Related Research Articles

The human leg is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or buttock region. The major bones of the leg are the femur, tibia, and adjacent fibula. The thigh is between the hip and knee, while the calf (rear) and shin (front) are between the knee and foot.

The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The latissimus dorsi is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi comes from Latin and means "broadest [muscle] of the back", from "latissimus" ' and "dorsum". The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is the largest muscle in the upper body.
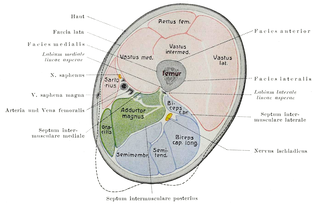
In human anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The bench press, or chest press, is a weight training exercise where a person presses a weight upwards while lying horizontally on a weight training bench. Although the bench press is a full-body exercise, the muscles primarily used are the pectoralis major, the anterior deltoids, and the triceps, among other stabilizing muscles. A barbell is generally used to hold the weight, but a pair of dumbbells can also be used.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.

The pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle of the human chest. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor muscle.

Pectoralis minor muscle is a thin, triangular muscle, situated at the upper part of the chest, beneath the pectoralis major in the human body. It arises from ribs III-V; it inserts onto the coracoid process of the scapula. It is innervated by the medial pectoral nerve. Its function is to stabilise the scapula by holding it fast in position against the chest wall.

The axilla is the area on the human body directly under the shoulder joint. It includes the axillary space, an anatomical space within the shoulder girdle between the arm and the thoracic cage, bounded superiorly by the imaginary plane between the superior borders of the first rib, clavicle and scapula, medially by the serratus anterior muscle and thoracolumbar fascia, anteriorly by the pectoral muscles and posteriorly by the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscle.

Lordosis is historically defined as an abnormal inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms lordosis and lordotic are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to abnormal convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed kyphosis or kyphotic. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from lordos.
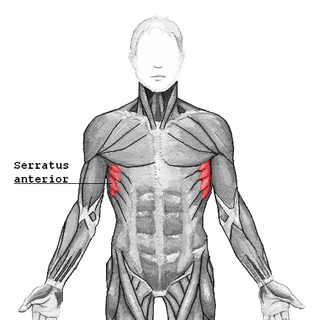
The serratus anterior is a muscle of the chest. It originates at the side of the chest from the upper 8 or 9 ribs; it inserts along the entire length of the anterior aspect of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the long thoracic nerve from the brachial plexus. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax.

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall which is deep to the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core.
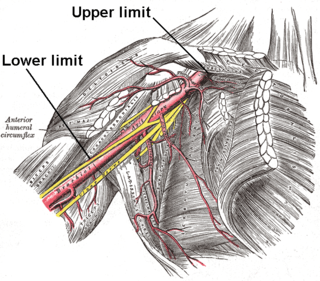
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The medial pectoral nerve is (typically) a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1. It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor muscle, and the lower half of the pectoralis major muscle. It runs along the inferior border of the pectoralis minor muscle.

The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during quiet breathing. The elasticity of these muscles is crucial to the health of the respiratory system and to maximize its functional capabilities.

A fly or flye is a strength training exercise in which the hand and arm move through an arc while the elbow is kept at a constant angle. Flies are used to work the muscles of the upper body. Because these exercises use the arms as levers at their longest possible length, the amount of weight that can be moved is significantly less than equivalent press exercises for the same muscles . Due to this leverage, fly exercises of all types have a large potential to damage the shoulder joint and its associated ligaments and the tendons of the muscles connecting to it. They should be done with caution and their effects first tested while using very light weights; which are gradually incremented after more strength is gained.
References
- ↑ Joanne Elphinston, Stability, Sport, and Performance Movement, p. 45, North Atlantic Books, 2008 ISBN 1556437463
- ↑ Bret Contreras, Bodyweight Strength Training Anatomy, p. 87, Human Kinetics, 2013 ISBN 1450429297.