The history of Islam concerns the political, social, economic and cultural developments of Islamic civilization. Most historians accept that Islam originated in Mecca and Medina at the start of the 7th century CE. Muslims regard Islam as a return to the original faith of the prophets, such as Jesus, Solomon, David, Moses, Abraham, Noah and Adam, with the submission (islam) to the will of God.

Homs, known in pre-Islamic Syria as Emesa, is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is 501 metres (1,644 ft) above sea level and is located 162 kilometres (101 mi) north of Damascus. Located on the Orontes River, Homs is also the central link between the interior cities and the Mediterranean coast.
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Syrian governorate. With an official population of 4.6 million in 2010, Aleppo was the largest Syrian city before the Syrian Civil War; however, it is now the second-largest city in Syria, after the capital Damascus.

Latakia is the principal port city of Syria, as well as the capital of the Latakia Governorate. Historically, it has also been known as Laodicea in Syria or Laodicea ad Mare. In addition to serving as a port, the city is a manufacturing center for surrounding agricultural towns and villages. According to the 2004 official census, the population of the city is 383,786, Its population greatly increased as a result of the ongoing Syrian Civil War due to the influx of refugees from rebel held areas. It is the 4th-largest city in Syria after Aleppo, Damascus and Homs, and it borders Tartus to the south, Hama to the east, and Idlib to the north while Cape Apostolos Andreas, the most north-eastern tip of Cyprus is about 68 miles (109 km) away.

Tripoli is the largest city in northern Lebanon and the second-largest city in the country. Situated 85 kilometers north of the capital Beirut, it is the capital of the North Governorate and the Tripoli District. Tripoli overlooks the eastern Mediterranean Sea, and it is the northernmost seaport in Lebanon. It holds a string of four small islands offshore, and they are also the only islands in Lebanon. The Palm Islands were declared a protected area because of their status of haven for endangered loggerhead turtles, rare monk seals and migratory birds. Tripoli borders the city of El Mina, the port of the Tripoli District, which it is geographically conjoined with to form the greater Tripoli conurbation.

Following the Islamic conquest in 639, Lower Egypt was ruled at first by governors acting in the name of the Rashidun Caliphs and then the Ummayad Caliphs in Damascus, but in 747 the Ummayads were overthrown. Throughout the Islamic rule, Askar was named the capital and housed the ruling administration. The conquest led to two separate provinces all under one ruler: Upper and Lower Egypt. These two very distinct regions would be heavily governed by the military and followed the demands handed down by the governor of Egypt and imposed by the heads of their communities.

Antakya is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes River, about 20 kilometers (12 mi) from the Levantine Sea.

Tripolitania is a historic region and former province of Libya.

A caliphate is an Islamic state under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph, a person considered a politico-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim Community (ummah). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517. Throughout the history of Islam, a few other Muslim states, almost all hereditary monarchies, such as the Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo) and Ayyubid Caliphate have claimed to be caliphates.

The Burji or Circassian Mamluk dynasty ruled Egypt from 1382 until 1517, during the Mamluk Sultanate. It proved especially turbulent, with short-lived sultans. Political power-plays often became important in designating a new sultan. During this time Mamluks fought Timur and conquered Cyprus. Constant bickering may have contributed to the ability of the Ottomans to challenge them. Their name means 'of the tower', referring to them ruling from the Citadel east of Cairo.

This timeline tries to compile dates of important historical events that happened in or that led to the rise of the Middle East. The Middle East is the territory that comprises today's Egypt, the Persian Gulf states, Iran, Iraq, Palestine, Cyprus and Northern Cyprus, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, Gaza Strip, UAE, & Yemen. The Middle East with its particular characteristics was not to emerge until the late second millennium AD. To refer to a concept similar to that of today's Middle East but earlier in time, the term Ancient Near East is used.

Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been known by the traditional Arabic name of al-Jazira and the Syriac variant Gāzartā or Gozarto (ܓܙܪܬܐ). The Euphrates and Tigris rivers transform Mesopotamia into almost an island, as they are joined together at the Shatt al-Arab in the Basra Governorate of Iraq, and their sources in eastern Turkey are in close proximity.

Idlib is a city in northwestern Syria, 59 kilometers (37 mi) southwest of Aleppo, which is the capital of the Idlib Governorate. It has an elevation of nearly 500 meters (1,600 ft) above sea level. The city was taken over by Syrian rebel militias at the beginning of the Syrian Civil War in 2011, and by 2017 was the seat of the Syrian Salvation Government.

The Citadel of Aleppo is a large medieval fortified palace in the centre of the old city of Aleppo, northern Syria. It is considered to be one of the oldest and largest castles in the world. Usage of the Citadel hill dates back at least to the middle of the 3rd millennium BC. Occupied by many civilizations over time – including the Greeks, Byzantines, Ayyubids, Mamluks and Ottomans – the majority of the construction as it stands today is thought to originate from the Ayyubid period. An extensive conservation work took place in the 2000s by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture, in collaboration with Aleppo Archeological Society. Dominating the city, the Citadel is part of the Ancient City of Aleppo, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1986. During the 2010s, the Citadel received significant damage during the lengthy Battle of Aleppo. It was reopened to the public in early 2017 with repairs to damaged parts underway.

Al-Bab is a city, de jure administratively belonging to the Aleppo Governorate of the Syrian Arab Republic. As of December 2016, the city is under the control of pro-Turkish militias, as part of the Turkish buffer zone. Al-Bab is located 40 kilometres (25 mi) northeast of Aleppo, 30 kilometres (19 mi) south of the Turkish border, and has an area of 30 square kilometres. Al-Bab has an altitude of 471 metres. According to the Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), it had a population of 63,069 in 2004. The population has surged to about 100,000 during the Syrian Civil War. Prior to the Syrian Civil War, al-Bab's inhabitants were composed of Sunni Arabs and Arabized Kurds, thus being much more ethnically homogeneous than those of the neighbouring city of Manbij.

The Great Mosque of Aleppo or the Banu Umayya Mosque of Aleppo is the largest and one of the oldest mosques in the city of Aleppo, Syria. It is located in al-Jalloum district of the Ancient City of Aleppo, a World Heritage Site, near the entrance to Al-Madina Souq. The mosque is purportedly home to the remains of Zechariah, the father of John the Baptist, both of whom are revered in Islam and Christianity. It was built in the beginning of the 8th century CE. However, the current building dates back to the 11th through 14th centuries. The minaret was built in 1090, and was destroyed during fighting in the Syrian civil war in April 2013.
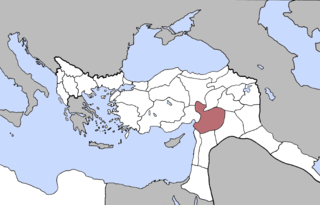
The Vilayet of Aleppo was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, centered on the city of Aleppo.

Aleppo Eyalet was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. After the Ottoman conquest it was governed from Damascus, but by 1534 Aleppo was made the capital of a new eyalet. Its reported area in the 19th century was 8,451 square miles (21,890 km2). Its capital, Aleppo, was the third largest city of the Ottoman Empire during the 16th and 17th century.

The region of Syria, known in modern literature as "Greater Syria", "Syria-Palestine", or the Levant, is an area east of the Mediterranean Sea. Throughout history, the region has been controlled by numerous different peoples, including ancient Egyptians, Canaanites, Israelites, Assyria, Babylonia, the Achaemenid Empire, the ancient Macedonians, the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire, the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimid Caliphate, the Crusaders, the Ayyubid dynasty, the Mamluk Sultanate, the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom and the French Third Republic.

Afrin Region was the westernmost of the three original regions of the de facto autonomous Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria, most commonly known as Rojava.


















