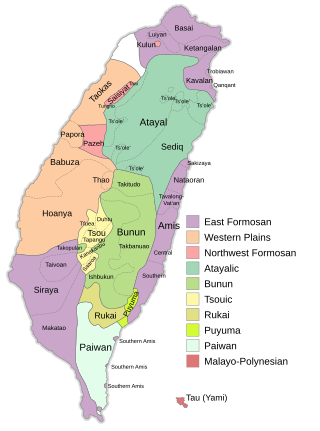
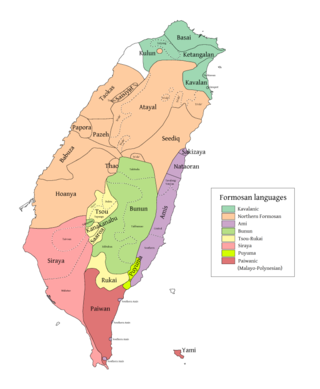
The Formosan languages are a geographic grouping comprising the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, all of which are Austronesian. They do not form a single subfamily of Austronesian but rather nine separate subfamilies. The Taiwanese indigenous peoples recognized by the government are about 2.3% of the island's population. However, only 35% speak their ancestral language, due to centuries of language shift. Of the approximately 26 languages of the Taiwanese indigenous peoples, at least ten are extinct, another four are moribund, and all others are to some degree endangered.
Academia Sinica, headquartered in Nangang, Taipei, is the national academy of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Founded in Nanking, the academy supports research activities in a wide variety of disciplines, ranging from mathematical and physical sciences, to life sciences, and to humanities and social sciences. As an educational institute, it provides PhD training and scholarship through its English-language Taiwan International Graduate Program in biology, agriculture, chemistry, physics, informatics, and earth and environmental sciences.

The Sinkang Manuscripts are a series of leases, mortgages, and other commerce contracts written in the Sinckan, Taivoan, and Makatao languages. Among Han Chinese, they are commonly referred to as the "barbarian contracts". Some are written only in a Latin-based script, considered the first script to be developed in Taiwan itself, while others were bilingual with adjacent Han writing. Currently there are approximately 140 extant documents written in Sinckan; they are important in the study of Siraya and Taivoan culture, and Taiwanese history in general although there are only a few scholars who can understand them.

National Hsinchu Senior High School is a high school in East District, Hsinchu City, Taiwan. Student enrollment averages around 2200.

The Siraya people are a Taiwanese indigenous people. The Siraya settled flat coastal plains in the southwest part of the island of Taiwan and corresponding sections of the east coast; the area is identified today with Tainan City and Taitung County. At least four communities make up the group: Mattauw, Soelangh, Baccloangh, and Sinckan. The first four communities correspond to the modern-day districts of Madou, Jiali, Shanhua, and Sinshih, respectively.

Institute of Economics, Academia Sinica is an economic research organizations in Taiwan. Early in its history, it focused on local issues, and later, expanded to explore more theoretical issues.
The Niaosung Culture was an archaeological culture in southern Taiwan. It distributed around the region of Tainan and Kaohsiung. The culture existed in the Iron Age of Taiwan island. Some evidences suggested that Niaosung Culture was directly relative to the Siraya people, an aboriginal tribe which is still living in this area.
Siraya is a Formosan language spoken until the end of the 19th century by the indigenous Siraya people of Taiwan, derived from Proto-Siraya. Some scholars believe Taivoan and Makatao are two dialects of Siraya, but now more evidence shows that they should be classified as separate languages.
The Atayalic languages are a group of Formosan languages spoken in northern Taiwan. Robert Blust considers them to form a primary branch within the Austronesian language family, However, Paul Jen-kuei Li groups them into the Northern Formosan branch, which includes the Northwestern Formosan languages.

The East Formosan languages consist of various Formosan languages scattered across Taiwan, including Kavalan, Amis, and the extinct Siraya language. This grouping is supported by both Robert Blust and Paul Jen-kuei Li. Li considers the Siraya-speaking area in the southwestern plains of Taiwan to be the most likely homeland of the East Formosan speakers, where they then spread to the eastern coast of Taiwan and gradually migrated to the area of modern-day Taipei.

The Northern Formosan languages is a proposed grouping of Formosan languages that includes the Atayalic languages, the Western Plains languages, and the Northwest Formosan languages.

Daniel Gravius (1616–1681) was a Dutch missionary to Formosa. He was a gifted linguist, who translated portions of the Bible and other Christian texts into the Siraya language. After falling out with Governor of Formosa Nicolas Verburg, he was accused of libel and censured. Later he was completely exonerated and returned to his native Netherlands with his reputation intact.
This article describes the personal pronoun systems of various Austronesian languages.
Paul Li, or Li Jen-kuei, is a Taiwanese linguist. Li is a research fellow at the Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan. Li is a leading specialist on Formosan languages and has published dictionaries on the Pazeh and Kavalan languages.

Luilang, or ambiguously Ketagalan, was a Formosan language spoken south of modern-day Taipei in northern Taiwan by one of several peoples that have been called Ketagalan. The language probably went extinct in the mid-20th century and it is very poorly attested.

Taivoan or Taivuan, is a Formosan language spoken until the end of the 19th century by the indigenous Taivoan people of Taiwan. Taivoan used to be regarded as a dialect of Siraya, but now more evidence has shown that they should be classified as separate languages. The corpora previously regarded as Siraya like the Gospel of St. Matthew and the Notes on Formulary of Christianity translated into "Siraya" by the Dutch people in the 17th century should be in Taivoan majorly.

Zhu Jiahua or Chu Chia-hua was a Chinese scientist, geologist and Kuomintang politician in the Republic of China. In the early 1930s he served as Minister of Communications for the Nationalist Government in Nanjing. He was the Vice Premier in 1949–1950. Zhu became acting president of Academia Sinica upon the death of Cai Yuanpei in 1940, and was responsible organizing the relocation of its institutes from China to Taiwan during the Chinese Civil War and a period of low monetary funds. Zhu repurposed funds originally set aside for Chinese students to study abroad. Although the Kuomintang government agreed with Zhu's actions when he first proposed them, Chiang Kai-shek later withdrew his approval and Zhu resigned as president of the Academia Sinica in 1957. Zhu was elected an academician of Academia Sinica in 1948. Following his death, Academia Sinica began hosting a lecture series in Zhu's honor.
The Lingnan Fine Arts Museum of the Academia Sinica is an art museum in Nangang District, Taipei, Taiwan.

The Taivoan or Tevoranghpeople or Shisha, also written Taivuan and Tevorang, Tivorang, Tivorangh, are a Taiwanese indigenous people.

Sirayaic languages is one of the sub-branches of the Formosan branch, under the Austronesian languages family. Both Blust (1999) and Li (2010) considers Proto-Siraya belongs to East Formosan languages, along with Kavalanic and Amis languages.











