Albania is a country on the Balkan Peninsula in south-eastern Europe.
Contents
- Places
- Territories related to present-day Albania
- Territories not related to present-day Albania
- Populated places
- Other uses
- See also
Albania may also refer to:
Albania is a country on the Balkan Peninsula in south-eastern Europe.
Albania may also refer to:
The Enchele's polity was the earliest to emerge and centered in Albania. Also the earliest known Illyrian king, Bardylis, emerged in what is now Albania around 400 BC, aiming to make Illyria a regional power interfering with Macedon. He united many southern Illyrian tribes under his realm and defeated the Macedonians and Molossians several times, expanding his dominion over Upper Macedonia and Lynkestis. Before the Rise of Macedon Illyrians were the dominant power in the region. The kingdom of the Taulantii under Glaukias' rule was based in central Albania and dominated southern Illyrian affairs in the late 4th century BC, exerting great influence on the Epirote state through the close ties with the Molossian king Pyrrhus. Under the Ardiaei the greatest known Illyrian kingdom emerged in the 3rd century BC encompassing also northern Albania in its core territory. It became a formidable power both on land and sea by assembling a great army and fleet, and directly ruling over a large area made up of different Illyrian tribes and cities that stretched from the Neretva River in the north to the borders of Epirus in the south, while its influence extended throughout Epirus and down into Acarnania. The dominant power of the Illyrian kingdom in the region ceased after the Illyrian defeat in the Illyro-Roman Wars. The last known "King of the Illyrians" was Gentius, of the Labeatae tribe.

Durrës is the second-most-populous city of the Republic of Albania and seat of Durrës County and Durrës Municipality. It is one of Albania's oldest continuously inhabited cities, with roughly 2,500 years of recorded history. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of the Erzen and Ishëm at the southeastern corner of the Adriatic Sea. Durrës' climate is profoundly influenced by a seasonal Mediterranean climate.

Vlorë is the third most populous city of Albania and seat of Vlorë County and Vlorë Municipality. Located in southwestern Albania, Vlorë sprawls on the Bay of Vlorë and is surrounded by the foothills of the Ceraunian Mountains along the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea Coasts. It experiences a Mediterranean climate, which is affected by the Ceraunian Mountains and the proximity to the Mediterranean Sea.

Greater Albania is an irredentist and nationalist concept that seeks to annex the lands that many Albanians consider to form their national homeland. It is based on claims on the present-day or historical presence of Albanian populations in those areas. In addition to the existing Albania, the term incorporates claims to regions in the neighbouring states, the areas include Kosovo, the Preševo Valley of Serbia, territories in southern Montenegro, northwestern Greece, and a western part of North Macedonia. The combination of the populations of these countries and territories of other countries sustaining large ethnic Albanian communities enumerate to over 4 million people.
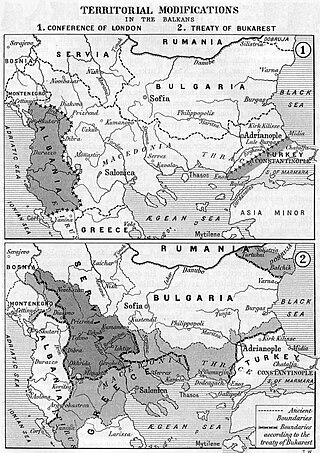
The Treaty of London (1913) was signed on 30 May following the London Conference of 1912–1913. It dealt with the territorial adjustments arising out of the conclusion of the First Balkan War. The London Conference had ended on 23 January 1913, when the 1913 Ottoman coup d'état took place and Ottoman Grand Vizier Kâmil Pasha was forced to resign. Coup leader Enver Pasha withdrew the Ottoman Empire from the Conference, and the Treaty of London was signed without the presence of the Ottoman delegation.
The Balkans and parts of this area may also be placed in Southeastern, Southern, Eastern Europe and Central Europe. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often turbulent history regarding centuries of Ottoman conquest and to its very mountainous geography.

The Kingdom of Serbia was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Principality was ruled by the Obrenović dynasty. The Principality, under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire, de facto achieved full independence when the very last Ottoman troops left Belgrade in 1867. The Congress of Berlin in 1878 recognized the formal independence of the Principality of Serbia, and in its composition Nišava, Pirot, Toplica and Vranje districts entered the South part of Serbia.
The Vilayet of Kosovo ; Косовски вилает (Macedonian) was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire in the Balkan Peninsula which included the modern-day territory of Kosovo and the north-western part of the Republic of North Macedonia. The areas today comprising Sandžak (Raška) region of Serbia and Montenegro, although de jure under Ottoman control, were de facto under Austro-Hungarian occupation from 1878 until 1909, as provided under Article 25 of the Treaty of Berlin. Üsküb (Skopje) functioned as the capital of the province and the midway point between Istanbul and its European provinces. Üsküb's population of 32,000 made it the largest city in the province, followed by Prizren, also numbering at 30,000.

