
When the Roman Empire divided into east and west in 395, the territories of modern Albania became a part of the Byzantine Empire. At the end of the 12th century, the Principality of Arbanon was formed which lasted until mid 13th century, after its dissolution it was followed with the creation of the Albanian Kingdom after an alliance between the Albanian noblemen and Angevin dynasty. After a war against the Byzantine empire led the kingdom occasionally decrease in size until the Angevins eventually lost their rule in Albania and led the territory ruled by several different Albanian chieftains until the mid 14th century which for a short period of time were conquered by the short-lived empire of Serbia. After its fall in 1355 several chieftains regained their rule and significantly expanded until the arrival of the Ottomans after the Battle of Savra.

The Kingdom of Albania was established by Charles of Anjou in the Albanian territories he conquered from the Byzantine Empire in 1271, with the help of the local Albanian nobility. The Kingdom of Albania was declared in late February 1272. The kingdom extended from the region of Durazzo south along the coast to Butrint. A major attempt to advance further in direction of Constantinople failed at the Siege of Berat (1280–1281). A Byzantine counteroffensive soon ensued, which drove the Angevins out of the interior by 1281. The Sicilian Vespers further weakened the position of Charles, and the Kingdom was soon reduced by the Byzantines to a small area around Durazzo. The Angevins held out here, however, until 1368, when the city was captured by Karl Thopia. In 1392, Karl Thopia's son surrendered the city to the Republic of Venice.

Balša Balšić died September 18, 1385) or Balša II was the Lord of Lower Zeta from 1378 to 1385. He was a member of the Balšić noble family, which ruled Zeta from c. 1362 to 1421.

The Arianiti were a noble Albanian family that ruled large parts of Albania and neighboring territories from the 11th to the 16th century. Their domain stretched across the Shkumbin valley and the old Via Egnatia road and reached east to today's Bitola.

The Principality of Muzaka, also known as the Lordship of Berat, was an independent realm ruled by the Albanian Muzaka family with its capital at Berat, covering territories in Central and Southern Albania, Western Macedonia and Northern Greece. One of the first rulers was Andrea I Muzaka whose reign was recognized by the Byzantine Emperor. During the Battle of Savra, the Ottomans captured Berat from Balša II, together with Kruja and Ulcinj. They soon retreated from all of those towns keeping only Castoria under their permanent control. Some sources explain that Ottomans probably remained in Berat with intention to use it as foothold to capture Valona. By 1396 Muzaka family took over control of Berat. In 1417 the territories of the Principality, including Vlorë and Berat, became a part of the Ottoman Empire.
The term Albanian Principalities refers to a number of principalities created in the Middle Ages in Albania and the surrounding regions in the western Balkans that were ruled by Albanian nobility. The 12th century marked the first Albanian principality, the Principality of Arbanon. It was later, however, in the 2nd half of the 14th century that these principalities became stronger, especially with the fall of the Serbian Empire after 1355. Some of these principalities were notably united in 1444 under the military alliance called League of Lezhë up to 1480 which defeated the Ottoman Empire in more than 28 battles. They covered modern day Albania,western and central Kosovo, Epirus, areas up to Corinth, western North Macedonia, southern Montenegro. The leaders of these principalities were some of the most noted Balkan figures in the 14th and 15th centuries such as Gjin Bua Shpata, Andrea II Muzaka, Gjon Zenebishi, Karl Topia, Andrea Gropa, Balsha family, Gjergj Arianiti, Gjon Kastrioti, Skanderbeg, Dukagjini family and Lek Dukagjini.
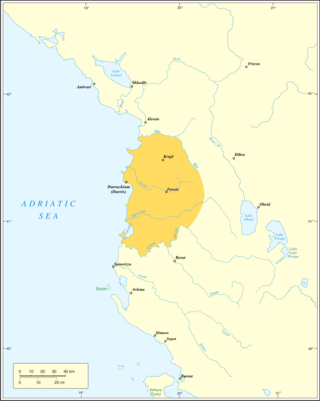
The Principality of Albania was an Albanian principality ruled by the Albanian dynasty of Thopia. The first notable ruler was Tanusio Thopia, who became Count of Mat in 1328. The principality would reach its zenith during the rule of Karl Thopia, who emerged in 1359 after the Battle of Achelous, conquering the cities of Durrës and Krujë and consolidating his rule of central Albania between the rivers of Mat and Shkumbin. The principality would last up until 1415, when it was conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
After the weakening of the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire in the middle and late 13th century, the northern territory of modern-day Albania became part of Serbia. Firstly, as part of Serbian Grand Principality and later as part of Serbian Empire. Serb control in southern Albania is unclear. Some suggest they acquired towns, but others believe they only obtained submission, possibly nominal, from Albanian tribes. Central and southern Albanian towns were not conquered until 1343–45. Between 1272 and 1368, some areas of the modern-day state were also ruled by the Angevins as the Kingdom of Albania. In the late 14th century, Albanian Principalities were created throughout Albania.
The Principality of Valona and Kanina, also known as the Despotate of Valona and Kanina or simply the Principality of Valona (1346–1417) was a medieval principality in Albania, roughly encompassing the territories of the modern counties of Vlorë (Valona), Fier, and Berat. Initially a vassal of the Serbian Empire, it became an independent lordship after 1355, although de facto under Venetian influence, and remained as such until it was conquered by the Ottoman Turks in 1417.

