
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging, warm forging, or hot forging. For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons. Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery.

The SS William G. Mather is a retired Great Lakes bulk freighter now restored as a museum ship in Cleveland, Ohio, one of five in the Great Lakes region. She transported cargo such as ore, coal, stone, and grain to ports throughout the Great Lakes, and was nicknamed "The Ship That Built Cleveland" because Cleveland's steel mills were a frequent destination.

The Hulett was an ore unloader that was widely used on the Great Lakes of North America. It was unsuited to tidewater ports because it could not adjust for rising and falling tides, although one was used in New York City.

Terminal Tower is a 52-story, 215.8 m (708 ft), landmark skyscraper located on Public Square in the downtown core of Cleveland, Ohio, United States. Built during the skyscraper boom of the 1920s and 1930s, it was the second-tallest building in the world when it was completed. Terminal Tower stood as the tallest building in North America outside of New York City from its completion in 1927 until 1964. It was the tallest building in the state of Ohio until the completion of Key Tower in 1991, and remains the second-tallest building in the state. The building is part of the Tower City Center mixed-use development, and its major tenants include Forest City Enterprises, which maintained its corporate headquarters there until 2018, and Riverside Company.

The Johnstown Inclined Plane is a 896.5-foot (273.3 m) funicular in Johnstown, Cambria County, Pennsylvania, U.S. The incline and its two stations connect the city of Johnstown, situated in a valley at the confluence of the Stonycreek and the Little Conemaugh rivers, to the borough of Westmont on Yoder Hill. The Johnstown Inclined Plane is billed as the "world's steepest vehicular inclined plane". It can carry automobiles and passengers, up or down a slope with a grade of 71.9%. The travel time between stations is 90 seconds.

The Peterborough Lift Lock is a boat lift located on the Trent Canal in the city of Peterborough, Ontario, Canada, and is Lock 21 on the Trent-Severn Waterway.

The Duquesne Incline is a funicular scaling Mount Washington near the South Side neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Designed by Hungarian-American engineer Samuel Diescher, the incline was completed in 1877.

The Monongahela Incline is a funicular on the South Side in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States, near the Smithfield Street Bridge. Designed and built by Prussian-born engineer John Endres in 1870, it is the oldest continuously operating funicular in the U.S.

Public Square is the central plaza of Downtown Cleveland, Ohio. Based on an 18th-century New England model, it was part of the original 1796 town plat overseen by city founder General Moses Cleaveland of the Connecticut Land Company. The historical center of the city's downtown, it was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1975.

The Hope Memorial Bridge is a 4,490-foot-long (1,370 m) art deco truss bridge crossing the Cuyahoga River in Cleveland, Ohio. The bridge connects Lorain Avenue on Cleveland's west side and Carnegie Avenue on the east side, terminating just short of Progressive Field.

The Creusot steam hammer is a giant steam hammer built in 1877 by Schneider and Co. in the French industrial town of Le Creusot. With the ability to deliver a blow of up to 100 tons, the Creusot hammer was the most powerful in the world until 1891, when the Bethlehem Iron Company of the United States purchased patent rights from Schneider and built a steam hammer of almost identical design but capable of delivering a 125-ton blow.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Cleveland, Ohio.

The Main Avenue Bridge is a cantilever truss bridge in Cleveland, Ohio carrying Ohio State Route 2/Cleveland Memorial Shoreway over the Cuyahoga River. The bridge, completed in 1939, is 8,000 feet (2,400 m) in length, and was the longest elevated structure in Ohio until the 2007 completion of the Veterans' Glass City Skyway in Toledo. It was named for Harold H. Burton, 45th mayor of Cleveland, in late January 1986. The bridge replaced an 1869 bridge at the same site, and was built in conjunction with construction of the Cleveland Memorial Shoreway.

The Chapin Mine Steam Pump Engine, also known as The Cornish Pump, is a steam-driven pump located at the corner of Kent Street and Kimberly Avenue in Iron Mountain, Michigan, USA. It is the largest reciprocating steam-driven engine ever built in the United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981, and designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1958.
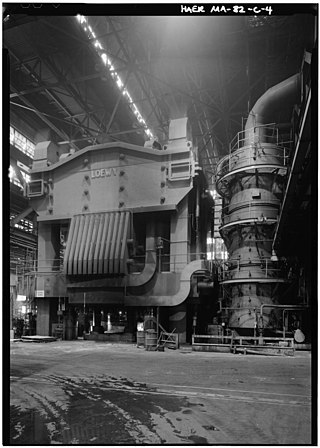
The Heavy Press Program was a Cold War-era program of the United States Air Force to build the largest forging presses and extrusion presses in the world. These machines greatly enhanced the US defense industry's capacity to forge large complex components out of light alloys, such as magnesium and aluminum. The program began in 1944 and concluded in 1957 after construction of four forging presses and six extruders, at an overall cost of $279 million. Six of them are still in operation today, manufacturing structural parts for military and commercial aircraft. They still hold the records for size in North America, though they have since been surpassed by presses in Japan, France, Russia and China.

Wyman-Gordon is a company that designs and manufactures complex metal components. Founded in 1883 as a manufacturer of crankshafts for looms, it has a long history of making forged metal components, particularly for the aerospace industry. Wyman-Gordon is a wholly owned subsidiary of Precision Castparts Corp., and is based in Houston, Texas. It has thirteen (13) plants in five countries, and employed about 2,500 people as of 2012.
Wyman-Gordon Grafton Plant, formerly known as Air Force Plant 63, is a plant of Wyman-Gordon located in North Grafton, Massachusetts. It was purchased by Wyman-Gordon in 1982 from the United States Air Force, although the company had been operating as a contractor for the plant since its establishment. The plant is also home to the one of two of the nation's largest forging presses.
Mesta Machinery was a leading industrial machinery manufacturer based in the Pittsburgh area town of West Homestead, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1898 by George Mesta when he merged his machine shop with another. Mesta "machines" can be found in factories throughout the world and as of 1984 had equipment in 500 steel mills. Mesta was the 488th largest American company in 1958 and the 414th largest in 1959.

















