Related Research Articles
The Goodtimes virus, also styled as Good Times virus, was a computer virus hoax that spread during the early years of the Internet's popularity. Warnings about a computer virus named "Good Times" began being passed around among Internet users in 1994. The Goodtimes virus was supposedly transmitted via an email bearing the subject header "Good Times" or "Goodtimes", hence the virus's name, and the warning recommended deleting any such email unread. The virus described in the warnings did not exist, but the warnings themselves were, in effect, virus-like. In 1997 the Cult of the Dead Cow hacker collective announced that they had been responsible for the perpetration of the "Good Times" virus hoax as an exercise to "prove the gullibility of self-proclaimed 'experts' on the Internet".

This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events.

Antivirus software, also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.
A logic bomb is a piece of code intentionally inserted into a software system that will set off a malicious function when specified conditions are met. For example, a programmer may hide a piece of code that starts deleting files, should they ever be terminated from the company.

Spybot – Search & Destroy (S&D) is a spyware and adware removal computer program compatible with Microsoft Windows. Dating back to the first Adwares in 2000, Spybot scans the computer hard disk and/or RAM for malicious software.
Norton AntiVirus is an anti-virus or anti-malware software product founded by Peter Norton, developed and distributed by Symantec since 1990 as part of its Norton family of computer security products. It uses signatures and heuristics to identify viruses. Other features included in it are e-mail spam filtering and phishing protection.
Norton Internet Security, developed by Symantec Corporation, is a discontinued computer program that provides malware protection and removal during a subscription period. It uses signatures and heuristics to identify viruses. Other features include a personal firewall, email spam filtering, and phishing protection. With the release of the 2015 line in summer 2014, Symantec officially retired Norton Internet Security after 14 years as the chief Norton product. It was superseded by Norton Security, a rechristened adaptation of the Norton 360 security suite.

Microsoft Anti-Virus (MSAV) is an antivirus program introduced by Microsoft for its MS-DOS operating system. The program first appeared in MS-DOS version 6.0 (1993) and last appeared in MS-DOS 6.22. The first version of the antivirus program was basic, had no inbuilt update facility and could scan for 1,234 different viruses. Microsoft Anti-Virus for Windows (MWAV), included as part of the package, was a front end that allowed MSAV to run properly on Windows 3.1x.
SULFNBK.EXE is an internal component of the Microsoft Windows operating system for restoring long file names.
Tuxissa is a fictional computer virus hoax made up by Humorix, a humor website on Linux.
CTX is a computer virus created in Spain in 1999. CTX was initially discovered as part of the Cholera worm, with which the author intentionally infected with CTX. Although the Cholera worm had the capability to send itself via email, the CTX worm quickly surpassed it in prevalence. Cholera is now considered obsolete, while CTX remains in the field, albeit with only rare discoveries.
The Vundo Trojan is either a Trojan horse or a computer worm that is known to cause popups and advertising for rogue antispyware programs, and sporadically other misbehavior including performance degradation and denial of service with some websites including Google and Facebook. It also is used to deliver other malware to its host computers. Later versions include rootkits and ransomware.
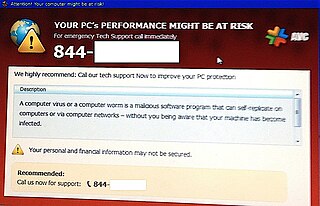
A computer virus hoax is a message warning the recipients of a non-existent computer virus threat. The message is usually a chain e-mail that tells the recipients to forward it to everyone they know, but it can also be in the form of a pop-up window.
W32.Navidad is a mass-mailing worm program or virus, discovered in December 2000 that ran on Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, and Windows 2000 systems. It was designed to spread through email clients such as Microsoft Outlook while masquerading as an executable electronic Christmas card. Infected computers can be identified by blue eye icons which appear in the Windows system tray.
Norton AntiBot, developed by Symantec, monitored applications for damaging behavior. The application was designed to prevent computers from being hijacked and controlled by hackers. According to Symantec, over 6 million computers have been hijacked, and the majority of users are unaware of their computers being hacked.

A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses.
Happy99 is a computer worm for Microsoft Windows. It first appeared in mid-January 1999, spreading through email and usenet. The worm installs itself and runs in the background of a victim's machine, without their knowledge. It is generally considered the first virus to propagate by email, and has served as a template for the creation of other self-propagating viruses. Happy99 has spread on multiple continents, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
The jdbgmgr.exe virus hoax involved an e-mail spam in 2002 that advised computer users to delete a file named jdbgmgr.exe because it was a computer virus. jdbgmgr.exe, which had a little teddy bear like icon, was actually a valid Microsoft Windows file, the Debugger Registrar for Java.
Shamoon, also known as W32.DistTrack, is a modular computer virus that was discovered in 2012, targeting then-recent 32-bit NT kernel versions of Microsoft Windows. The virus was notable due to the destructive nature of the attack and the cost of recovery. Shamoon can spread from an infected machine to other computers on the network. Once a system is infected, the virus continues to compile a list of files from specific locations on the system, upload them to the attacker, and erase them. Finally the virus overwrites the master boot record of the infected computer, making it unusable.
Norton 360 was an "all-in-one" security suite for the consumer market developed by Symantec. Originally released in 2006, it was discontinued in 2014; its features were carried over to its successor, Norton Security. However, in 2019, Symantec released a "NEW Norton 360", as a product replacement for Norton Security.
References
- ↑ "Symantec - Vs Norton" . Retrieved 2023-11-30.
- ↑ Gutierrez, Ralph (July 2001). "Antichrist Hoax". Archived from the original on 28 April 2009. Retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ↑ "Is McAfee the Antichrist?" . Retrieved 2023-11-30.
- ↑ Kuster, Judith Maginnis (2002-09-24). "Viruses and Virus Hoaxes". ASHA Leader. 7 (17): 16. ISSN 1085-9586 . Retrieved 2023-11-29.
- ↑ Machlis, Sharon (1997), Virus hoaxes make IS sick. (E-mail warnings spread hysteria, waste time), Computerworld, Inc