
Left: 2-Aminophenol (o-aminophenol)
Center: 3-Aminophenol (m-aminophenol)
Right: 4-Aminophenol (p-aminophenol)
Aminophenol may refer to any of three isomeric chemical compounds:

Aminophenol may refer to any of three isomeric chemical compounds:

In the processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black. The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halides that have been exposed to light. Paper left in developer will eventually reduce all the silver halides and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image.

Hair coloring, or hair dyeing, is the practice of changing the hair color. The main reasons for this are cosmetic: to cover gray or white hair, to change to a color regarded as more fashionable or desirable, or to restore the original hair color after it has been discolored by hairdressing processes or sun bleaching.
Copper sulfate may refer to:

Acetanilide is an odourless solid chemical of leaf or flake-like appearance. It is also known as N-phenylacetamide, acetanil, or acetanilid, and was formerly known by the trade name Antifebrin.

Metol (or Elon) are trade names for the organic compound with the formula [HOC6H4NH2(CH3)]HSO4. It is the hydrogen sulfate (HSO4−) salt of the protonated derivative of N-methylaminophenol. This colourless salt is a popular photographic developer used in black & white photography.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.
The Bamberger rearrangement is the chemical reaction of phenylhydroxylamines with strong aqueous acid, which will rearrange to give 4-aminophenols. It is named for the German chemist Eugen Bamberger (1857–1932).
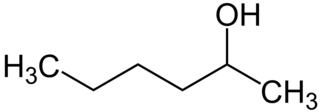
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:
Apap or APAP may refer to:
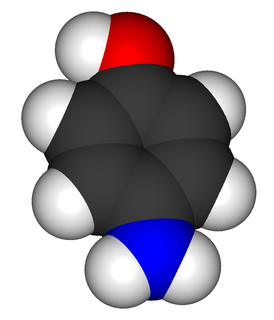
4-Aminophenol (or para-aminophenol or p-aminophenol) is the organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it was commonly used as a developer for black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal.
3-Aminophenol is an organic compound with formula C6H4(NH2)(OH). It is an aromatic amine and aromatic alcohol. It is the meta isomer of 2-aminophenol and 4-aminophenol.
Grif may refer to:
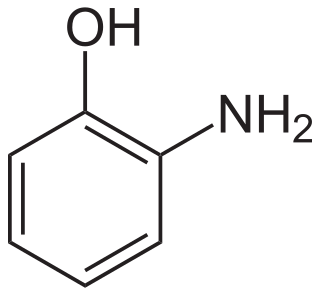
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H7NO. Along with its isomer 4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dyes and heterocyclic compounds. Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water.
p-Anisidine (para-anisidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4NH2. A white solid, commercial samples can appear grey-brown owing to air oxidation. It is one of three isomers of anisidine, methoxy-containing anilines. It is prepared by reduction of 4-nitroanisole.
Dioxin may refer to:
The molecular formula C6H7NO may refer to:

Robert Lincoln McNeil Jr. was an American chemist and pharmaceutical industry executive. He was responsible for, among other things, the commercial development, naming, and introduction of the pain reliever Tylenol.
Phosphorus nitride refers to several chemical compounds of phosphorus and nitrogen:
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has published four sets of rules to standardize chemical nomenclature.
Ortho effect refers mainly to the set of steric effects and some bonding interactions along with polar effects caused by the various substituents which are in a given molecule altering its chemical properties and physical properties. In a general sense the ortho effect is associated with substituted benzene compounds.