Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, whether organized as a corporation, partnership or sole proprietorship, and to individuals, although it is most prominently used by corporate entities. In contrast, Chapter 7 governs the process of a liquidation bankruptcy, though liquidation may also occur under Chapter 11; while Chapter 13 provides a reorganization process for the majority of private individuals.
Chapter 7 of Title 11 U.S. Code is the bankruptcy code that governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the U.S. In contrast to bankruptcy under Chapter 11 and Chapter 13, which govern the process of reorganization of a debtor, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common form of bankruptcy in the U.S.

In corporate finance, a debenture is a medium- to long-term debt instrument used by large companies to borrow money, at a fixed rate of interest. The legal term "debenture" originally referred to a document that either creates a debt or acknowledges it, but in some countries the term is now used interchangeably with bond, loan stock or note. A debenture is thus like a certificate of loan or a loan bond evidencing the company's liability to pay a specified amount with interest. Although the money raised by the debentures becomes a part of the company's capital structure, it does not become share capital. Senior debentures get paid before subordinate debentures, and there are varying rates of risk and payoff for these categories.

Usury is the practice of making unethical or immoral monetary loans that unfairly enrich the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is charged in excess of the maximum rate that is allowed by law. A loan may be considered usurious because of excessive or abusive interest rates or other factors defined by the laws of a state. Someone who practices usury can be called a usurer, but in modern colloquial English may be called a loan shark.
A mortgage is a legal instrument of the common law which is used to create a security interest in real property held by a lender as a security for a debt, usually a mortgage loan. Hypothec is the corresponding term in civil law jurisdictions, albeit with a wider sense, as it also covers non-possessory lien.
Title 11 of the United States Code sets forth the statutes governing the various types of relief for bankruptcy in the United States. Chapter 13 of the United States Bankruptcy Code provides an individual with the opportunity to propose a plan of reorganization to reorganize their financial affairs while under the bankruptcy court's protection. The purpose of chapter 13 is to enable an individual with a regular source of income to propose a chapter 13 plan that provides for their various classes of creditors. Under chapter 13, the Bankruptcy Court has the power to approve a chapter 13 plan without the approval of creditors as long as it meets the statutory requirements under chapter 13. Chapter 13 plans are usually three to five years in length and may not exceed five years. Chapter 13 is in contrast to the purpose of Chapter 7, which does not provide for a plan of reorganization, but provides for the discharge of certain debt and the liquidation of non-exempt property. A Chapter 13 plan may be looked at as a form of debt consolidation, but a Chapter 13 allows a person to achieve much more than simply consolidating his or her unsecured debt such as credit cards and personal loans. A chapter 13 plan may provide for the four general categories of debt: priority claims, secured claims, priority unsecured claims, and general unsecured claims. Chapter 13 plans are often used to cure arrearages on a mortgage, avoid "underwater" junior mortgages or other liens, pay back taxes over time, or partially repay general unsecured debt. In recent years, some bankruptcy courts have allowed Chapter 13 to be used as a platform to expedite a mortgage modification application.
A creditor or lender is a party that has a claim on the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided some property or service to the second party under the assumption that the second party will return an equivalent property and service. The second party is frequently called a debtor or borrower. The first party is called the creditor, which is the lender of property, service, or money.
Nexum was a debt bondage contract in the early Roman Republic. A debtor pledged his person as collateral if he defaulted on his loan. Details as to the contract are obscure and some modern scholars dispute its existence. It was allegedly abolished either in 326 or 313 BC.
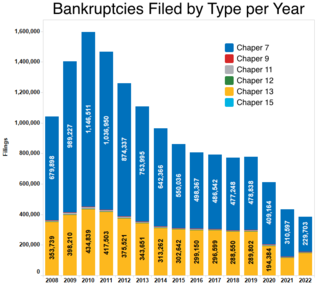
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).
In finance, unsecured debt refers to any type of debt or general obligation that is not protected by a guarantor, or collateralized by a lien on specific assets of the borrower in the case of a bankruptcy or liquidation or failure to meet the terms for repayment. Unsecured debts are sometimes called signature debt or personal loans. These differ from secured debt such as a mortgage, which is backed by a piece of real estate.
Hypothec, sometimes tacit hypothec, is a term used in civil law systems or mixed legal systems to refer to a registered non-possessory real security over real estate, but under some jurisdictions it may sometimes also denote security on other collaterals such as securities, intellectual property rights or corporeal movable property, either ships only as opposed to other movables covered by a different type of right (pledge) in the legal systems of some countries, or any movables in legal systems of other countries. Common law has two main equivalents to the term: mortgages and non-possessory liens.

The Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA) is a legislative act that made several significant changes to the United States Bankruptcy Code.
In finance, a floating charge is a security interest over a fund of changing assets of a company or other legal person. Unlike a fixed charge, which is created over ascertained and definite property, a floating charge is created over property of an ambulatory and shifting nature, such as receivables and stock.
A bankruptcy discharge is a court order that releases an individual or business from specific debts and obligations they owe to creditors. In other words, it's a legal process that eliminates the debtor's liability to pay certain types of debts they owe before filing the bankruptcy case.

In finance, a security interest is a legal right granted by a debtor to a creditor over the debtor's property which enables the creditor to have recourse to the property if the debtor defaults in making payment or otherwise performing the secured obligations. One of the most common examples of a security interest is a mortgage: a person borrows money from the bank to buy a house, and they grant a mortgage over the house so that if they default in repaying the loan, the bank can sell the house and apply the proceeds to the outstanding loan.
A secured loan is a loan in which the borrower pledges some asset as collateral for the loan, which then becomes a secured debt owed to the creditor who gives the loan. The debt is thus secured against the collateral, and if the borrower defaults, the creditor takes possession of the asset used as collateral and may sell it to regain some or all of the amount originally loaned to the borrower. An example is the foreclosure of a home. From the creditor's perspective, that is a category of debt in which a lender has been granted a portion of the bundle of rights to specified property. If the sale of the collateral does not raise enough money to pay off the debt, the creditor can often obtain a deficiency judgment against the borrower for the remaining amount.
A pledge is a bailment that conveys possessory title to property owned by a debtor to a creditor to secure repayment for some debt or obligation and to the mutual benefit of both parties. The term is also used to denote the property which constitutes the security. The pledge is a type of security interest.
In Bulgaria, the law of obligations is set out by the Obligations and Contracts Act (OCA). According to article 20a, OCA contracts shall have the force of law for the parties that conclude them.
Debt relief, or debt forgiveness, has been practiced in many societies since antiquity. Periodic debt remission was institutionalised in the Ancient Near East and contributed to the stability of its societies. In ancient Greece and Rome the laws were more creditor-friendly and debt cancellation was one of the major demands of the poor, only occasionally implemented by the government. Medieval canon law contained provisions for the annulment of debts owed by borrowers in distress, which influenced modern personal bankruptcy law.



