Related Research Articles
A proton is a subatomic particle, symbol
p
or
p+
, with a positive electric charge of +1e elementary charge and a mass slightly less than that of a neutron. Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons".

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
A radionuclide is an atom that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are powerful enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single element the decay rate, and thus the half-life (t1/2) for that collection, can be calculated from their measured decay constants. The range of the half-lives of radioactive atoms has no known limits and spans a time range of over 55 orders of magnitude.
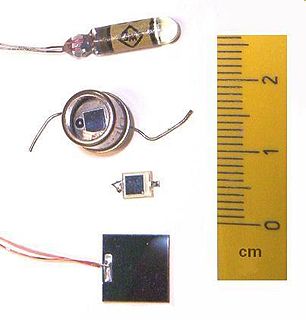
A photodiode is a semiconductor p-n junction device that converts light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. Photodiodes may contain optical filters, built-in lenses, and may have large or small surface areas. Photodiodes usually have a slower response time as their surface area increases. The common, traditional solar cell used to generate electric solar power is a large area photodiode.
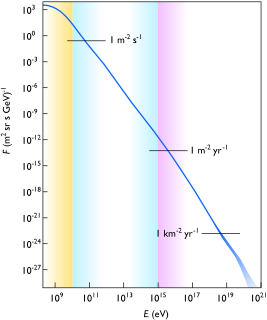
Cosmic rays are high-energy protons and atomic nuclei that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface; although the bulk is intercepted by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere.
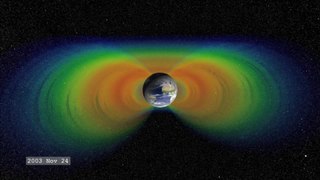
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The belts are named after James Van Allen, who is credited with their discovery. Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 640 to 58,000 km above the surface, in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays. By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the atmosphere from destruction.

Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from but conceptually related to the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth. The term space weather was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s.

The Cosmic Background Explorer, also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology, which operated from 1989 to 1993. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.
Ionizing radiation consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. The particles generally travel at a speed that is greater than 1% of that of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". Exposure can be from a source of radiation external to the human body or due to internal irradiation caused by the ingestion of radioactive contamination.

Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new isotopes—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an electron antineutrino with a mean lifetime of 887 seconds.

Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) is a NASA Explorers program Solar and space exploration mission to study matter comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources.
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation, especially for environments in outer space, around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare.
In electronics and computing, a soft error is a type of error where a signal or datum is wrong. Errors may be caused by a defect, usually understood either to be a mistake in design or construction, or a broken component. A soft error is also a signal or datum which is wrong, but is not assumed to imply such a mistake or breakage. After observing a soft error, there is no implication that the system is any less reliable than before. One cause of soft errors is single event upsets from cosmic rays.
A single-event upset (SEU) is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle striking a sensitive node in a micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element. The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error.

Error correction code memory is a type of computer data storage that uses an error correction code (ECC) to detect and correct n-bit data corruption which occurs in memory. ECC memory is used in most computers where data corruption cannot be tolerated under any circumstances, like industrial control applications, critical databases, and infrastructural memory caches.
Astronautical hygiene evaluates, and mitigates, hazards and health risks to those working in low-gravity environments. The discipline of astronautical hygiene includes such topics as the use and maintenance of life support systems, the risks of the extravehicular activity, the risks of exposure to chemicals or radiation, the characterization of hazards, human factor issues, and the development of risk management strategies. Astronautical hygiene works side by side with space medicine to ensure that astronauts are healthy and safe when working in space.
Health threats from cosmic rays are the dangers posed by cosmic rays to astronauts on interplanetary missions or any missions that venture through the Van-Allen Belts or outside the Earth's magnetosphere. They are one of the greatest barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft, but space radiation health risks also occur for missions in low Earth orbit such as the International Space Station (ISS).
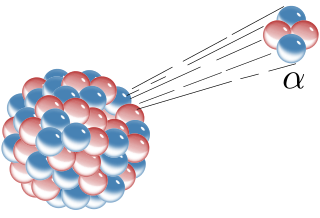
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+
or 4
2He2+
indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge. Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal helium atom 4
2He.

ESRO-2B or Iris or sometimes ESRO II, was a European astrophysical spin-stabilised research satellite which was launched in 1968. Operated by the European Space Research Organisation, ESRO 2B made astronomical surveys primarily in x-ray and solar particles detectors.
References
- ↑ "Alpha particles". 26 April 2017.
- 1 2 Mukherjee, Shubu (2008). "Device- and Circuit-Level Modeling, Measurement, and Mitigation". Architecture Design for Soft Errors. pp. 43–78. doi:10.1016/B978-012369529-1.50004-5. ISBN 978-0-12-369529-1.
- 1 2 Rauch, Stewart E. (2007). "Terrestrial Radiation Induced Soft Errors in Integrated Circuits" (PDF). Radiation Induced Soft Errors. IEEE.
- 1 2 "Particles from outer space are wreaking low-grade havoc on personal electronics". phys.org.
- ↑ Binder, D.; Smith, E. C.; Holman, A. B. (1975). "Satellite Anomalies from Galactic Cosmic Rays". IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science. 22 (6): 2675–2680. Bibcode:1975ITNS...22.2675B. doi:10.1109/TNS.1975.4328188. S2CID 3032512.
- ↑ Talyzin, Alexandr V.; Luzan, Serhiy; Anoshkin, Ilya V.; Nasibulin, Albert G.; Jiang, Hua; Kauppinen, Esko I.; Mikoushkin, Valery M.; Shnitov, Vladimir V.; Marchenko, Dmitry E.; Noréus, Dag (28 June 2011). "Hydrogenation, Purification, and Unzipping of Carbon Nanotubes by Reaction with Molecular Hydrogen: Road to Graphane Nanoribbons". ACS Nano. 5 (6): 5132–5140. doi:10.1021/nn201224k. PMID 21504190.
- ↑ Wilson, J.W.; Shinn, J.L.; Tripathi, R.K.; Singleterry, R.C.; Clowdsley, M.S.; Thibeault, S.A.; Cheatwood, F.M.; Schimmerling, W.; Cucinotta, F.A.; Badhwar, G.D.; Noor, A.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Badavi, F.F.; Heinbockel, J.H.; Miller, J.; Zeitlin, C.; Heilbronn, L. (August 2001). "Issues in deep space radiation protection". Acta Astronautica. 49 (3–10): 289–312. Bibcode:2001AcAau..49..289W. doi:10.1016/s0094-5765(01)00107-2. PMID 11669118.