The Muzaka family was an noble Albanian family that ruled over the region of Myzeqe in the Late Middle Ages. The Muzaka are also referred to by some authors as a tribe or a clan. The earliest historical document that mentions the Muzaka family is written by the Byzantine historian Anna Komnene. At the end of the 13th and beginning of the 14th century members of the Muzaka family controlled a region between the rivers of Devoll and Vjosë. Some of them were loyal to the Byzantine Empire while some of them allied with Charles of Anjou who gave them impressive Byzantine-like titles in order to subdue them more easily. In the 1340s, Stefan Dušan pressed further south into Albania, and by 1343-45 had taken central towns and territories in southern Albania, including domains of the Muzaka family. However, they would fall back under local control after his death in 1355. After the Battle of Savra in 1385 the territory of Albania came under the Ottoman Empire; they served the Ottomans until 1444 when Theodor Corona Musachi joined Skanderbeg's rebellion. When the Ottomans suppressed Skanderbeg's rebellion and captured the territory of Venetian Albania in the 15th century many members of the Muzaka family retreated to Italy. Those who stayed in Ottoman Albania lost their feudal rights, some converted to Islam and achieved high ranks in the Ottoman military and administrative hierarchy.

Teodor I Muzaka was an Albanian nobleman that ruled the Lordship of Berat between 1319 and 1331. According to John Musachi, he had the nickname "këshetesi", meaning the one with braided hair. He had a brother Count Mentula Muzaka of Clissura or today called Kelcyra.

The Thopia were one of the most powerful Albanian feudal families in the Late Middle Ages, part of the nobility of the Angevin Kingdom of Albania.

The Mataranga, Matranga, Matarango or Matrangolo were an Albanian noble family during the 13th and 15th centuries. Members of this family included local rulers, Byzantine officials and writers. After the occupation of Albania by the Ottoman Empire, part of the family emigrated to Italy and settled in the Arbëresh villages of Piana degli Albanesi and Santa Cristina Gela in Southern Italy, where they have continued to maintain the Arbëresh language.
The Albanian nobility was an elite hereditary ruling class in Albania, parts of the western Balkans and later in parts of the Ottoman world. The Albanian nobility was composed of landowners of vast areas, often in allegiance to states like the Byzantine Empire, various Serbian states, the Republic of Venice, the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Naples in addition to the Albanian principalities. They often used Byzantine, Latin or Slavic titles, such as sebastokrator, despot, dux, conte and zupan.
Andrea II Thopia was a 15th century Albanian nobleman whose domains included the territory of Scuria. He was a member of the Thopia family and one of the founders of the League of Lezhë.

Theodor Corona Musachi or Teodor III Korona Muzaka, was an Albanian nobleman who led the 1437–38 revolt against the Ottomans and was one of the founders of the League of Lezhë in 1444.

Andrea II Muzaka was an Albanian nobleman of the Muzaka family and the ruler of the Principality of Muzaka in the 14th century. He inherited the principality from his father, Teodor I Muzaka, who died around 1331. Andrea II is known for having expanded the Principality of Muzaka to its greatest extent, from the southern Adriatic coastline of Albania in the west to Kastoria in the east by the time of his death in 1372.

Stoya Muzaka, also known as Stoja, was an Albanian nobleman, the Lord of Kastoria, and a member of the influential Albanian Muzaka family, which played a significant role in ruling parts of Southern Albania and Epirus.

Paul Mataranga, also known as Paul Matarango or Paolo Matarango was an Albanian Lord and member of the Mataranga family.
The Muzaka-Serbian Conflict was a series of armed engagements and battles throughout the Middle Ages fought by the Albanian Principality of Muzaka against the Serbian Empire, during a span of around 20 years.














