Related Research Articles
The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge is a divergent tectonic plate boundary located on the seafloor of the South Pacific Ocean, separating the Pacific Plate from the Antarctic Plate. It is regarded as the southern section of the East Pacific Rise in some usages, generally south of the Challenger Fracture Zone and stretching to the Macquarie Triple Junction south of New Zealand.

In geography, the antipode of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it. A pair of points antipodal to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Earth's center. Antipodal points are as far away from each other as possible. The North and South Poles are antipodes of each other.
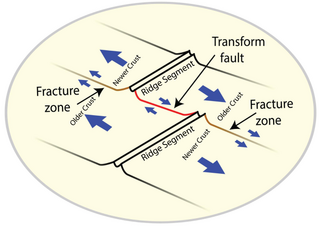
A fracture zone is a linear feature on the ocean floor—often hundreds, even thousands of kilometers long—resulting from the action of offset mid-ocean ridge axis segments. They are a consequence of plate tectonics. Lithospheric plates on either side of an active transform fault move in opposite directions; here, strike-slip activity occurs. Fracture zones extend past the transform faults, away from the ridge axis; are usually seismically inactive, although they can display evidence of transform fault activity, primarily in the different ages of the crust on opposite sides of the zone.

The Diamantina Fracture Zone is an area of the south-eastern Indian Ocean seafloor, consisting of a range of ridges and trenches. It lies to the south of the mideastern Indian Ocean features of the Wharton Basin and Perth Basin, and to the south west of the Naturaliste Plateau.
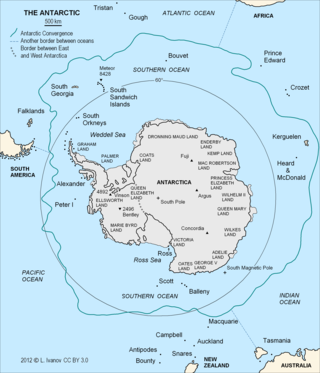
The Antarctic Convergence or Antarctic Polar Front is a marine belt encircling Antarctica, varying in latitude seasonally, where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the sub-Antarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath the warmer subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone very high in marine productivity, especially for Antarctic krill.
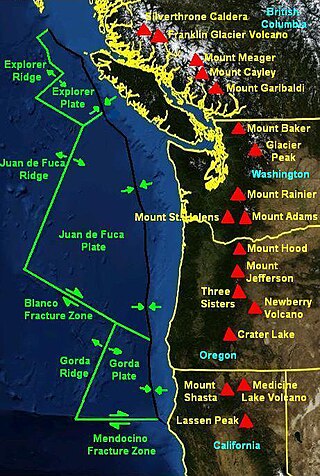
The Mendocino Fracture Zone is a fracture zone and transform boundary over 4000 km long, starting off the coast of Cape Mendocino in far northern California. It runs westward from a triple junction with the San Andreas Fault and the Cascadia subduction zone to the southern end of the Gorda Ridge. It continues on west of its junction with the Gorda Ridge, as an inactive remnant section which extends for several hundred miles.
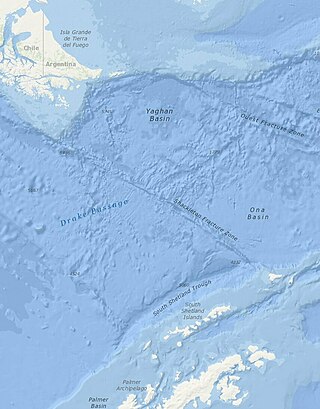
The Shackleton Fracture Zone (SFZ) is an undersea fracture zone, mid-oceanic ridge and fault located in the Drake Passage, at the separation between the Scotia plate from the Antarctic plate. It extends between 59° and 60°40' south latitude and between 56°30' and 61° west longitude and runs in a northwest to southeast direction from the South American continental shelf to the South Shetland Islands. Chile claims the area as part of its Outer Continental Shelf boundary.
Astrid Ridge is an undersea ridge on the continental margin of Dronning Maud Land, East Antarctica. It is present on the GEBCO 5th edition charts. The name was approved by the Advisory Committee for Undersea Features in June 1987.
The Tehuantepec Ridge is a linear undersea ridge located off the west coast of Mexico in the Pacific Ocean. It is the remnant of an old fracture zone, and not a tectonic spreading center ridge. It extends from the eastern end of the Clipperton Fracture Zone northeastward toward Mexico into Chiapas and El Chichón until it is subducted into the Middle America Trench. It lies within the tectonic Cocos Plate, separating the lower and older seafloor of the Guatemala Basin which lies southeast of the ridge from higher and younger seafloor which lies to its north-west.

USS San Carlos (AVP-51) was a Barnegat-class seaplane tender built for the United States Navy during World War II. San Carlos, named after San Carlos Bay, Florida, was in commissioned from 1944 to 1947 and earned three battle stars for service in the Pacific during World War II. After eleven years in reserve, San Carlos was converted to oceanographic research ship USNS Josiah Willard Gibbs (T-AGOR-1)—named after American scientist Josiah Willard Gibbs—and placed in service as a non-commissioned ship of the Military Sea Transportation Service from 1958 to 1971. In December 1971, the ship was transferred to the Hellenic Navy as Hephaistos (A413), a motor torpedo boat tender. Hephaistos was struck from the rolls of the Hellenic Navy in April 1976.
Balleny Fracture Zone is a fracture zone in the Southern Ocean that extends south towards the Balleny Islands. The name was approved by the Advisory Committee for Undersea Features in December 1971.
Kosminskaya Fracture Zone is an undersea fracture zone named for Professor Irina Kosminskaya, a Russian scientist specializing in Marine Geophysics and Seismology. The name was proposed by Dr. Galina Agapova of the Geological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and was approved by the Advisory Committee on Undersea Features in September 1997.
Vinogradov Fracture Zone is an Antarctic undersea fracture zone named for Alexandr Vinogradov, a Russian scientist/geochemist and first Director of the Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry (GEOKHI). The name was proposed by Dr. Galina Agapova of the Geological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and was approved in September 1997.
Pitman fracture zone is an undersea fracture zone named for Dr. Walter C. Pitman III, a geophysicist and pioneer in studies of continental drift and seafloor spreading. Name proposed by Drs. Cande, Haxby and Raymond, Lamont–Doherty Geological Observatory ; name approved 3/93.
The Emerald Fracture Zone is an undersea fracture zone running the distance from the southwest corner of the Campbell Plateau to the northern tip of Iselin Bank. The name was proposed by Dr. Steven C. Cande of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography for the vessel Emerald, which traversed this region in 1821, and was approved by the Advisory Committee for Undersea Features in June 1997. The Emerald Basin to its north west was named from the same source. Some have restricted the name to the southern east west orientated transform fault zone but the north south orientated faults that define the eastern boundary of the Emerald Basin are generally included in the literature.
The Heirtzler fracture zone is an undersea fracture zone located south of New Zealand, near Antarctica.
The Hjort Fracture Zone is an undersea fracture zone in Antarctica. The name was approved by the Advisory Committee for Undersea Features in December 1971.
The Hero Fracture Zone is an undersea fracture zone in the Antarctic. Its name was approved by the Advisory Committee on Undersea Features in June 1987.

Charlie–Gibbs fracture zone is a system of two parallel fracture zones. It is the most prominent interruption of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between the Azores and Iceland, with the longest faults in the North Atlantic, and is ecologically an important biosystems boundary. It can be traced over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi), from north-east of Newfoundland to south-west of Ireland. It took 90 million years for the fault to grow to this length.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Antipodes fracture zone". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Antipodes fracture zone". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.