
An archipelago, sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or a sea containing a small number of scattered islands. An archipelago may be on a lake, river, or an ocean. The list of archipelagos includes the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, the Stockholm Archipelago, the Malay Archipelago, the Bahamian Archipelago, the nation of Japan and the state of Hawaii.

This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the other lists of islands below.

Oceania is a geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, at the centre of the water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about 9,000,000 square kilometres (3,500,000 sq mi) and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the second-least populated after Antarctica.

The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland

The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaiʻi in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly called the Sandwich Islands by Europeans, the present name for the archipelago is derived from the name of its largest island, Hawaiʻi.

Kure Atoll or Ocean Island is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean 48 nautical miles west-northwest of Midway Atoll in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands at 28°25′N178°20′W. A coral ring 6 miles (9.7 km) across encloses a lagoon several meters deep. The atoll's largest island is called Green Island, and is a habitat for hundreds of thousands of seabirds in the present day and wildlife staff. A short, unused, and unmaintained runway and a portion of one building, both from a former United States Coast Guard LORAN station, are located on the island. Politically, it is part of Hawaii, though the nearest island is Midway, which is a separate unorganized territory. Kure Atoll, in addition to being the nesting grounds for tens of thousands of seabirds, has recorded several vagrant terrestrial birds, including snow bunting, eyebrowed thrush, brambling, olive-backed pipit, black kite, Steller's sea eagle and Chinese sparrowhawk. It is currently managed as a Wildlife Bird Sanctuary by the State of Hawaii's Department of Land and Natural Resource–Division of Forestry and Wildlife as one of the co-trustees of Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument with support from the Kure Atoll Conservancy. Kure is one of the most westernmost islands of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands.

The Mariana Islands, also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east. They lie south-southeast of Japan, west-southwest of Hawaii, north of New Guinea, and east of the Philippines, demarcating the Philippine Sea's eastern limit. They are found in the northern part of the western Oceanic sub-region of Micronesia, and are politically divided into two jurisdictions of the United States: the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and, at the southern end of the chain, the territory of Guam. The islands were named after the influential Spanish queen Mariana of Austria following their colonization in the 17th century.

The Bonin Islands, also known as the Ogasawara Islands (小笠原諸島), is a Japanese archipelago of over 30 subtropical and tropical islands located around 1,000 kilometers (620 mi) SSE of Tokyo and 1,600 kilometers (1,000 mi) northwest of Guam. The group as a whole has a total area of 84 square kilometers (32 sq mi) but only two of the islands are permanently inhabited, Chichijima and Hahajima. Together, their population was 2,560 as of 2021. Administratively, Tokyo's Ogasawara Subprefecture also includes the settlements on the Volcano Islands and the Self-Defense Force post on Iwo Jima. The seat of government is Chichijima.

Wotje Atoll is a coral atoll of 75 islands in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands.
Matthijs Hendrikszoon Quast, anglicized as Matthys and Matthew Quast, was a Dutch merchant and explorer in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). Quast made several voyages on the VOC's behalf to Tokugawa Japan, the Qing Empire (China), and Ayutthaya Kingdom ("Siam") but is primarily remembered for his failed 1639 expedition in search of the phantom islands of Rica de Oro and Rica de Plata previously reported by Spanish mariners. He is sometimes credited with the first recorded discovery of the Bonin Islands during the voyage, although the VOC did nothing with the information and they remained unimportant and sparsely settled until the 19th century.
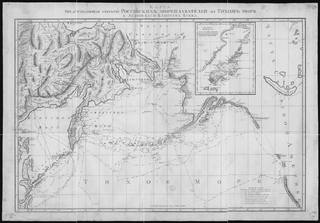
Martin Spanberg was a Danish-born Russian naval officer who took part with his compatriot Vitus Bering in both Kamchatka expeditions as second in command. He is best known for finding a sea route to Japan from Russian territory and for exploring the Kuril Islands. Shikotan, one of the Kurils, was renamed in his honor by the Russians in 1796.

Determining the boundaries between the continents is generally a matter of geographical convention. Several slightly different conventions are in use. The number of continents is most commonly considered seven but may range as low as four when Afro-Eurasia and the Americas are both considered as single continents. An island can be considered to be associated with a given continent by either lying on the continent's adjacent continental shelf or being a part of a microcontinent on the same principal tectonic plate. An island can also be entirely oceanic while still being associated with a continent by geology or by common geopolitical convention. Another example is the grouping into Oceania of the Pacific Islands with Australia and Zealandia.
Los Jardines or Los Buenos Jardines are phantom islands supposedly located northeast of the Mariana Islands.
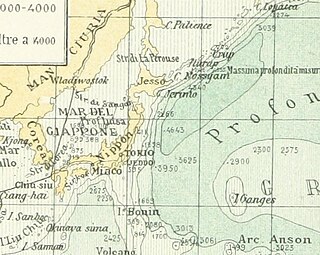
Ganges Island, a phantom island known as Nakanotorishima in Japanese, appeared at 30°45′N154°25′E on maps of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Reports of its disappearance appeared in 1933.

The Aleutian Islands —also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain of 14 main, larger volcanic islands and 55 smaller ones. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, with the archipelago encompassing the Aleutians West Census Area and the Aleutians East Borough. The Commander Islands, located further to the west, belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai, of the Russian Far East. The islands form part of the Aleutian Arc of the Northern Pacific Ocean, and occupy a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) that extends westward roughly 1,200 mi (1,900 km) from the Alaskan Peninsula mainland, in the direction of the Kamchatka Peninsula; the archipelago acts as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost and easternmost parts of the United States, by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island, in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.



















