Related Research Articles
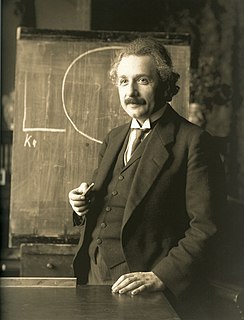
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory of relativity, but he also made important contributions to the development of the theory of quantum mechanics. Relativity and quantum mechanics are together the two pillars of modern physics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from relativity theory, has been dubbed "the world's most famous equation". His work is also known for its influence on the philosophy of science. He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory. His intellectual achievements and originality resulted in "Einstein" becoming synonymous with "genius".

General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations.

Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist.

Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac was an English theoretical physicist who is regarded as one of the most significant physicists of the 20th century. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge, a professor of physics at Florida State University and the University of Miami, and a 1933 Nobel Prize recipient.
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics, and where quantum effects cannot be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects, and where the effects of gravity are strong, such as neutron stars.

Sir Roger Penrose is an English mathematician, mathematical physicist, philosopher of science and Nobel Laureate in Physics. He is Emeritus Rouse Ball Professor of Mathematics in the University of Oxford, an emeritus fellow of Wadham College, Oxford, and an honorary fellow of St John's College, Cambridge and University College London.

The theory of relativity usually encompasses two interrelated theories by Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity, proposed and published in 1905 and 1915, respectively. Special relativity applies to all physical phenomena in the absence of gravity. General relativity explains the law of gravitation and its relation to other forces of nature. It applies to the cosmological and astrophysical realm, including astronomy.

Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. The idea of a time machine was popularized by H. G. Wells' 1895 novel The Time Machine.

Wolfgang Ernst Pauli was an Austrian theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers of quantum physics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics for his "decisive contribution through his discovery of a new law of Nature, the exclusion principle or Pauli principle". The discovery involved spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the structure of matter.
In the philosophy of space and time, eternalism is an approach to the ontological nature of time, which takes the view that all existence in time is equally real, as opposed to presentism or the growing block universe theory of time, in which at least the future is not the same as any other time. Some forms of eternalism give time a similar ontology to that of space, as a dimension, with different times being as real as different places, and future events are "already there" in the same sense other places are already there, and that there is no objective flow of time.

Kip Stephen Thorne is an American theoretical physicist known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. A longtime friend and colleague of Stephen Hawking and Carl Sagan, he was the Richard P. Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) until 2009 and is one of the world's leading experts on the astrophysical implications of Einstein's general theory of relativity. He continues to do scientific research and scientific consulting, most notably for the Christopher Nolan film Interstellar. Thorne was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves".

John Archibald Wheeler was an American theoretical physicist. He was largely responsible for reviving interest in general relativity in the United States after World War II. Wheeler also worked with Niels Bohr in explaining the basic principles behind nuclear fission. Together with Gregory Breit, Wheeler developed the concept of the Breit–Wheeler process. He is best known for popularizing the term "black hole," as to objects with gravitational collapse already predicted during the early 20th century, for inventing the terms "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit", and for hypothesizing the "one-electron universe".

Nathan Rosen was an American-Israeli physicist noted for his study on the structure of the hydrogen atom and his work with Albert Einstein and Boris Podolsky on entangled wave functions and the EPR paradox. The Einstein–Rosen bridge, later named the wormhole, was a theory of Nathan Rosen.

Robert M. Wald is an American theoretical physicist who studies gravitation. His research interests include general relativity, black holes, and quantum gravity. He is also a science communicator and textbook author.

Thanu Padmanabhan was an Indian theoretical physicist and cosmologist whose research spanned a wide variety of topics in gravitation, structure formation in the universe and quantum gravity. He published nearly 300 papers and reviews in international journals and ten books in these areas. He made several contributions related to the analysis and modelling of dark energy in the universe and the interpretation of gravity as an emergent phenomenon. He was a Distinguished Professor at the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) at Pune, India.

Nathaniel David Mermin is a solid-state physicist at Cornell University best known for the eponymous Mermin–Wagner theorem, his application of the term "boojum" to superfluidity, his textbook with Neil Ashcroft on solid-state physics, and for contributions to the foundations of quantum mechanics and quantum information science.
Harvey Robert Brown is a British philosopher of physics. He is a professor of philosophy at the University of Oxford and an emeritus fellow of Wolfson College, Oxford, as well as a fellow of the British Academy.
Tim William Eric Maudlin is an American philosopher of science who has done influential work on the metaphysical foundations of physics and logic.

(George) Andrew Davidson Briggs is a British scientist. He is Professor of Nanomaterials in the Department of Materials at the University of Oxford. He is best known for his early work in acoustic microscopy and his current work in materials for quantum technologies.

Subtle is the Lord: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein is a biography of Albert Einstein written by Abraham Pais. First published in 1982 by Oxford University Press, the book is one of the most acclaimed biographies of the scientist. This was not the first popular biography of Einstein, but it was the first to focus on his scientific research as opposed to his life as a popular figure. Pais, renowned for his work in theoretical particle physics, was a friend of Einstein's at the Institute for Advanced Study in his early career. Originally published in English in the United States and the United Kingdom, the book has translations in over a dozen languages. Pais later released a sequel to the book in 1994 titled Einstein Lived Here and, after his death in 2000, the University Press released a posthumous reprint of the biography in 2005, with a new foreword by Roger Penrose. Considered very popular for a science book, the biography sold tens of thousands of copies of both paperback and hardcover versions in its first year. The book has received many reviews and, the year after its initial publication, it won both the 1983 National Book Award for Nonfiction, in Science (Hardcover), and the 1983 Science Writing Award.
References
- ↑ Bussey, Peter J. (2013). "Review: Relativity Made Relatively Easy by Andrew M. Steane". Contemporary Physics. 54 (2): 124. Bibcode:2013ConPh..54..124B. doi:10.1080/00107514.2013.800151. S2CID 118470390.
- ↑ Holder, Rodney (2015). "Review: Faithful to Science: The Role of Science in Religion by Andrew Steane". The Journal of Theological Studies : flv044. doi:10.1093/jts/flv044.