
London Docklands is the riverfront and former docks in London. It is located in inner east and southeast London, in the boroughs of Southwark, Tower Hamlets, Lewisham, Newham and Greenwich. The docks were formerly part of the Port of London, at one time the world's largest port. After the docks closed, the area had become derelict and poverty-ridden by the 1980s. The Docklands' regeneration began later that decade; it has been redeveloped principally for commercial and residential use. The name "London Docklands" was used for the first time in a government report on redevelopment plans in 1971 and has since been almost universally adopted. The redevelopment created wealth, but also led to some conflict between the new and old communities in the area.

Stratford is a town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Newham. Part of the Lower Lea Valley, Stratford is situated 6 miles (9.7 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, and includes the localities of Maryland and East Village.

The London Borough of Barking and Dagenham is a London borough in East London. It lies around 9 miles (14 km) east of Central London. The borough was created in 1965 as the London Borough of Barking; the name was changed in 1980. It is an Outer London borough and the south is within the London Riverside section of the Thames Gateway; an area designated as a national priority for urban regeneration. At the 2011 census it had a population of 187,000. The borough's three main towns are Barking, Chadwell Heath and Dagenham. The local authority is the Barking and Dagenham London Borough Council. Barking and Dagenham was one of six London boroughs to host the 2012 Summer Olympics.
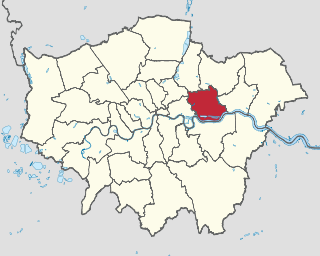
The London Borough of Newham is a London borough created in 1965 by the London Government Act 1963. It covers an area previously administered by the Essex county boroughs of West Ham and East Ham, authorities that were both abolished by the same act. The name Newham reflects its creation and combines the compass points of the old borough names. Situated in the Inner London part of East London, Newham has a population of 387,576, which is the fourth highest of the London boroughs and also makes it the 26th most populous district in England. The local authority is Newham London Borough Council.

Greenwich is an area in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated 5.5 miles (8.9 km) east-south-east of Charing Cross.

Greenwich Hospital was a permanent home for retired sailors of the Royal Navy, which operated from 1692 to 1869. Its buildings, initially Greenwich Palace, in Greenwich, London, were later used by the Royal Naval College, Greenwich and the University of Greenwich, and are now known as the Old Royal Naval College. The word "hospital" was used in its original sense of a place providing hospitality for those in need of it, and did not refer to medical care, although the buildings included an infirmary which, after Greenwich Hospital closed, operated as Dreadnought Seaman's Hospital until 1986.

Bromley, commonly known as Bromley-by-Bow, is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London, located on the western banks of the River Lea, in the Lower Lea Valley in East London. It is an inner-city suburb located 4.7 miles east of Charing Cross.

Canning Town is a district in the London Borough of Newham, East London, England, north of the Royal Victoria Dock. Its urbanisation was largely due to the creation of the dock. The area was part of the ancient parish and County Borough of West Ham, in the historic county of Essex. It forms part of the London E16 postcode district.

Royal Docks is an area in the London Borough of Newham in the London Docklands in East London, England.

The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) is a public research university in Bloomsbury, central London, and a member institution of the University of London that specialises in public health and tropical medicine. The institution was founded in 1899 by Sir Patrick Manson, after a donation from the Indian Parsi philanthropist B. D. Petit.

Beckton is a suburb in east London, England, located 8 miles (12.9 km) east of Charing Cross and part of the London Borough of Newham. Adjacent to the River Thames, the area consisted of unpopulated marshland known as the East Ham Levels in the parishes of Barking, East Ham, West Ham and Woolwich. The development of major industrial infrastructure in the 19th century to support the growing metropolis of London caused an increase in population with housing built in the area for workers of the Beckton Gas Works and Beckton Sewage Treatment Works. The area has a convoluted local government history and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. Between 1981 and 1995 it was within the London Docklands Development Corporation area, which caused the population to increase as new homes were built and the Docklands Light Railway was constructed.

The Lower Lea Valley is the southern end of the Lea Valley which surrounds the River Lea in eastern Greater London. It is part of the Thames Gateway redevelopment area and was the location of the 2012 Summer Olympics.

East London is the northeastern part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London's docklands and the primary industrial centre. The expansion of railways in the 19th century encouraged the eastward expansion of the East End of London and a proliferation of new suburbs. The industrial lands of East London are today an area of regeneration, which are well advanced in places such as Canary Wharf and ongoing elsewhere.

The Royal Albert Dock is one of three docks in the Royal Group of Docks of East London in the United Kingdom.

West Ham was a local government district in the extreme south west of Essex from 1886 to 1965, forming part of the built-up area of London, although outside the County of London. It was immediately north of the River Thames and east of the River Lea.

The Hospital for Tropical Diseases (HTD) is a specialist tropical disease hospital located in London, United Kingdom. It is part of the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and is closely associated with University College London and the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. It is the only NHS hospital dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of tropical diseases and travel-related infections. It employs specialists in major tropical diseases including malaria, leprosy and tuberculosis. It also provides an infectious disease treatment service for University College Hospital.
The Seafarers Hospital Society, formerly the Seamen's Hospital Society, is a charity for people currently or previously employed by the British Merchant Navy and fishing fleets, and their families. It was established in 1821.

Newham London Borough Council also known as Newham Council, is the local authority for the London Borough of Newham in Greater London, England. It is a London borough council, one of 32 in London. The council has been under Labour majority control since 1971. It has been led by a directly elected mayor since 2002. The council meets at Newham Town Hall in East Ham and at Stratford Town Hall, and has its main offices at 1000 Dockside Road, overlooking the Royal Albert Dock.

George Carmichael Low was a Scottish parasitologist.

The Royal Hamadryad Hospital was a seamen's hospital and later a psychiatric hospital in the docklands area of Cardiff, Wales. It had replaced a hospital ship, the former HMS Hamadryad, in 1905. After it closed in 2002 the site was redeveloped for residential use.



















