Related Research Articles

A chemical engineer is a professional equipped with the knowledge of chemistry and other basic sciences who works principally in the chemical industry to convert basic raw materials into a variety of products and deals with the design and operation of plants and equipment. This person applies the principles of chemical engineering in any of its various practical applications, such as
- Design, manufacture, and operation of plants and machinery in industrial chemical and related processes ;
- Development of new or adapted substances for products ranging from foods and beverages to cosmetics to cleaners to pharmaceutical ingredients, among many other products ;
- Development of new technologies such as fuel cells, hydrogen power and nanotechnology, as well as working in fields wholly or partially derived from chemical engineering such as materials science, polymer engineering, and biomedical engineering. This can include working of geophysical projects such as rivers, stones, and signs.
An artificial membrane, or synthetic membrane, is a synthetically created membrane which is usually intended for separation purposes in laboratory or in industry. Synthetic membranes have been successfully used for small and large-scale industrial processes since the middle of the twentieth century. A wide variety of synthetic membranes is known. They can be produced from organic materials such as polymers and liquids, as well as inorganic materials. Most commercially utilized synthetic membranes in industry are made of polymeric structures. They can be classified based on their surface chemistry, bulk structure, morphology, and production method. The chemical and physical properties of synthetic membranes and separated particles as well as separation driving force define a particular membrane separation process. The most commonly used driving forces of a membrane process in industry are pressure and concentration gradient. The respective membrane process is therefore known as filtration. Synthetic membranes utilized in a separation process can be of different geometry and flow configurations. They can also be categorized based on their application and separation regime. The best known synthetic membrane separation processes include water purification, reverse osmosis, dehydrogenation of natural gas, removal of cell particles by microfiltration and ultrafiltration, removal of microorganisms from dairy products, and dialysis.
Downstream processing refers to the recovery and the purification of biosynthetic products, particularly pharmaceuticals, from natural sources such as animal tissue, plant tissue or fermentation broth, including the recycling of salvageable components as well as the proper treatment and disposal of waste. It is an essential step in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics, hormones, antibodies and vaccines; antibodies and enzymes used in diagnostics; industrial enzymes; and natural fragrance and flavor compounds. Downstream processing is usually considered a specialized field in biochemical engineering, which is itself a specialization within chemical engineering. Many of the key technologies were developed by chemists and biologists for laboratory-scale separation of biological and synthetic products, whilst the role of biochemical and chemical engineers is to develop the technologies towards larger production capacities.
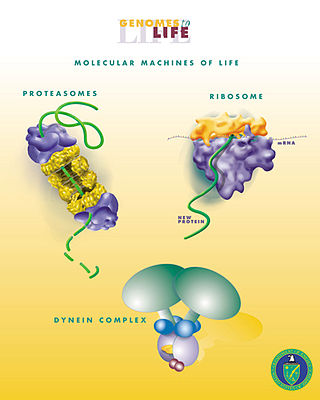
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies.

George Harry Heilmeier was an American engineer, manager, and a pioneering contributor to liquid crystal displays (LCDs), for which he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame. Heilmeier's work is an IEEE Milestone.
Harry George Drickamer, born Harold George Weidenthal, was a pioneer experimentalist in high-pressure studies of condensed matter. His work generally concerned understanding the electronic properties of matter.

Cato T. Laurencin FREng SLMH is an American engineer, physician, scientist, innovator and a University Professor of the University of Connecticut.
Edward L. Cussler is an American chemical engineer and professor in the department of chemical engineering and materials science at the University of Minnesota. He is internationally known for his work in fluid mechanics, transport phenomena, and gas separations, especially in the areas of membranes and gas sorption. Cussler is an author of more than 250 academic papers, dozens of patents, and five books including the acclaimed text: “Diffusion”. He has served as director, vice president and president of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, and he presented the AIChE Institute Lecture in 2014. Cussler and his wife Betsy, a former teacher at Edina High School, are long-time residents of Minneapolis, Minnesota.

