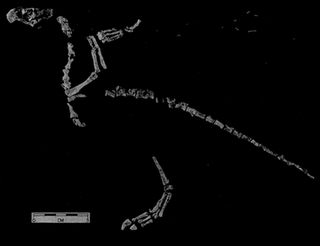
Protoavis is a problematic taxon known from fragmentary remains from Late Triassic Norian stage deposits near Post, Texas. The animal's true classification has been the subject of much controversy, and there are many different interpretations of what the taxon actually is. When it was first described, the fossils were described as being from a primitive bird which, if the identification is valid, would push back avian origins some 60-75 million years.

Longisquama is a genus of extinct reptile. There is only one species, Longisquama insignis, known from a poorly preserved skeleton and several incomplete fossil impressions from the Middle to Late Triassic Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan. It is known from the type fossil specimen, slab and counterslab and five referred specimens of possible integumentary appendages. All specimens are in the collection of the Paleontological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow.

Nicrosaurus (/nɛkroʊˈsɔrəs/) is an extinct genus of phytosaur reptile existing during the Late Triassic period. Although it looked like a crocodile, it was not closely related to these creatures, instead being an example of parallel evolution. The main difference between Nicrosaurus and modern crocodiles is the position of the nostrils – Nicrosaurus's nostrils, or external nares, were placed directly in front of the forehead, whereas in crocodiles, the nostrils are positioned on the end of the snout. A 2013 study has also found that ilium of Nicrosaurus is quite distinctive from all other phytosaurs.

Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit. These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly seen in the fossilized skulls of dinosaurs and other sauropsids. The major reptile group Diapsida, for example, is defined by the presence of two temporal fenestrae on each side of the skull. The infratemporal fenestra, also called the lateral temporal fenestra or lower temporal fenestra, is the lower of the two and is exposed primarily in lateral (side) view.

Proterochampsa is an extinct genus of proterochampsid, non-archosaur archosauriformes from the Late Triassic of South America. The genus forms a monophyly within the family Proterochampsidae, and more broadly within the clade Proterochampsia. Like other proterochampsids, Proterochampsa are quadruped tetrapods superficially similar in appearance to modern crocodiles, although the two groups are not closely related. Proterochampsids can be distinguished from other related archosauriformes by characters such as a dorsoventrally flattened, triangular skull with a long, narrow snout at the anterior end and that expands transversally at the posterior end, asymmetric feet, and a lack of postfrontal bones in the skull, with the nares located near the midline. Proterochampsa is additionally defined by characters of dermal sculpturing consisting of nodular protuberances on the skull, antorbital fenestrae facing dorsally, and a restricted antorbital fossa on the maxilla. The genus comprises two known species: Proterochampsa barrionuevoi and Proterochampsa nodosa, with the species names potentially recalling “new neighborhood” in Spanish and the large nodular growths of P. nodosa, respectively. P. barrionuevoi specimens have been discovered in the Ischigualasto Formation in northwestern Argentina, while P. nodosa specimens have been found in the Santa Maria supersequence in southeastern Brazil. The two species are distinct in several characters, including that P. nodosa has larger, more well-developed nodular protuberances, a more gradually narrowing snout, and a higher occiput than P. barrionuevoi. Of the two, P. nodosa is thought to have less derived features than P. barrionuevoi.

Turfanosuchus is a genus of archosauriform reptile, likely a gracilisuchid archosaur, which lived during the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of northwestern China. The type species, T. dabanensis, was described by C.C. Young in 1973, based on a partially complete but disarticulated fossil skeleton found in the Kelamayi Formation of the Turfan Basin.

Parringtonia is an extinct genus of Triassic archosaur within the family Erpetosuchidae, known from the type species Parringtonia gracilis. It is known from a single specimen, NHMUK R8646, found from the Anisian-age Manda Formation of Tanzania. This specimen, like most archosaur material from the Manda Formation, is fragmentary, including only a maxilla and a few postcranial bones. They show similarities with those of another archosaur called Erpetosuchus, known from the Middle Triassic of Scotland and the eastern United States. The phylogenetic placement of Parringtonia and Erpetosuchus are uncertain; some studies placed them close to the group Crocodylomorpha, which includes all modern crocodylians and many extinct forms that diversified after the Triassic, but this relationship has more recently been questioned.

Proceratosauridae is a family or clade of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous.

