Related Research Articles

Breast reconstruction is the surgical process of rebuilding the shape and look of a breast, most commonly in women who have had surgery to treat breast cancer. It involves using autologous tissue, prosthetic implants, or a combination of both with the goal of reconstructing a natural-looking breast. This process often also includes the rebuilding of the nipple and areola, known as nipple-areola complex (NAC) reconstruction, as one of the final stages.

The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.

The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in females, milk leaves the breast through the lactiferous ducts to feed an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively or it can be ejected by smooth muscle contractions that occur along with the ductal system. Male mammals also have nipples but without the same level of function, and often surrounded by body hair.

The human areola is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. Areola, more generally, is a small circular area on the body with a different histology from the surrounding tissue, or other small circular areas such as an inflamed region of skin.

Paget's disease of the breast is a rare skin change at the nipple nearly always associated with underlying breast cancer. Paget's disease of the breast was first described by Sir James Paget in 1874. The condition is an uncommon disease accounting for 1 to 4% of all breast cancers cases. 92% to 100% of patients with Paget's disease of the breast have an underlying breast cancer.

Areolar glands, also known as glandulae areolares, Montgomery glands, and tubercula areolae, are 10-15 elevations found on the areola. They are usually arranged in a circle around the nipple, and can be particularly visible when the nipple is erect. Their role is to promote adequate breastfeeding of the infant.

An inverted nipple is a condition where the nipple, instead of pointing outward, is retracted into the breast. In some cases, the nipple will be temporarily protruded if stimulated. Both women and men can have inverted nipples.

A nipple shield is a piece of body jewelry worn on the nipple, partially or fully covering the areola. The shield encircles the nipple, and can be attached by several means, including suction, friction and the action of glue, but is most often held in place by a nipple piercing. Usually, its primary intent is to lift, highlight, and ornament the nipple, as well as the whole breast, much as other pieces of jewelry do for other parts of the body.

A nipple shield is a nipple-shaped sheath worn over the areola and nipple during breastfeeding. Modern nipple shields are made of soft, thin, flexible silicone and have holes at the end of the nipple section to allow the breast milk to pass through.

Male chest reconstruction refers to any of various surgical procedures to masculinise the chest by removing breast tissue or altering the nipples and areolae. Male chest reconstruction may be performed in cases of gynecomastia and gender dysphoria. Transmasculine people may pursue chest reconstruction, also known as top surgery, as part of transitioning.
Mastopexy is the plastic surgery mammoplasty procedure for raising sagging breasts upon the chest of the woman, by changing and modifying the size, contour, and elevation of the breasts. In a breast-lift surgery to re-establish an aesthetically proportionate bust for the woman, the critical corrective consideration is the tissue viability of the nipple-areola complex (NAC), to ensure the functional sensitivity of the breasts for lactation and breast-feeding.
Amastia refers to a rare clinical anomaly in which both internal breast tissue and the visible nipple are absent on one or both sides. It affects both men and women. Amastia can be either isolated or comorbid with other syndromes, such as ectodermal dysplasia, Syndactyly and lipoatrophic diabetes. This abnormality can be classified into various types, and each could result from different pathologies. Amastia differs from amazia and athelia. Amazia is the absence of one or both mammary glands but the nipples remain present, and athelia is the absence of one or both nipples, but the mammary gland remains.

Breastfeeding difficulties refers to problems that arise from breastfeeding, the feeding of an infant or young child with milk from a woman's breasts. Although babies have a sucking reflex that enables them to suck and swallow milk, and human breast milk is usually the best source of nourishment for human infants, there are circumstances under which breastfeeding can be problematic, or even in rare instances, contraindicated.
SPAIR is a short-scar breast surgery technique developed by Dennis C. Hammond, assistant professor of surgery at Michigan State University. The technique was designed to allow a better-shaped breast, a limited amount of scarring, and a more accelerated healing process, by eliminating the lateral scar beneath the breast found in conventional breast reduction surgery. The technique is considered to be a good alternative to vertical mammoplasty.

A nipple adenoma is a rare benign tumour of the breast.

Nipple stimulation or breast stimulation is stimulation of the breast. Stimulation may be by breastfeeding, sexual activity, or an indirect non-sexual response. As part of sexual activity, the practice may be performed upon, or by, people of any gender or sexual orientation. It may occur with the use of fingers, orally, such as by sucking or licking, as well as by use of an object.
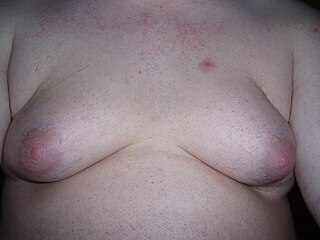
Adipomastia, also known colloquially as fatty breasts, is a condition defined as an excess of skin and/or a flat layer of adipose tissue in the breasts without true gynecomastia. It is commonly present in men with obesity, and is particularly apparent in men who have undergone massive weight loss. A related/synonymous term is pseudogynecomastia. The condition is different and should be distinguished from gynecomastia, which involves female-like protruding fat tissue and/or glandular tissue in a male. The two conditions can usually be distinguished easily by palpation to check for the presence of glandular tissue. Another difference between the conditions is that breast pain/tenderness does not occur in pseudogynecomastia. Sometimes, gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia are present together; this is related to the fact that fat tissue expresses aromatase, the enzyme responsible for the synthesis of estrogen, and estrogen is produced to a disproportionate extent in men with excessive amounts of fat, resulting in simultaneous glandular enlargement.
Cracked nipple is a condition that can occur in breastfeeding women as a result of a number of possible causes. Developing a cracked nipple can result in soreness, dryness or irritation to, or bleeding of, one or both nipples during breastfeeding. The mother with a cracked nipple can have severe nipple pain when the baby is nursing. This severe pain is a disincentive for continued breastfeeding. The crack can appear as a cut across the tip of the nipple and may extend to its base. Cracked nipple can develop after the birth of the infant and is managed with pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatment.

Latch refers to how the baby fastens onto the breast while breastfeeding. A good latch promotes high milk flow and minimizes nipple discomfort for the mother, whereas poor latch results in poor milk transfer to the baby and can quickly lead to sore and cracked nipples. In a good latch, both the nipple and a large portion of the areola are in the baby's mouth.
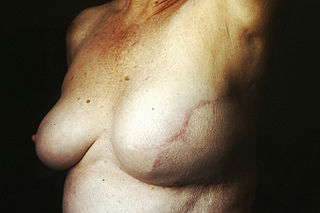
Nipple reconstruction, specifically nipple-areola complex (NAC) reconstruction, is a procedure commonly done for patients who had part or all of their nipple removed due to medical reasons. For example, NAC reconstruction can apply to breast cancer patients who underwent a mastectomy, the surgical removal of a breast. NAC reconstruction can also be applied to patients with trauma, burn injuries, and congenital or pathological abnormalities in nipple development.