The Science History Institute is an institution that preserves and promotes understanding of the history of science. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it includes a library, museum, archive, research center and conference center.
Edwin Niblock Lightfoot, Jr. was an American chemical engineer and Hilldale Professor Emeritus in the department of chemical and biological engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He is known for his research in transport phenomena, including biological mass-transfer processes, mass-transport reaction modeling, and separations processes. He, along with R. Byron Bird and Warren E. Stewart, co-authored the classic textbook Transport Phenomena. In 1974 Lightfoot wrote Transport Phenomena and Living Systems: Biomedical Aspects of Momentum and Mass Transport. He was the recipient of the 2004 National Medal of Science in Engineering Sciences.
The Penn State College of Engineering is the engineering school of the Pennsylvania State University, headquartered at the University Park campus in University Park, Pennsylvania. It was established in 1896, under the leadership of George W. Atherton. Today, with 13 academic departments and degree programs, over 11,000 enrolled undergraduate and graduate students, and research expenditures of $124 million for the 2016-2017 academic year, the Penn State College of Engineering is in the top 20 of engineering schools in the United States. It is estimated that at least one out of every fifty engineers in the United States got their bachelor's degree from Penn State. Dr. Justin Schwartz currently holds the position of Harold and Inge Marcus Dean of Engineering.
Donald Laverne Katz was an American chemist and chemical engineer.
Howard Allaker Chase FREng is a British academic and chemical engineer. He is Head of the School of Technology and Professor of Biochemical Engineering at the University of Cambridge. From 1998 to 2006 he was Head of the Department of Chemical Engineering at the University of Cambridge. Chase has been a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering since 2005. He is also a Fellow of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, a Member of the Royal Society of Chemistry, a Chartered Engineer, a Chartered Chemist, and a Chartered Scientist. In 2010 he was awarded the Donald Medal, an award of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, in recognition of his industrially related research in the field of bioseparations technology. Chase was an undergraduate, and a research student (biochemistry) at Magdalene College, Cambridge, between 1972 and 1978. He held a research fellowship at St John's College, Cambridge, from 1978 to 1982. In 1984 he was elected to a fellowship at Magdalene College, Cambridge where he became director of studies in chemical engineering. He was tutor for graduate students 1987–1994, tutor 1994-1996 and senior tutor 1993–1996.

Ralph Landau was an American chemical engineer and entrepreneur active in the chemical and petrochemical industries. He is considered one of the top fifty foundational chemical engineers of the first half of the 20th century, and one of the 75 most distinguished contributors to chemical enterprise. He has published extensively on chemical engineering and holds a significant number of patents.
Arthur Earl Humphrey is an American chemical engineer.
Wei-Shou Hu is a Taiwanese-American chemical engineer. He is currently the Distinguished McKnight University Professor of Chemical Engineering and Material Science at the University of Minnesota.
Laxmangudi Krishnamurthy Doraiswamy (1927–2012) was an Indian-American chemical engineer, author and academic, known for his contributions in developing Organic synthesis engineering as a modern science discipline. Chemical Engineering journal of McGraw Hill listed him among the 10 most distinguished chemical engineers in the world in 1988. He was the author of nine texts in chemical engineering, including Organic Synthesis Engineering, a 2001 publication which is known to have introduced the topic as a definitive scientific stream and Heterogeneous reactions: Analysis, Examples, and Reactor Design, reportedly the first comprehensive text in chemical engineering.

Ganapati Dadasaheb Yadav is an Indian chemical engineer, inventor and academic, known for his research on nanomaterials, gas absorption with chemical reaction and phase transfer catalysis. He served as the vice chancellor of the Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai from 2009 until November 2019. He is currently the Emeritus Professor of Eminence at ICT Mumbai.
Giorgio Carta is an Italian chemical engineer.
David W. Wood is an American chemical engineer who is professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at Ohio State University. Wood is also associated with the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics Training Program.
References
- ↑ "Andrew Zydney". psu.edu. Retrieved April 16, 2017.