
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense (DoD) Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command (MAJCOM), responsible for Cold War command and control of two of the three components of the U.S. military's strategic nuclear strike forces, the so-called "nuclear triad," with SAC having control of land-based strategic bomber aircraft and intercontinental ballistic missiles or ICBMs.

Loring Air Force Base was a United States Air Force installation in northeastern Maine, near Limestone and Caribou in Aroostook County. It was one of the largest bases of the U.S. Air Force's Strategic Air Command during its existence, and was transferred to the newly created Air Combat Command in 1992.

Royal Air Force Fairford or more simply RAF Fairford is a Royal Air Force (RAF) station in Gloucestershire, England which is currently a standby airfield and therefore not in everyday use. Its most prominent use in recent years has been as an airfield for United States Air Force B-52s during the 2003 Iraq War, Operation Allied Force in 1999, and the first Gulf War in 1991. It is the US Air Force's only European airfield for heavy bombers.

Kincheloe Air Force Base was a U.S. Air Force base during the Cold War. Built in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in 1943 during World War II, the base was in service until 1977.

The Twentieth Air Force is a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). It is headquartered at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming.

The 42nd Air Base Wing is a United States Air Force unit assigned to Air University of Air Education and Training Command. It is stationed at Maxwell-Gunter Air Force Base, Alabama and is the host unit for Maxwell-Gunter. The wing's primary mission is to support all activities of Air University, the 908th Airlift Wing and other tenant units stationed at Maxwell-Gunter.

The 9th Bomb Squadron is a squadron of the United States Air Force. It is assigned to the 7th Operations Group, Global Strike Command, stationed at Dyess Air Force Base, Texas. The squadron is equipped with the Rockwell B-1B Lancer bomber.

The 194th Fighter Squadron is a unit of the California Air National Guard's 144th Fighter Wing at Fresno Air National Guard Base, California. The 194th is equipped with the F-15 Eagle and like its parent wing, is operationally-gained within the active U.S. Air Force by the Air Combat Command (ACC).
Operation Head Start was an experimental program by the United States Air Force during the Cold War where Strategic Air Command bombers were launched from Loring Air Force Base and loitered off of the coast of western Greenland and eastern Canada. It was operational from mid-September to mid-December 1958. It would eventually lead to Operation Chrome Dome, as it was part of a series of programs which showed that a continuous airborne alert could be achieved.

The 385th Air Expeditionary Group is a provisional United States Air Force unit assigned to Air Mobility Command to activate or inactivate as needed. It was last known to be stationed at Incirlik AB, Turkey. It is currently a tenant unit of the 379th Air Expeditionary Wing at Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar.

The 906th Air Refueling Squadron is an active United States Air Force unit. It is an active associate squadron and part of the 375th Air Mobility Wing at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois.

The 69th Bomb Squadron is an active United States Air Force unit. After being inactivated on 31 December 1993, it was reactivated on 3 September 2009 at Minot Air Force Base, and assigned to the 5th Bomb Wing. The squadron operates Boeing B-52H Stratofortress aircraft.

The 30th Tactical Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. In 1985 the squadron was formed by combining three United States Air Force and Army Air Forces units that had served in World War II and the Cold War into a single unit with a common heritage. However, the combined unit has not since been active.

A minimum interval takeoff (MITO) is a technique of the United States Air Force for scrambling all available bomber and tanker aircraft at twelve- and fifteen-second intervals, respectively. Before takeoff, the aircraft perform an elephant walk to the runway. It is designed to maximize the number of aircraft launched in the least amount of time possible before the base suffers a nuclear strike, which would obliterate all remaining aircraft.
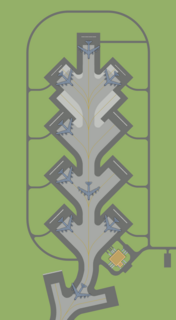
A mole hole, officially designated the Readiness Crew Building (RCB), is a type of structure built by the United States Air Force at former Strategic Air Command (SAC) bases around the country during the 1950s and 1960s. RCBs were located adjacent to an Alert Ramp, also called a "Christmas Tree", where Ready Alert aircraft were parked. These aircraft were initially Boeing B-47 Stratojet aircraft armed with nuclear weapons, augmented by Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter aerial refueling aircraft. As SAC introduced newer bomber and aerial tanker aircraft into its inventory, the B-47 and KC-97 were later superseded by Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, Convair B-58 Hustler, General Dynamics FB-111 or Rockwell B-1 Lancer bombers, augmented by Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker or McDonnell Douglas KC-10 Extender aerial refueling aircraft.
The Loring Air Force Base Alert Area is a former alert area for B-52 Stratofortress aircraft of the 42d Bombardment Wing situated at the former Loring Air Force Base at Limestone, Maine. It was constructed in 1960 due to a demand by the Strategic Air Command that its bomber bases have a staging area to launch alerts from.
An alert crew is a term used in the armed forces, most often in military aviation and in land-based missile forces, where members of their units and formations, will maintain a level of combat readiness as a group of persons. Although it sometimes encompasses the entire unit, today the term is more used for a set group of individuals.

The 968th Expeditionary Airborne Air Control Squadron is a provisional unit of the United States Air Force. It has been activated twice during the Global War on Terror.
Blytheville Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base from 1942, until it closed in 1992. In 1988, the facility was renamed Eaker Air Force Base in honor of World War II General of the Eighth Air Force, Ira C. Eaker. It was located 3 miles (4.8 km) northwest of Blytheville, Arkansas. The facility now operates as the Arkansas Aeroplex and Arkansas International Airport.



















