
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support.
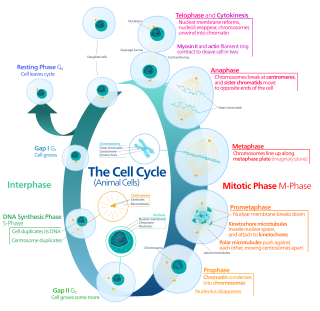
In cell biology, mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of a cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other.
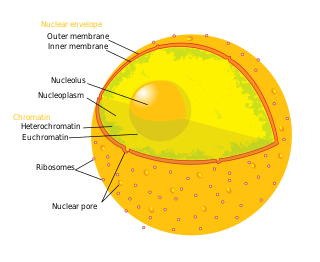
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in the nuclear envelope of a vertebrate cell, but this number varies depending on cell type and the stage in the life cycle. The human nuclear pore complex (hNPC) is a 110 megadalton (MDa) structure. The proteins that make up the nuclear pore complex are known as nucleoporins; each NPC contains at least 456 individual protein molecules and is composed of 34 distinct nucleoporin proteins. About half of the nucleoporins typically contain solenoid protein domains—either an alpha solenoid or a beta-propeller fold, or in some cases both as separate structural domains. The other half show structural characteristics typical of "natively unfolded" or intrinsically disordered proteins, i.e. they are highly flexible proteins that lack ordered tertiary structure. These disordered proteins are the FG nucleoporins, so called because their amino-acid sequence contains many phenylalanine–glycine repeats.
Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases.
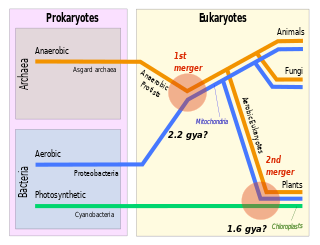
Symbiogenesis is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. Mitochondria appear to be phylogenetically related to Rickettsiales bacteria, while chloroplasts are thought to be related to cyanobacteria.

The nucleoplasm, also known as karyoplasm, is the type of protoplasm that makes up the cell nucleus, the most prominent organelle of the eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed by the nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane. The nucleoplasm resembles the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell in that it is a gel-like substance found within a membrane, although the nucleoplasm only fills out the space in the nucleus and has its own unique functions. The nucleoplasm suspends structures within the nucleus that are not membrane-bound and is responsible for maintaining the shape of the nucleus. The structures suspended in the nucleoplasm include chromosomes, various proteins, nuclear bodies, the nucleolus, nucleoporins, nucleotides, and nuclear speckles.

Telophase is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration.

Karyogamy is the final step in the process of fusing together two haploid eukaryotic cells, and refers specifically to the fusion of the two nuclei. Before karyogamy, each haploid cell has one complete copy of the organism's genome. In order for karyogamy to occur, the cell membrane and cytoplasm of each cell must fuse with the other in a process known as plasmogamy. Once within the joined cell membrane, the nuclei are referred to as pronuclei. Once the cell membranes, cytoplasm, and pronuclei fuse, the resulting single cell is diploid, containing two copies of the genome. This diploid cell, called a zygote or zygospore can then enter meiosis, or continue to divide by mitosis. Mammalian fertilization uses a comparable process to combine haploid sperm and egg cells (gametes) to create a diploid fertilized egg.

The nuclear lamina is a dense fibrillar network inside the nucleus of eukaryote cells. It is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins. Besides providing mechanical support, the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as DNA replication and cell division. Additionally, it participates in chromatin organization and it anchors the nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope.
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
A polygene is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance, a type of non-Mendelian inheritance, as opposed to single-gene inheritance, which is the core notion of Mendelian inheritance. The term "monozygous" is usually used to refer to a hypothetical gene as it is often difficult to distinguish the effect of an individual gene from the effects of other genes and the environment on a particular phenotype. Advances in statistical methodology and high throughput sequencing are, however, allowing researchers to locate candidate genes for the trait. In the case that such a gene is identified, it is referred to as a quantitative trait locus (QTL). These genes are generally pleiotropic as well. The genes that contribute to type 2 diabetes are thought to be mostly polygenes. In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355 genes from the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all organisms living on Earth.

The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.

Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute.

The middle lamella is a layer that cements together the primary cell walls of two adjoining plant cells. It is the first formed layer to be deposited at the time of cytokinesis. The cell plate that is formed during cell division itself develops into middle lamella or lamellum. The middle lamella is made up of calcium and magnesium pectates. In a mature plant cell it is the outermost layer of cell wall.
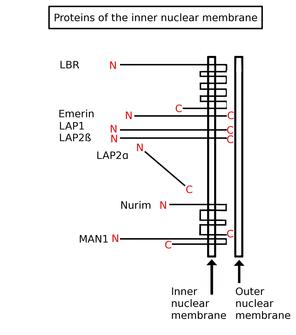
Inner nuclear membrane proteins are membrane proteins that are embedded in or associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are about 60 INM proteins, most of which are poorly characterized with respect to structure and function. Among the few well-characterized INM proteins are lamin B receptor (LBR), lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), lamina-associated polypeptide-2 (LAP2), emerin and MAN1.
The leptotene stage, also known as the leptonema, is the first of five substages of prophase I in meiosis. The term leptonema derives from Greek words meaning "thin threads". A cell destined to become a gamete enters the leptotene stage after its chromosomes are duplicated during interphase. During the leptotene stage those duplicated chromosomes—each consisting of two sister chromatids—condense from diffuse chromatin into long, thin strands that are more visible within the nucleoplasm. The next stage of prophase I in meiosis is the zygotene stage.

Acceleration in human development process is the phenomenon which has been registered in many populations around the world. This applies equally to the growth of certain anthropometric parameters and the speed of reaching sexual maturity. These facts illustrate the results of secular changes in body height and appearance of the first menstruation (menarche).

Unsuccessful transfer or abortive transfer is any bacterial DNA transfer from donor cells to recipient cells that fails to survive transduction and conjugation. In all cases, the transferred fragment could be diluted during the proliferation phase. Failures in the integration of the transferred DNA in the genetic material of the recipient cells may be due to:
Bacterial recombination is a type of genetic recombination in bacteria characterized by DNA transfer from one organism called donor to another organism as recipient. This process occurs in three main ways:
This glossary of cell biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology and related disciplines in biology, including developmental biology, genetics, microbiology, molecular biology, and biochemistry.











