
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees.

Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection. It can be taken by mouth, applied as a cream, or injected.
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replication of HIV and other retroviruses.

Valaciclovir, also spelled valacyclovir, is an antiviral medication used to treat outbreaks of herpes simplex or herpes zoster (shingles). It is also used to prevent cytomegalovirus following a kidney transplant in high risk cases. It is taken by mouth.

Vidarabine or 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ara-A) is an antiviral drug which is active against herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses.

Nucleoside analogues are structural analogues of a nucleoside, which normally contain a nucleobase and a sugar. Nucleotide analogues are analogues of a nucleotide, which normally has one to three phosphates linked to a nucleoside. Both types of compounds can deviate from what they mimick in a number of ways, as changes can be made to any of the constituent parts. They are related to nucleic acid analogues.

Antiviral Therapy is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by International Medical Press. It publishes primary papers and reviews on all aspects of the clinical development of antiviral drugs, including clinical trial results, drug resistance, viral diagnostics, drug safety, pharmacoepidemiology, and vaccines. Antiviral Therapy is an official publication of the International Society for Antiviral Research.
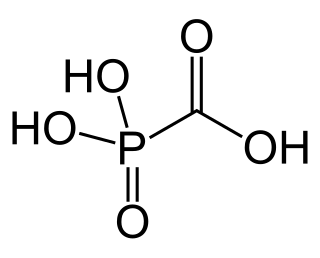
Foscarnet (phosphonomethanoic acid), known by its brand name Foscavir, is an antiviral medication which is primarily used to treat viral infections involving the Herpesviridae family. It is classified as a pyrophosphate analog DNA polymerase inhibitor. Foscarnet is the conjugate base of a chemical compound with the formula HO2CPO3H2 (Trisodium phosphonoformate).

Umifenovir, sold under the brand name Arbidol, is sold and used as an antiviral medication for influenza in Russia and China. The drug is manufactured by Pharmstandard. It is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment or prevention of influenza.

Nitazoxanide, sold under the brand name Alinia among others, is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and broad-spectrum antiviral medication that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, and viral infections. It is indicated for the treatment of infection by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia in immunocompetent individuals and has been repurposed for the treatment of influenza. Nitazoxanide has also been shown to have in vitro antiparasitic activity and clinical treatment efficacy for infections caused by other protozoa and helminths; evidence as of 2014 suggested that it possesses efficacy in treating a number of viral infections as well.

Inosine pranobex is an antiviral drug that is a combination of inosine and dimepranol acedoben in a ratio of 1 to 3. It is used primarily in European countries, especially as a treatment for acute viral infections, such as the common cold.
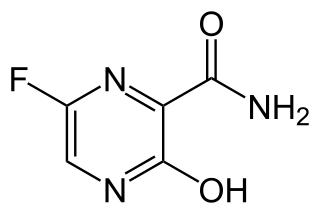
Favipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative.
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is the clinical application of antimicrobial agents to treat infectious diseases.

Riamilovir, sold under the brand name Triazavirin, is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed in Russia through a joint effort of Ural Federal University, Russian Academy of Sciences, Ural Center for Biopharma Technologies and Medsintez Pharmaceutical. It has a novel triazolotriazine core, which represents a new structural class of non-nucleoside antiviral drugs.

MK-608 is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog. It was originally developed by Merck & Co. as a treatment for hepatitis C, but despite promising results in animal studies, it was ultimately unsuccessful in clinical trials. Subsequently it has been widely used in antiviral research and has shown activity against a range of viruses, including Dengue fever, tick-borne encephalitis virus, poliovirus, and most recently Zika virus, in both in vitro and animal models. Since it has already failed in human clinical trials previously, it is unlikely MK-608 itself will be developed as an antiviral medication, but the continuing lack of treatment options for these emerging viral diseases means that much research continues using MK-608 and related antiviral drugs.
Broad-spectrum antivirals (BSAs) are a class of molecules or compounds, which inhibit the infection of multiple viruses from the same or different virus families. BSAs could be divided into experimental and investigational agents, and approved drugs. BSAs work by inhibiting viral proteins or by targeting host cell factors and processes exploited by different viruses during infection. As of 2021, there are 150 known BSAs in varying stages of development, effective against 78 human viruses. BSAs are potential candidates for treatment of emerging and re-emerging viruses, such as ebola, marburg, and SARS-CoV-2. Many BSAs show antiviral activity against other viruses than originally investigated. Efforts in drug repurposing for SARS-CoV-2 is currently underway. A database of BSAs and viruses they inhibit could be found here.

CMX521 is an antiviral drug discovered by Chimerix, which was developed for the treatment of norovirus, though it also shows efficacy against related viral diarrheas such as rotovirus and some sapoviruses, astroviruses and adenoviruses. It is a nucleoside analogue which acts as an inhibitor of viral RNA-dependant RNA polymerase.
The Fabunan Antiviral Injection (FAI) is a patented medicine administered to patients by US-based Filipino doctors Ruben and Willie Fabunan, who assured that it can treat dengue fever, chikungunya, dog bite, snakebite, and HIV/AIDS.

Ensitrelvir, sold under the brand name Xocova is an antiviral medication used as a treatment for COVID-19. It was developed by Shionogi in partnership with Hokkaido University and acts as an orally active 3C-like protease inhibitor. It is taken by mouth.














