Works
Cousu is better known as a theorist than a composer, having left an important treatise on music and a single fantasy with four parts.
The Système royal
Around 1633, Cousu published a "Système Royal", dedicated to Louis XIII, probably a simple method of solfeggio which seems to have earned him some fame, and perhaps his canonicality at Saint-Quentin. That's what Annibal Gantez suggests in 1643: ou pour Monsieur Du Cousu, qui a plus attrapé du roy avec une gamme ou un main qu’il luy a présentée, que je n’ay su faire avec mes deux pieds en parcourant tout le royaume, puisqu’il est chanoine de Saint-Quentin. [6] ... This work is lost.
The Fantaisie en faveur de la quarte

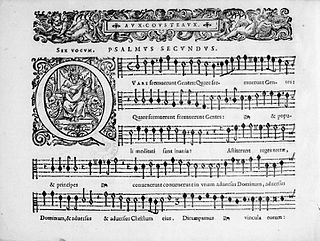
This four-part piece is published in separate parts in the Harmonie universelle by Marin Mersenne, (pp. 199–204) (as a matter of fact pp. 299–304) of the Cinquiesme livre de la composition de musique; he emphasizes the great know-how of the composer and the perfect correction of the writing. The fantasy is republished by Athanasius Kircher in 1650 in his Musurgia Universalis (Book VII, pp. 627–634), this time in a score. Kircher also underlines the originality and value of this piece.
- Modern edition by Olivier Trachier: Strasbourg : Cahiers du Tourdion , [2014], 8 p.
The Musique universelle

The two mentions that Mersenne made of Cousu in 1636 [7] reveal that he was already working on an important musical treatise at that time. This treatise was published more than twenty years later, in 1658, by Robert III Ballard, but the author's death interrupted his publication.
The Musique universelle, contenant toute la pratique, et toute la théorie. Paris : Robert III Ballard, around 1657-1658. 2°, 208 p. RISM B-VI (p. 241), Guillo 2003 n° 1658-F. Brussel BR : Fétis 5357 C RP. Prov. Sébastien de Brossard, with a historical note by François-Joseph Fétis at the beginning. Paris Mazarine: Rés D 4727. Prov. Abbaye de Saint-Germain-des-Prés. The only two known copies contain only pages 1-208, i. e., complete Books I and II, and the first chapters of Book III.. IMSLP Read online
- Fétis' note at the beginning of the Brussels copy states the following:
.On 16 January 1656 he [Cousu] was granted a leave of absence from the chapter [of St. Quentin] in case he printed his music book. He went to Paris to make arrangements with the printer Ballard for the publication of this book; he was back in Saint-Quentin on 3 July of the same year. On 22 March 1658 he was granted a new leave of absence to go to Paris to monitor the impression of his Musique Universelle; when he returned to Saint-Quentin, he died there on 11 August 1658. (Extract from a business diary of the Saint-Quentin chapter, from 1645 to 1685, by the canon of the Cross of this church, whose ms., volume 8° (800 pages), exists today (1860) at M. Le Serrurier, counselor at the Cour de cassation of Paris.)
- As for Sébastien de Brossard, he specifies in his catalogue: [8]
This reference proves that the book was printed at the author's expense, which often happened at the time.This book was started to print at Sr Ballard's home "[...]" and the autheur was a man named Mr. de Cousu canon from St Quentin who made it print at his own expense, but this book remained, by the death of the author, on the 208th page, and it is a shame, because what remains of it is the most excellent. Fortunately, I was at Sr Ballard's house, in the moment that he was sorting through the useless papers in his shop, and I saved this fragment of the nauffrage, which I therefore believe is unique..
- Fétis' note at the beginning of the Brussels copy states the following:
The book by Cousu contains a systematic presentation of the principles and rules of music (as Mersenne had done in 1636), its notation and counterpoint. The work is considered honest and thorough, but it does not contain any fundamentally new ideas. But he was one of the first theorists to put theory and practice at the same level: "Practice being joined to theory, or theory to practice, is much better than when they are separated."
However, Cousu was still strangely attached to explaining the ancient signs of measurements and ligatures, whereas their use was already falling into disuse (which supports the hypothesis that the treaty had been composed a few decades earlier). This is also apparent from a letter from Mersenne to Giovanni Battista Doni, which quotes Cousu and his work in 1635: [9]
We also have a young man, a master of the music of S. Quentin, who has made a very ample traicté of the signs and various values of the measures. But since he is perhaps the most skillful man in France among practitioners for theoretical music, we find it so long and useless that we don't want to print it. For we no longer use in all tunes only binary and ternary, and he wants to show that all the alders musicians do not know anything and that they commit a thousand abuses to the signs and circles etc., instead of us all desiring like you, that we are released from this burden and embarrassment of poinctz, demy poictz, decreases etc.[...] I'll give you advisories from our musician's book if he prints it.