
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction. It has low resistance in one direction, and high resistance in the other.

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation is performed by an inverter.

A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the Zener voltage, is reached.
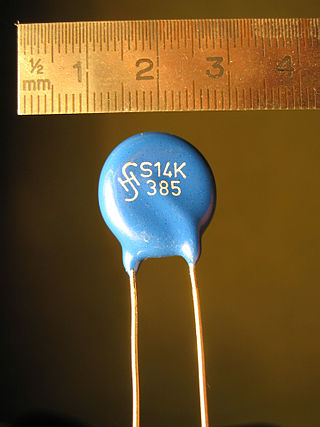
A varistor is a surge protecting electronic component with an electrical resistance that varies with the applied voltage. It has a nonlinear, non-ohmic current–voltage characteristic that is similar to that of a diode. Unlike a diode however, it has the same characteristic for both directions of traversing current. Traditionally, varistors were indeed constructed by connecting two rectifiers, such as the copper-oxide or germanium-oxide rectifier in antiparallel configuration. At low voltage the varistor has a high electrical resistance which decreases as the voltage is raised. Modern varistors are primarily based on sintered ceramic metal-oxide materials which exhibit directional behavior only on a microscopic scale. This type is commonly known as the metal-oxide varistor (MOV).
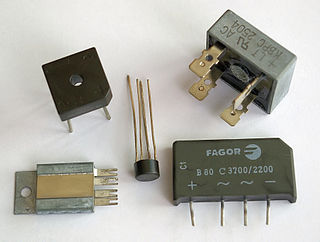
A diode bridge is a bridge rectifier circuit of four diodes that is used in the process of converting alternating current (AC) from the input terminals to direct current on the output terminals. Its function is to convert the negative voltage portions of the AC waveform to positive voltage, after which a low-pass filter can be used to smooth the result into DC.

A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch, conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reverse-biased, or until the voltage is removed. There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large.

A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.

A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek στρόβος (stróbos), meaning "act of whirling".

A dimmer is a device connected to a light fixture and used to lower the brightness of the light. By changing the voltage waveform applied to the lamp, it is possible to lower the intensity of the light output. Although variable-voltage devices are used for various purposes, the term dimmer is generally reserved for those intended to control light output from resistive incandescent, halogen, and compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) and light-emitting diodes (LEDs). More specialized equipment is needed to dim fluorescent, mercury-vapor, solid-state, and other arc lighting.
An antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path, an antifuse starts with a high resistance, and programming it converts it into a permanent electrically conductive path. This technology has many applications.

A solar inverter or photovoltaic (PV) inverter is a type of power inverter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network. It is a critical balance of system (BOS)–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment. Solar power inverters have special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
A shunt is a device that is designed to provide a low-resistance path for an electrical current in a circuit. It is typically used to divert current away from a system or component in order to prevent overcurrent. Electrical shunts are commonly used in a variety of applications including power distribution systems, electrical measurement systems, automotive and marine applications.

In electronics, an LED circuit or LED driver is an electrical circuit used to power a light-emitting diode (LED). The circuit must provide sufficient current to light the LED at the required brightness, but must limit the current to prevent damaging the LED. The voltage drop across an LED is approximately constant over a wide range of operating current; therefore, a small increase in applied voltage greatly increases the current. Very simple circuits are used for low-power indicator LEDs. More complex, current source circuits are required when driving high-power LEDs for illumination to achieve correct current regulation.

Charlieplexing is a technique for driving a multiplexed display, keypad or touchscreen, in which relatively few I/O wires from a microcontroller are woven in a diagonally-intersecting pattern to access a large number of I/O entities.
Aviation obstruction lighting is used to enhance the visibility of structures or fixed obstacles which may conflict with the safe navigation of aircraft. Obstruction lighting is commonly installed on towers, buildings, and even fences located in areas where aircraft may be operating at low altitudes. In certain areas, some aviation regulators mandate the installation, operation, color, and/or status notification of obstruction lighting. For maximum visibility and collision-avoidance, these lighting systems commonly employ one or more high-intensity strobe or LED devices which can be seen by pilots from many miles away from the obstruction.

Electroluminescent wire is a thin copper wire coated in a phosphor that produces light through electroluminescence when an alternating current is applied to it. It can be used in a wide variety of applications—vehicle and structure decoration, safety and emergency lighting, toys, clothing etc.—much as rope light or Christmas lights are often used. Unlike these types of strand lights, EL wire is not a series of points, but produces a continuous unbroken line of visible light. Its thin diameter makes it flexible and ideal for use in a variety of applications such as clothing or costumes.

A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters.
Holiday lighting technology has been subject to considerable development and variation since the replacement of candles by electric lights. While originally used during the Christmas holidays as Christmas lights, modern electric light arrays have become popular around the world in many cultures and are used both during religious festivals and for other purposes unconnected to any festivities.
An HVDC converter converts electric power from high voltage alternating current (AC) to high-voltage direct current (HVDC), or vice versa. HVDC is used as an alternative to AC for transmitting electrical energy over long distances or between AC power systems of different frequencies. HVDC converters capable of converting up to two gigawatts (GW) and with voltage ratings of up to 900 kilovolts (kV) have been built, and even higher ratings are technically feasible. A complete converter station may contain several such converters in series and/or parallel to achieve total system DC voltage ratings of up to 1,100 kV.
A twinkle bulb is a special type of light bulb which blinks on and off for decorative effect. They are most commonly used on Christmas lights and other string lights, but can also be used for other ornamental purposes like electric jack-o-lanterns for Halloween and replica traffic lights.