Daemonosaurus is an extinct genus of possible theropod dinosaur from the Late Triassic of New Mexico. The only known fossil is a skull and neck fragments from deposits of the latest Triassic Chinle Formation at Ghost Ranch. Daemonosaurus was an unusual dinosaur with a short skull and large, fang-like teeth. It lived alongside early neotheropods such as Coelophysis, which would have been among the most common dinosaurs by the end of the Triassic. However, Daemonosaurus retains several plesiomorphic ("primitive") traits of the snout, and it likely lies outside the clade Neotheropoda. It may be considered a late-surviving basal theropod or non-theropod basal saurischian, possibly allied to other early predatory dinosaurs such as herrerasaurids or Tawa.
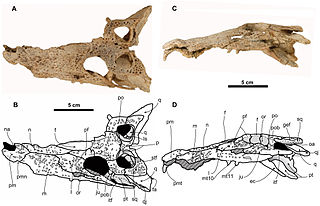
Arenysuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of allodaposuchid eusuchian crocodylomorph from Late Cretaceous deposits of north Spain. It is known from the holotype MPZ ELI-1, a partial skull from Elías site, and from the referred material MPZ2010/948, MPZ2010/949, MPZ2010/950 and MPZ2010/951, four teeth from Blasi 2 site. It was found by the researchers José Manuel Gasca and Ainara Badiola from the Tremp Formation, in Arén of Huesca, Spain. It was first named by Eduardo Puértolas, José I. Canudo and Penélope Cruzado-Caballero in 2011 and the type species is Arenysuchus gascabadiolorum.

Smok is an extinct genus of large carnivorous archosaur. It lived during the latest Triassic period. Its remains have been found in Lisowice, southern Poland. The only species is Smok wawelski and was named in 2012. It is larger than any other known predatory archosaur from the Late Triassic or Early Jurassic of central Europe. The relation of Smok to other archosaurs has not yet been thoroughly studied; it may be a rauisuchid, prestosuchid, an ornithosuchid pseudosuchian or a theropod dinosaur.

Erpetosuchidae is an extinct family of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Erpetosuchidae was named by D. M. S. Watson in 1917 to include Erpetosuchus. It includes the type species Erpetosuchus granti from the Late Triassic of Scotland, Erpetosuchus sp. from the Late Triassic of eastern United States and Parringtonia gracilis from the middle Middle Triassic of Tanzania; the group might also include Dyoplax arenaceus from the Late Triassic of Germany, Archeopelta arborensis and Pagosvenator candelariensis from Brazil and Tarjadia ruthae from Argentina.

Asperoris is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile known from the Middle Triassic Manda Beds of southwestern Tanzania. It is the first archosauriform known from the Manda Beds that is not an archosaur. However, its relationships with other non-archosaurian archosauriforms are uncertain. It was first named by Sterling J. Nesbitt, Richard J. Butler and David J. Gower in 2013 and the type species is Asperoris mnyama. Asperoris means "rough face" in Latin, referring to the distinctive rough texture of its skull bones.
This glossary explains technical terms commonly employed in the description of dinosaur body fossils. Besides dinosaur-specific terms, it covers terms with wider usage, when these are of central importance in the study of dinosaurs or when their discussion in the context of dinosaurs is beneficial. The glossary does not cover ichnological and bone histological terms, nor does it cover measurements.
Triopticus is a genus of archosauriform reptile from the Late Triassic of Texas, United States. It contains a single species, Triopticus primus, described in 2016 by Stocker et al. It has an unusually domed head reminiscent of the later pachycephalosaurian dinosaurs in an example of convergent evolution.
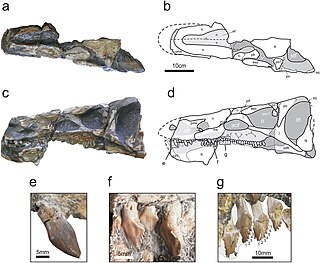
Isaberrysaura is a genus of stegosaurian ornithischian dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Los Molles Formation of Patagonia, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, I. mollensis, described by Salgado et al. in 2017 from a single specimen. Although initially classified as a basal neornithischian, subsequent analysis has allied it with the Stegosauria; the morphology of its skull resembles those of other members of the group.
Shuangbaisaurus is genus of theropod dinosaur, possibly a junior synonym of Sinosaurus. It lived in the Early Jurassic of Yunnan Province, China, and is represented by a single species, S. anlongbaoensis, known from a partial skull. Like the theropods Dilophosaurus and Sinosaurus,Shuangbaisaurus bore a pair of thin, midline crests on its skull. Unusually, these crests extended backwards over the level of the eyes, which, along with the unusual orientation of the jugal bone, led the describers to name it as a new genus. However, Shuangbaisaurus also possesses a groove between its premaxilla and maxilla, a characteristic which has been used to characterize Sinosaurus as a genus. Among the two morphotypes present within the genus Sinosaurus, Shuangbaisaurus more closely resembles the morphotype that is variably treated as a distinct species, S. sinensis, in its relatively tall skull.

Caelestiventus is a pterosaur genus from the Late Triassic found in western North America. The type species, Caelestiventus hanseni, honors Robin Hansen, the Bureau of Land Management geologist (BLM), who facilitated access to the excavation site.

Caihong is a genus of small paravian theropod dinosaur from China that lived during the Late Jurassic period.

Gnathovorax is a genus of herrerasaurid saurischian dinosaur from the Santa Maria Formation in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The type and only species is Gnathovorax cabreirai, described by Pacheco et al. in 2019.
