The London Conference of 1912–1913, also known as the London Peace Conference or the Conference of the Ambassadors, was an international summit of the six Great Powers of that time convened in December 1912 due to the successes of the Balkan League armies against the Ottoman Empire in the First Balkan War. In particular, the conference intended to arbitrate between the warring powers as to territorial acquisitions, and also to determine the future of Albania, whose independence was proclaimed during the conflict.

The siege of Scutari, also referred to as the siege of Shkodër, known in Turkish as İşkodra Müdafaası(in Turkish) or İşkodra Savunması, took place from 28 October 1912 to 23 April 1913 when the army of the Kingdom of Montenegro defeated the forces of the Ottoman Empire and invaded Shkodër.
Independent Albania was proclaimed on 28 November 1912. This chapter of Albanian history was shrouded in controversy and conflict as the larger part of the self-proclaimed region had found itself controlled by the Balkan League states: Serbia, Montenegro and Greece from the time of the declaration until the period of recognition when Albania relinquished many of the lands originally included in the declared state. Since the proclamation of the state in November 1912, the Provisional Government of Albania asserted its control over a small part of central Albania including the important cities of Vlorë and Berat.

The Republic of Central Albania was a short-lived unrecognised state established on 16 October 1913, with its administrative centre in Durrës, today in Albania.

The Albanian Vilayet was a projected vilayet of the Ottoman Empire in the western Balkan Peninsula, which was to include the four Ottoman vilayets with substantial ethnic Albanian populations: Kosovo Vilayet, Scutari Vilayet, Manastir Vilayet, and Janina Vilayet. In some proposals, it included the Salonica Vilayet as well. The creation of the Vilayet was confirmed in September 1912, but negotiations were interrupted a month later in October by the beginning of the First Balkan War. Plans for an Albanian Vilayet were lost with the Partition of Albania.

The All-Albanian Congress was a held in Vlorë on November 28, 1912. Congress participants constituted the Assembly of Vlorë which established Albanian Provisional Government and elected Ismail Kemal as its president.

The Sanjak of Dibra, Debar, or Dibër was one of the sanjaks of the Ottoman Empire. Its capital was Debar, Macedonia. Today, the western part of its territory belongs to Albania and the eastern part to North Macedonia.

The Sanjak of Prizren was one of the sanjaks in the Ottoman Empire with Prizren as its administrative centre. It was founded immediately after Ottoman Empire captured Prizren from Serbian Despotate in 1455. The rest of the territory of Serbian Despotate was conquered after the fall of Smederevo in 1459, and divided into following sanjaks: Sanjak of Viçitrina, Sanjak of Kruševac and Sanjak of Smederevo. At the beginning of the First Balkan War in 1912, the territory of Sanjak of Prizren was occupied by the army of the Kingdom of Serbia. Based on Treaty of London signed on 30 May 1913, the territory of Sanjak of Prizren became part of Serbia.

The Partition of Albania is a term used for the partition of the Albanian state, which proclaimed its independence on 28 November 1912. The delineation of the newly established Principality of Albania under the terms of the London Conference of 1912–1913 and the Ambassadors of the six Great Powers of that time left Albanian and non-Albanian populations on both sides of the border. Representatives of the Albanian national movement viewed this as a partition of claimed Albanian-inhabited territories, also territories contained in a proposed Albanian Vilayet.

Independent Albania was a parliamentary state declared in Vlorë on 28 November 1912 during the First Balkan War. Its assembly was constituted on the same day while its government and senate were established on 5 December 1912.

The Sanjak of Durrës was one of the sanjaks of the Ottoman Empire. It was named for its capital Durrës and was also known as the Sanjak of Durazzo from its capital's Italian name. The sanjak was composed of the kazas of Durrës, Tirana, Shijak, Kavajë, and Krujë. The Sanjak of Durrës formed the southern half of the Vilayet of Scutari. The northern half was the Sanjak of Scutari. Durrës Sanjak also bordered the sanjaks of Manastir and Dibra to its northeast and the sanjak of Elbasan to the east and south. Its western border was the Adriatic Sea. Its terrain is generally flat and plain. Only the eastern parts of the kazas of Tirana and Kavajë were mountainous.