
A film format is a technical definition of a set of standard characteristics regarding image capture on photographic film for still images or film stock for filmmaking. It can also apply to projected film, either slides or movies. The primary characteristic of a film format is its size and shape.

Letterboxing is the practice of transferring film shot in a widescreen aspect ratio to standard-width video formats while preserving the film's original aspect ratio. The resulting videographic image has mattes above and below it; these mattes are part of each frame of the video signal. LBX and LTBX are identifying abbreviations for films and images thus formatted.

Pan and scan is a method of adjusting widescreen film images so that they can be shown in fullscreen proportions of a standard-definition 4:3 aspect ratio television screen, often cropping off the sides of the original widescreen image to focus on the composition's most important aspects.

Standard-definition television is a television system which uses a resolution that is not considered to be either high or enhanced definition. "Standard" refers to it being the prevailing specification for broadcast television in the mid- to late-20th century, and compatible with legacy analog broadcast systems.

Widescreen images are displayed within a set of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35 mm film.

35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips 1.377 ± 0.001 inches (34.976 ± 0.025 mm) wide. The standard image exposure length on 35 mm for movies is four perforations per frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film.

VistaVision is a higher resolution, widescreen variant of the 35 mm motion picture film format which was created by engineers at Paramount Pictures in 1954.

CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.55:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope lens.
Anamorphic widescreen is a process by which a comparatively wide widescreen image is horizontally compressed to fit into a storage medium with a narrower aspect ratio, reducing the horizontal resolution of the image while keeping its full original vertical resolution. Compatible play-back equipment can then expand the horizontal dimension to show the original widescreen image. This is typically used to allow one to store widescreen images on a medium that was originally intended for a narrower ratio, while using as much of the frame – and therefore recording as much detail – as possible.
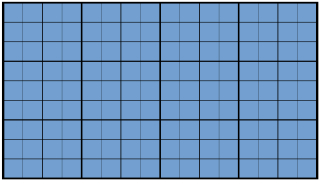
16:9 is a widescreen aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9 units.

Panavision is an American motion picture equipment company founded in 1953 specializing in cameras and lenses, based in Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk as a small partnership to create anamorphic projection lenses during the widescreen boom in the 1950s, Panavision expanded its product lines to meet the demands of modern filmmakers. The company introduced its first products in 1954. Originally a provider of CinemaScope accessories, the company's line of anamorphic widescreen lenses soon became the industry leader. In 1972, Panavision helped revolutionize filmmaking with the lightweight Panaflex 35 mm movie camera. The company has introduced other cameras such as the Millennium XL (1999) and the digital video Genesis (2004).

The Big Trail is a 1930 American pre-Code Western early widescreen film shot on location across the American West starring 23-year-old John Wayne in his first leading role and directed by Raoul Walsh.

The pillarbox effect occurs in widescreen video displays when black bars are placed on the sides of the image. It becomes necessary when film or video that was not originally designed for widescreen is shown on a widescreen display, or a narrower widescreen image is displayed within a wider aspect ratio, such as a 16:9 image in a 2.39:1 frame. The original material is shrunk and placed in the middle of the widescreen frame.
Kinopanorama is a three-lens, three-film widescreen film format. Although Kinopanorama was initially known as Panorama in the Soviet Union the name was later revised to include its current name prior to the premiere screenings in Moscow in 1958. In some countries, including Cuba, Greece, Norway and Sweden, it was usually marketed as Soviet Cinerama. When Great Is My Country and The Enchanted Mirror, were exhibited at the Mayfair Theatre in New York City in 1958, it was briefly advertised as Cinepanorama. Kinopanorama is for the most part identical in operation to that of Fred Waller's American-designed Cinerama format.

Billy the Kid is a 1930 American pre-Code Western film directed in widescreen by King Vidor about the relationship between frontier outlaw Billy the Kid and lawman Pat Garrett. In February 2020, the film was shown at the 70th Berlin International Film Festival, as part of a retrospective dedicated to King Vidor's career.

Old Ironsides is a 1926 American silent historical war film directed by James Cruze and starring Charles Farrell, Esther Ralston, Wallace Beery, and George Bancroft. It was produced and distributed by Paramount Pictures.

Kismet is a 1930 American pre-Code costume drama film photographed entirely in an early widescreen process using 65mm film that Warner Bros. called Vitascope. The film, now considered lost, was based on Edward Knoblock's play Kismet, and was previously filmed as a silent film in 1920 which also starred Otis Skinner.

Anamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen. The word anamorphic and its derivatives stem from the Greek anamorphoun, compound of morphé with the prefix aná. In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however, in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of popularity, due in large part to the higher base ISO sensitivity of digital sensors, which facilitates shooting at smaller apertures.
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as 16:9, sixteen-to-nine. For the x:y aspect ratio, the image is x units wide and y units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography.
Joseph Arthur Ball was an American inventor, physicist, and executive at Technicolor. He was the technical director of the first color movie, and one of only three founding technicians of the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences. He was awarded an Academy Honorary Award at the 11th Academy Awards for his contributions to color film photography. He held many patents in color photography and was credited with creating the three-component process.















