Related Research Articles

The United States Census Bureau is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce and its director is appointed by the President of the United States.
Laurel Bay is a census-designated place and military housing complex in Beaufort County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 5,891 at the 2010 census. As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, Laurel Bay is included within the Hilton Head Island-Bluffton-Beaufort, SC Metropolitan Statistical Area.
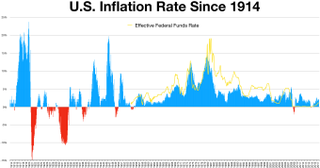
A Consumer Price Index measures changes in the price level of a weighted average market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.

The American Community Survey (ACS) is an ongoing survey by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educational attainment, income, language proficiency, migration, disability, employment, and housing characteristics. These data are used by many public-sector, private-sector, and not-for-profit stakeholders to allocate funding, track shifting demographics, plan for emergencies, and learn about local communities. Sent to approximately 295,000 addresses monthly, it is the largest household survey that the Census Bureau administers.

The Survey of Income and Program Participation (SIPP) is a statistical survey conducted by the United States Census Bureau.
A reverse mortgage is a mortgage loan, usually secured by a residential property, that enables the borrower to access the unencumbered value of the property. The loans are typically promoted to older homeowners and typically do not require monthly mortgage payments. Borrowers are still responsible for property taxes and homeowner's insurance. Reverse mortgages allow elders to access the home equity they have built up in their homes now, and defer payment of the loan until they die, sell, or move out of the home. Because there are no required mortgage payments on a reverse mortgage, the interest is added to the loan balance each month. The rising loan balance can eventually grow to exceed the value of the home, particularly in times of declining home values or if the borrower continues to live in the home for many years. However, the borrower is generally not required to repay any additional loan balance in excess of the value of the home.
Section 8 of the Housing Act of 1937, often called Section 8, as repeatedly amended, authorizes the payment of rental housing assistance to private landlords on behalf of low-income households in the United States. Of the 5.2 million American Households that received rental assistance in 2018, approximately 1.2 million of those households received a Section 8 based voucher. 68% of total rental assistance in the United States goes to seniors, children, and those with disabilities. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development manages Section 8 programs.
Poverty in Australia deals with the incidence of relative poverty in Australia and its measurement. Relative income poverty is measured as a percentage of the population that earns less in comparison to the median wage of the working population.
The Consumer Expenditure Survey is a Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) survey that collects information on the buying habits of U.S. consumers. The program consists of two components — the Interview Survey and the Diary Survey — each with its own sample. The surveys collect data on expenditures, income, and consumer unit characteristics.
Population census in Hong Kong, a collection of demographic data in Hong Kong, is conducted by the Census and Statistics Department of the Hong Kong Government. The census has been held every ten years since 1961 and the by-census is held between two census. The last census and by-census were in June 2011 and June 2016, respectively.

Household income is an economic standard that can be applied to one household, or aggregated across a large group such as a county, city, or the whole country. It is commonly used by the United States government and private institutions to describe a household's economic status or to track economic trends in the US.

The home-ownership rate in the United States is percentage of homes that are owned by their occupants. In 2009, it remained similar to that in some other post-industrial nations with 67.4% of all occupied housing units being occupied by the unit's owner. Home ownership rates vary depending on demographic characteristics of households such as ethnicity, race, type of household as well as location and type of settlement. In 2018, homeownership dropped to a lower rate than it was in 1994, with a rate of 64.2%.
The terms average Joe, ordinary Joe, Joe Sixpack, Joe Lunchbucket, Joe Snuffy, Joe Schmo and ordinary Jane, average Jane, and plain Jane, are used primarily in North America to refer to a completely average person, typically an average American. It can be used both to give the image of a hypothetical "completely average person" or to describe an existing person. Parallel terms in other languages for local equivalents exist worldwide.

Residential segregation in the United States is the physical separation of two or more groups into different neighborhoods—a form of segregation that "sorts population groups into various neighborhood contexts and shapes the living environment at the neighborhood level". While it has traditionally been associated with racial segregation, it generally refers to any kind of sorting based on some criteria populations.

Subsidized housing in the United States is administered by federal, state and local agencies to provide subsidized rental assistance for low-income households. Public housing is priced much below the market rate, allowing people to live in more convenient locations rather than move away from the city in search of lower rents. In most federally-funded rental assistance programs, the tenants' monthly rent is set at 30% of their household income. Now increasingly provided in a variety of settings and formats, originally public housing in the U.S. consisted primarily of one or more concentrated blocks of low-rise and/or high-rise apartment buildings. These complexes are operated by state and local housing authorities which are authorized and funded by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). More than 1.2 million households currently live in public housing of some type. Subsidized apartment buildings, often referred to as housing projects, have a complicated and often notorious history in the United States. While the first decades of projects were built with higher construction standards and a broader range of incomes and same applicants, over time, public housing increasingly became the housing of last resort in many cities. Several reasons have been cited for this negative trend including the failure of Congress to provide sufficient funding, a lowering of standards for occupancy, and mismanagement at the local level. Furthermore, housing projects have also been seen to greatly increase concentrated poverty in a community, leading to several negative externalities. Crime, drug usage, and educational under-performance are all widely associated with housing projects, particularly in urban areas.
The Panel Study of Income Dynamics (PSID) is a longitudinal panel survey of American families, conducted by the Survey Research Center at the University of Michigan.
Housing quality and health outcomes in the United States are inextricably linked. As a matter of U.S. public health, substandard housing is associated with outcomes such as injury, respiratory infections, heavy metal poisoning and asthma. It may also be associated with mental disability and with obesity and its related morbidities.
Housing insecurity is the lack of security in an individual shelter that is the result of high housing costs relative to income, poor housing quality, unstable neighborhoods, overcrowding, and/or homelessness.

Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a median household income as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. The challenges of promoting affordable housing varies by location.
References
- ↑ American Housing Survey site at HUD User
- ↑ US Census Bureau. Demographic surveys. Archived 2013-10-11 at the Wayback Machine Click on the Survey abstracts at the top of page; then see page 7 of PDF (4 of document).
- ↑ US Census Bureau. AHS FAQ
- ↑ Census MDAT
- ↑ 32 Years of Housing Data