Related Research Articles

Erysipelas is a relatively common bacterial infection of the superficial layer of the skin, extending to the superficial lymphatic vessels within the skin, characterized by a raised, well-defined, tender, bright red rash, typically on the face or legs, but which can occur anywhere on the skin. It is a form of cellulitis and is potentially serious.

Tinea cruris, also known as Jock itch, is a common type of contagious, superficial fungal infection of the groin region, which occurs predominantly but not exclusively in men and in hot-humid climates.

A boil, also called a furuncle, is a deep folliculitis, infection of the hair follicle. It is most commonly caused by infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in a painful swollen area on the skin caused by an accumulation of pus and dead tissue. Boils which are expanded are basically pus-filled nodules. Individual boils clustered together are called carbuncles. Most human infections are caused by coagulase-positive S. aureus strains, notable for the bacteria's ability to produce coagulase, an enzyme that can clot blood. Almost any organ system can be infected by S. aureus.
Ross River virus (RRV) is a small encapsulated single-strand RNA Alphavirus endemic to Australia, Papua New Guinea and other islands in the South Pacific. It is responsible for a type of mosquito-borne non-lethal but debilitating tropical disease known as Ross River fever, previously termed "epidemic polyarthritis". The virus is suspected to be enzootic in populations of various native Australian mammals, and has been found on occasion in horses.

Brome mosaic virus (BMV) is a small, positive-stranded, icosahedral RNA plant virus belonging to the genus Bromovirus, family Bromoviridae, in the Alphavirus-like superfamily.
A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: macules are small, flat discolored spots on the surface of the skin; and papules are small, raised bumps. It is also described as erythematous, or red.

The Semliki Forest virus was first isolated from mosquitoes in the Semliki Forest, Uganda by the Uganda Virus Research Institute in 1942 and described by Smithburn and Haddow. It is known to cause disease in animals including humans. It is an alphavirus found in central, eastern, and southern Africa.
Polyarthritis is any type of arthritis that involves 5 or more joints simultaneously. It is usually associated with autoimmune conditions and may be experienced at any age and is not sex specific.
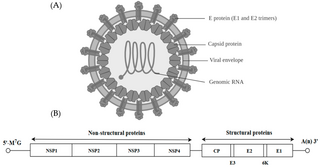
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical, and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.
The Western equine encephalomyelitis virus is the causative agent of relatively uncommon viral disease Western equine encephalomyelitis (WEE). An alphavirus of the family Togaviridae, the WEE virus is an arbovirus transmitted by mosquitoes of the genera Culex and Culiseta. WEE is a recombinant virus between two other alphaviruses, an ancestral Sindbis virus-like virus, and an ancestral Eastern equine encephalitis virus-like virus. There have been under 700 confirmed cases in the U.S. since 1964. This virus contains an envelope that is made up of glycoproteins and nucleic acids. The virus is transmitted to people and horses by bites from infected mosquitoes and birds during wet, summer months.

Sindbis virus (SINV) is a member of the Togaviridae family, in the Alphavirus genus. The virus was first isolated in 1952 in Cairo, Egypt. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes SINV causes sindbis fever in humans and the symptoms include arthralgia, rash and malaise. Sindbis fever is most common in Southern Africa, East Africa, Egypt, Palestine, the Philippines and parts of Australia.

Tinea faciei is a fungal infection of the face. It generally appears as a red rash on the face, followed by patches of small, raised bumps. The skin may peel while it is being treated.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focusses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract.

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.
Aeromonas infections include skin infections such as cellulitis, pustules, and furuncles. Aeromonas species can also cause gastroenteritis.
Mayaro virus disease is a mosquito-borne zoonotic pathogen endemic to certain humid forests of tropical South America. Infection with Mayaro virus causes an acute, self-limited dengue-like illness of 3–5 days' duration. The causative virus, abbreviated MAYV, is in the family Togaviridae, and genus Alphavirus. It is closely related to other alphaviruses that produce a dengue-like illness accompanied by long-lasting arthralgia. It is only known to circulate in tropical South America.

Middelburg virus (MIDV) is an alphavirus of the Old World Group that has likely endemic and zoonotic potential. It is of the viral family Togaviridae. It was isolated from mosquitos in 1957 in South Africa, MDIV antigens have now been found in livestock, horses, and humans.

Getah virus is a mosquito-borne arbovirus in the Alphavirus genus. The virus was first isolated in Malaysia in 1955 from the Culex gelidus mosquito. It has been known to infect pigs but more commonly affects horses. The virus was isolated near rubber plantations; the word Getah means rubber in Malay. The first outbreak among racehorses occurred in Japan September–November 1978. Getah virus is widely distributed in the countries of South-east Asian and in Northern Australia.
Salmon Pancreas disease is caused by a species of Salmonid Alphavirus (SAV) called Salmon pancreas disease virus (SPDV). The virus was first described in 1976 in Scotland and in 1989 in Norway. It affects farmed Atlantic salmon caused by Marine SAV2 and SAV3 and has also been identified in Rainbow trout in the seawater phase caused by SAV2 where the disease is commonly referred to as Sleeping Disease (SD).
Rio Negro virus is an alphavirus that was first isolated in Argentina in 1980. The virus was first called Ag80-663 but was renamed to Rio Negro virus in 2005. The virus is a member of the Venezuelan equine encephalitis complex (VEEC), which are a group of alphaviruses in the Americas that have the potential to emerge and cause disease. Closely related viruses include Mucambo virus and Everglades virus.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.