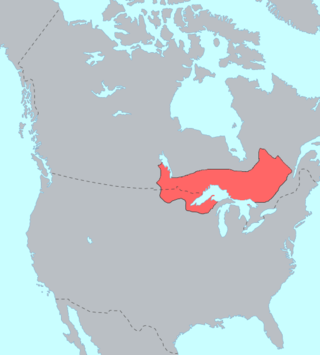
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. Ojibweg, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also understand themselves to be Ojibwe as well, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.

A totem is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system.

The Bad River LaPointe Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians or Bad River Tribe for short are a federally recognized tribe of Ojibwe people. The tribe had 6,945 members as of 2010. The Bad River Reservation is located on the south shore of Lake Superior and has a land area of about 193.11 square miles (500.15 km2) in northern Wisconsin, straddling Ashland and Iron counties. Odanah, the administrative and cultural center, is located five miles (8.0 km) east of the town of Ashland on U.S. Highway 2. The reservation population was 1,545 in 2020. Most of the reservation is managed as undeveloped forest and wetland, providing a habitat for wild rice and other natural resources.

The Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, also known as the Mille Lacs Band of Chippewa Indians, is a federally recognized American Indian tribe in east-central Minnesota. The Band has 4,302 members as of 2012. Its homeland is the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, consisting of District I, District II, District IIa, and District III.
The St. Croix Chippewa Indians are a historical Band of Ojibwe located along the St. Croix River, which forms the boundary between the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Minnesota. The majority of the St. Croix Band are divided into two groups: the federally recognized St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin, and the St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Minnesota, who are one of four constituent members forming the federally recognized Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe. The latter is one of six bands in the federally recognized Minnesota Chippewa Tribe.

The Lac Courte Oreilles Tribe is one of six federally recognized bands of Ojibwe people located in present-day Wisconsin. It had 7,275 enrolled members as of 2010. The band is based at the Lac Courte Oreilles Indian Reservation in northwestern Wisconsin, which surrounds Lac Courte Oreilles. The main reservation's land is in west-central Sawyer County, but two small plots of off-reservation trust land are located in Rusk, Burnett, and Washburn counties. The reservation was established in 1854 by the second Treaty of La Pointe.
The Mille Lacs Indians, also known as the Mille Lacs and Snake River Band of Chippewa, are a Band of Indians formed from the unification of the Mille Lacs Band of Mississippi Chippewa (Ojibwe) with the Mille Lacs Band of Mdewakanton Sioux (Dakota). Today, their successor apparent Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe consider themselves as being Ojibwe, but many on their main reservation have the ma'iingan (wolf) as their chief doodem (clan), which is an indicator of Dakota origins.

Hanging Cloud was an Ojibwe woman who was a full warrior among her people, and claimed by the Wisconsin Historical Society as the only woman to ever become one. She was the daughter of Chief Nenaa'angebi and his wife Niigi'o. Aazhawigiizhigokwe was of the Makwa-doodem, and was born and lived most of her life at Rice Lake, Wisconsin. Her community became part of the Lac Courte Oreilles Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indians after the 1854 Treaty of La Pointe.

Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa is a band of Ojibwe Native Americans. The Red Cliff Band is located on the Red Cliff Indian Reservation, on Lake Superior in Bayfield County, Wisconsin. Red Cliff, Wisconsin, is the administrative center. Red Cliff is notable for being the band closest to the spiritual center of the Ojibwe nation, Madeline Island. As of November 2010, there were 5,312 enrolled members, with about half living on the reservation and the rest living in the city of Bayfield or the Belanger Settlement.

Chief Buffalo was a major Ojibwa leader, born at La Pointe in Lake Superior's Apostle Islands, in what is now northern Wisconsin, USA.

