes present when considering the totality of the visual culture from the continent of Africa.

Kente refers to a Ghanaian textile made of hand-woven strips of silk and cotton. Historically the fabric was worn in a toga-like fashion by royalty among the Ashanti and Akan. According to Ashanti oral tradition, it originated from Bonwire in the Ashanti region of Ghana. In modern day Ghana, the wearing of kente cloth has become widespread to commemorate special occasions, and kente brands led by master weavers are in high demand. Kente is also worn in parts of Togo and Ivory Coast by the Ewe and Akan people there.
The Ashanti–Fante War (1806–1807) was a war fought between the Ashanti Empire and the Fante Confederacy in the region of what is currently the Republic of Ghana.

Ghana is a country of 33.48 million people and many native groups, such as:

The modern Mfantsefo or Fante confederacy is a combination of Akan people and aboriginal Guan people. The Fante people are mainly located in the Central and Western regions of Ghana, occupying the forest and coastal areas. Their land stretches from the eastern part of western region in the west to Gomoa in the east. The Fante can be broadly categorized into two groups - the Borbor Fante and the Etsii Fante who are also aboriginal Guan people. Over the last half century, Fante communities have been established as far as Gambia, Liberia, and even Angola due to fishing expeditions. Major Fante cities in modern Ghana include Oguaa, Edina (Elmina), Agona Swedru, Mankessim, Saltpond, Komenda and Anomabo.
Akan is a group of several closely related languages within the wider Central Tano languages. These languages are the principal native languages of the Akan people of Ghana, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population can speak an Akan language as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. There are populations of polyglots in Ghana who speak an Akan language as a third language. They are also spoken in parts of Côte d'Ivoire.
The Akan people are a Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi, Ashanti, Baoulé, Bono, Chakosi, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta, and Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal matrilineal descent in the inheritance of property, and for succession to high political office. All Akans are considered royals in status, but not all are in royal succession or hold titles.
The diverse culture of Ivory Coast, a coastal West African country bordered by Ghana, Liberia, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Guinea, is exemplified by a multitude of ethnic groups, events, festivals, music, and art.
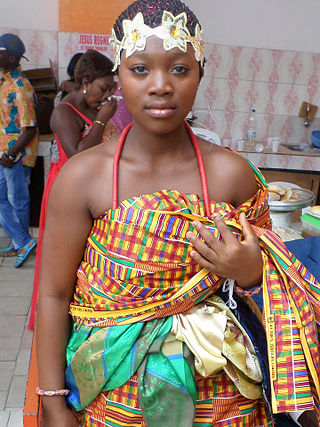
The Bono, also called the Brong and the Abron, are an Akan people of West Africa. Bonos are normally tagged Akan piesie or Akandifo of which Akan is a derivative name. Bono is the genesis and cradle of Akans. Bono is one of the largest ethnic group of Akan and are matrilineal people. Bono people speak the Bono Twi of Akan language. Twi language, thus the dialect of Bono is a derivative of a Bono King Nana Twi. In the late fifteenth century, the Bono people founded the Gyaaman kingdom as extension of Bono state in what is now Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire.

Fante, also known as Fanti, Fantse, or Mfantse, is one of the four principal members of the Akan dialect continuum, along with Asante, Bono and Akuapem, the latter three collectively known as Twi, with which it is mutually intelligible. It is principally spoken in the central and southern regions of Ghana as well as in settlements in other regions in western Ghana, Ivory Coast, as well as in Liberia, Gambia and Angola.

Adinkra are symbols from Ghana that represent concepts or aphorisms. Adinkra are used extensively in fabrics, logos and pottery. They are incorporated into walls and other architectural features. Adinkra symbols appear on some traditional Akan goldweights. The symbols are also carved on stools for domestic and ritual use. Tourism has led to new departures in the use of symbols in items such as T-shirts and jewellery.

Akan art is an art form that originated among the Akan people of Southern Ghana. Akan art is known for vibrant artistic traditions, including textiles, sculpture, Akan goldweights, as well as gold and silver jewelry. The Akan people are known for their strong connection between visual and verbal expressions and a distinctive blending of art and philosophy. Akan chiefs managed generations worth of gold regalia; finely crafted objects such as crowns, beads, bracelets, pectoral disks, swords and sword ornaments, linguist staffs, and umbrella finials.
Aggry beads are a type of decorated glass bead from Ghana, used by West Africans as ornaments in necklaces, bracelets and other jewelry.

The Asante Empire, also known as the Ashanti Empire, was an Akan state that lasted from 1701 to 1901, in what is now modern-day Ghana. It expanded from the Ashanti Region to include most of Ghana and also parts of Ivory Coast and Togo. Due to the empire's military prowess, wealth, architecture, sophisticated hierarchy and culture, the Asante Empire has been extensively studied and has more historic records written by European, primarily British, authors than any other indigenous culture of sub-Saharan Africa.

Akan goldweights are weights made of brass used as a measuring system by the Akan people of West Africa, particularly for wei and fair-trade arrangements with one another. The status of a man increased significantly if he owned a complete set of weights. Complete small sets of weights were gifts to newly wedded men. This insured that he would be able to enter the merchant trade respectably and successfully.

Asase Ya/Afua is the Akan goddess of fertility, love, procreation, peace, truth and the dry and lush earth in Ghana and Ivory Coast. She is also Mother of the Dead known as Mother Earth or Aberewaa.

Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups, so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans.
The Asafo flags are regimental flags of the Fante people, an ethnic group that mainly resides in Ghana's central coastal region. The flags are influenced by a combination of Akan proverbs, visual imagery, and European heraldic tradition.

The documented history of Elmina begins in 1482 with an agreement between the Portuguese navigator Diogo de Azambuja and the ruler of Elmina, called Caramansa by the Portuguese. In it, the Portuguese were allowed to build the first European fortress in sub-Saharan Africa. For the next 150 years until the conquest by the Dutch in 1637, Elmina was the capital of the Portuguese bases on the Gold Coast, then for about 250 years the capital of the Dutch Empire in West Africa. Since the capture of the lease for the two fortresses of Elmina by the Ashanti in 1701, the city was also important to the Ashanti Empire. Until the 19th century, Elmina was one of the most populous cities in the Gold Coast, surpassing Accra and Kumasi. The trade in gold, slaves and palm oil brought the city into direct contact with Europe, North America, Brazil and, through the recruitment of soldiers, also with Southeast Asia. It was not until the takeover and destruction of the city by the British in 1873 that Elmina lost its prominent position in the Gold Coast.