
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers make contributions in doing citizen science, such as by monitoring variable stars, double stars, sunspots, or occultations of stars by the Moon or asteroids, or by discovering transient astronomical events, such as comets, galactic novae or supernovae in other galaxies.
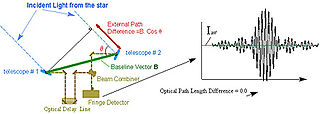
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.

The Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO) is a United States astronomical observatory located on Kitt Peak of the Quinlan Mountains in the Arizona-Sonoran Desert on the Tohono Oʼodham Nation, 88 kilometers (55 mi) west-southwest of Tucson, Arizona. With more than twenty optical and two radio telescopes, it is one of the largest gatherings of astronomical instruments in the Earth's northern hemisphere.

Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.

Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965. In 2011, the Observatory was named one of "The World's 100 Most Important Places" by Time Magazine. It was at the Lowell Observatory that the dwarf planet Pluto was discovered in 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh.

Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects outside of the visible spectrum of the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is accomplished through long time exposure as both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over long periods of time or using specialized optical filters which limit the photons to a certain wavelength.

The United Kingdom Infra-Red Telescope (UKIRT) is a 3.8 metre (150 inch) infrared reflecting telescope, the second largest dedicated infrared telescope in the world. It is located on Mauna Kea, Hawai'i as part of Mauna Kea Observatory. Until 2014 it was operated by the Joint Astronomy Centre in Hilo. It was owned by the United Kingdom Science and Technology Facilities Council. UKIRT is currently being funded by NASA and operated under scientific cooperation between Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, the University of Hawaii, and the U. S. Naval Observatory. The telescope is set to be decommissioned after completion of the Thirty Meter Telescope as part of the Mauna Kea Comprehensive Management Plan.

In astronomy, seeing is the degradation of the image of an astronomical object due to turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth that may become visible as blurring, twinkling or variable distortion. The origin of this effect is rapidly changing variations of the optical refractive index along the light path from the object to the detector. Seeing is a major limitation to the angular resolution in astronomical observations with telescopes that would otherwise be limited through diffraction by the size of the telescope aperture. Today, many large scientific ground-based optical telescopes include adaptive optics to overcome seeing.

Speckle imaging comprises a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add method and the speckle interferometry methods. These techniques can dramatically increase the resolution of ground-based telescopes, but are limited to bright targets.

During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it was erroneously believed that there were "canals" on the planet Mars. These were a network of long straight lines in the equatorial regions from 60° north to 60° south latitude on Mars, observed by astronomers using early telescopes without photography.

Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments.

The Gemini Observatory comprises two 8.1-metre (26.6 ft) telescopes, Gemini North and Gemini South, situated in Hawaii and Chile, respectively. These twin telescopes offer extensive coverage of the northern and southern skies and rank among the most advanced optical/infrared telescopes available to astronomers. (See List of largest optical reflecting telescopes).

The National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) was the United States national observatory for ground-based nighttime ultraviolet-optical-infrared (OUVIR) astronomy. The National Science Foundation (NSF) funded NOAO to provide forefront astronomical research facilities for US astronomers. Professional astronomers from any country in the world could apply to use the telescopes operated by NOAO under the NSF's "open skies" policy.

Eugène Michel Antoniadi was a Greek-French astronomer. He is known for creating the Antoniadi scale as well as for his observations of the planets. He was a major opponent of the notion of Martian canals and he also created the first map of Mercury, though it turned out to not be correct.

The Haute-Provence Observatory is an astronomical observatory in the southeast of France, about 90 km east of Avignon and 100 km north of Marseille. It was established in 1937 as a national facility for French astronomers. Astronomical observations began in 1943 using the 1.20 m telescope, and the first research papers based on observations made at the observatory were published in 1944. Foreign observers first used the observatory in 1949, when Geoffrey and Margaret Burbidge visited.
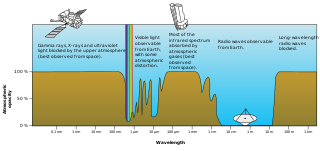
Visible-light astronomy encompasses a wide variety of astronomical observation via telescopes that are sensitive in the range of visible light. Visible-light astronomy is part of optical astronomy, and differs from astronomies based on invisible types of light in the electromagnetic radiation spectrum, such as radio waves, infrared waves, ultraviolet waves, X-ray waves and gamma-ray waves. Visible light ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers in wavelength.

Mills Observatory is the first purpose-built public astronomical observatory in the UK, located in Dundee, Scotland. Built in 1935, the observatory is classically styled in sandstone and has a distinctive 7 m dome, which houses a Victorian refracting telescope, a small planetarium, and display areas. The dome is one of two made from papier-mâché to survive in the UK, the other being at the Godlee Observatory.

The history of Mars observation is about the recorded history of observation of the planet Mars. Some of the early records of Mars' observation date back to the era of the ancient Egyptian astronomers in the 2nd millennium BCE. Chinese records about the motions of Mars appeared before the founding of the Zhou dynasty. Detailed observations of the position of Mars were made by Babylonian astronomers who developed arithmetic techniques to predict the future position of the planet. The ancient Greek philosophers and Hellenistic astronomers developed a geocentric model to explain the planet's motions. Measurements of Mars' angular diameter can be found in ancient Greek and Indian texts. In the 16th century, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed a heliocentric model for the Solar System in which the planets follow circular orbits about the Sun. This was revised by Johannes Kepler, yielding an elliptic orbit for Mars that more accurately fitted the observational data.

The Killarney Provincial Park Observatory is an astronomical observatory located at the George Lake Campground of Killarney Provincial Park . The Observatory is operated by Ontario Parks and houses two observatory buildings. The original facility contains a 10" telescope with solar filter, ideal for nighttime as well as daytime viewing of the Sun. The newer facility contains a 16" fully automated telescope with a 5" refractor and is ideal for research, astrophotography and public use. The telescopes are available for Discovery programs as well as private sign-out (self-use) by interested visitors.

Meudon Great Refractor is a double telescope with lenses, in Meudon, France. It is a twin refracting telescope built in 1891, with one visual and one photographic, on a single square-tube together on an equatorial mount, inside a dome. The Refractor was built for the Meudon Observatory, and is the largest double doublet refracting telescope in Europe, but about the same size as several telescopes in this period, when this style of telescope was popular. Other large telescopes of a similar type include the James Lick telescope (91.4), Potsdam Great Refractor (80+50 cm), and the Greenwich 28 inch refractor (71.1 cm).




