The Sandy Lake Tragedy was the culmination in 1850 of a series of events centered in Big Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in the deaths of several hundred Lake Superior Chippewa. Officials of the Zachary Taylor Administration and Minnesota Territory sought to relocate several bands of the tribe to areas west of the Mississippi River. By changing the location for fall annuity payments, the officials intended the Chippewa to stay at the new site for the winter, hoping to lower their resistance to relocation. Due to delayed and inadequate payments of annuities and lack of promised supplies, about 400 Ojibwe, mostly men and 12% of the tribe, died of disease, starvation and cold. The outrage increased Ojibwe resistance to removal. The bands effectively gained widespread public support to achieve permanent reservations in their traditional territories.
Cat Lake First Nation is an Ojibway First Nation reserve approximately 180 kilometres northwest of Sioux Lookout in northwestern Ontario, Canada, located on the central north shore of Cat Lake. As of 2021, their total registered population was 651 people.
The Battle of the Brule was an October 1842 battle between the La Pointe Band of Ojibwe Indians and a war party of Lakota Indians. The battle took place along the Brule River in what is today northern Wisconsin and resulted in a decisive victory for the Ojibwe.
The Anishinaabe, like most Algonquian-speaking groups in North America, base their system of kinship on clans or totems. The Ojibwe word for clan was borrowed into English as totem. The clans, based mainly on animals, were instrumental in traditional occupations, intertribal relations, and marriages. Today, the clan remains an important part of Anishinaabe identity. Each clan is forbidden from harming its representation animal by any means, as it is a bad omen to do so.

Chief Beautifying Bird or Dressing Bird, was a principal chief of the Prairie Rice Lake Band of the Lake Superior Chippewa, originally located near Rice Lake, Wisconsin. He served as the principal chief about the middle of the 19th century.

Beshekee, also Pezeke and other variant spellings of Ojibwe Bizhiki, was a noted war chief from the Bear doodem of the Pillager Chippewa Band during the 19th century in North America.
Waubojeeg, also written Waabojiig or other variants in Ojibwe, "White Fisher" was a warrior and chief of the Ojibwe people. He was born into the Adik (caribou) doodem (clan), some time in the mid-18th century near Zhaagawaamikong on the western end of Lake Superior. His father Mamongazeda was also a noted warrior, who fought for the French in the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. Although Waabojiig's family had intermarried with the Dakota people during times of peace, and he had several Dakota relatives, including the famous chief Wapasha I, he fought in several battles against the Dakota and Meskwaki during his lifetime. His children, notably his son Weshkii and his daughter Ozhaguscodaywayquay, became prominent in the Sault Ste. Marie area, a major fur trading post.
Chief Tagwagané was an Anishinaabe (Ojibwa) sub-chief of the La Pointe Band of Lake Superior Chippewa, located in the Chequamegon area in the first half of the 19th century. He was of the Ajijaak-doodem. His village was often located along Bay City Creek within the city limits of what now is Ashland, Wisconsin.
Ma-mong-a-ze-da was an 18th-century Ojibwa chief from Shagawamikong. He was a member of the Caribou doodem "Adik Reindeer Clan" and his ancestors came from Grand Portage on the north shore of Lake Superior. His father was his mother's second husband as she had been married to a chief of the Dakota people previously during a period of peace between the Ojibwa and Dakota. When war resumed the couple was obliged to divorce with the husband and children joining the Dakota and the wife marrying an Ojibwa man. In this way, Mamongazeda's older half-brother Wapasha became a chief of the Dakota while he became a chief of the Ojibwa. In addition to being an accomplished war leader, Mamongazeda was persuasive diplomat and strong ally of the French. During the French and Indian War, Mamongazeda raised a party of Lake Superior Ojibwa to fight with the French, and were part of Montcalm's army at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. He lived to a very old age and was succeeded by his son, the famous chief and warrior, Waubojeeg.

Nipissing First Nation, meaning "place of little waters", is a long-standing community of Nishnaabeg peoples, who traditionally speak Anishinaabemwin, located along the shorelines of Lake Nipissing in northern Ontario. They are referred to by many names in European historical records, since the colonists often adopted names given to them by other nations.











