
Ape House is a 2010 novel by Sara Gruen. [1] It received generally mixed reviews.

Ape House is a 2010 novel by Sara Gruen. [1] It received generally mixed reviews.
A group of reporters visit the Great Ape Language Lab - a laboratory where bonobos are trained to communicate with humans by using American Sign Language and computer software to communicate with the scientist involved. Perhaps the most amazing phenomenon is that the bonobos actually want to communicate with humans, so much so that they pass it down to their young. But soon after the reporters leave, the lab is blown up, with the bonobos and a scientist (Isabel Duncan) inside. Isabel is badly injured and taken to a hospital. The bonobos escape from the lab only to be sold to a man named Ken Faulks. He is a famous for making pornography and devises a plan to put the apes on the air, in a show called Ape House. When Isabel discovers the bonobos' predicament, she travels to Lizard, New Mexico, where Ape House is shooting. In order to free the apes from these horrendous conditions, Isabel joins forces with journalist, John Thigpen. The two work to free the apes and get them back "home."
People conduct language studies with six bonobos at the Great Ape Language Lab. Scientist Isabel Duncan and journalist John Thigpen are at the core of the novel as the main characters. John was sent to write a report about on the ape lab, but he gets involved significantly after the lab is blown up by a bomb and the animals go missing. He discovers that a reality television show is airing called Ape House which the apes are a part of. Isabel and John team up to save the apes and are helped by a variety of colorful characters.
The novel received generally mixed reviews, with the Los Angeles Times , [2] The New York Times , [3] Entertainment Weekly , [4] and The Washington Post , [5] all finding the novel flawed, especially in comparison to Gruen's earlier work. There were some very positive reviews, particularly one from The Dallas Morning News . [6]

The bonobo, also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus Pan. While bonobos are, today, recognized as a distinct species in their own right, they were initially thought to be a subspecies of Pan troglodytes, due to the physical similarities between the two species. Taxonomically, members of the chimpanzee/bonobo subtribe Panina—composed entirely by the genus Pan—are collectively termed panins.

The genus Pan consists of two extant species: the chimpanzee and the bonobo. Taxonomically, these two ape species are collectively termed panins. The two species were formerly collectively called "chimpanzees" or "chimps"; if bonobos were recognized as a separate group at all, they were referred to as "pygmy" or "gracile chimpanzees". Together with humans, gorillas, and orangutans they are part of the family Hominidae. Native to sub-Saharan Africa, chimpanzees and bonobos are currently both found in the Congo jungle, while only the chimpanzee is also found further north in West Africa. Both species are listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, and in 2017 the Convention on Migratory Species selected the chimpanzee for special protection.

Apes are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, which together with its sister group Cercopithecidae form the catarrhine clade, cladistically making them monkeys. Apes do not have tails due to a mutation of the TBXT gene. In traditional and non-scientific use, the term ape can include tailless primates taxonomically considered Cercopithecidae, and is thus not equivalent to the scientific taxon Hominoidea. There are two extant branches of the superfamily Hominoidea: the gibbons, or lesser apes; and the hominids, or great apes.
Yerkish is an artificial language developed for use by non-human primates. It employs a keyboard whose keys contain lexigrams, symbols corresponding to objects or ideas.

Franciscus Bernardus Maria de Waal was a Dutch-American primatologist and ethologist. He was the Charles Howard Candler Professor of Primate Behavior in the Department of Psychology at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, director of the Living Links Center at the Yerkes National Primate Research Center at Emory, and author of numerous books including Chimpanzee Politics (1982) and Our Inner Ape (2005). His research centered on primate social behavior, including conflict resolution, cooperation, inequity aversion, and food-sharing. He was a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.

Kanzi, also known by the lexigram , is a male bonobo who has been the subject of several studies on great ape language. According to Sue Savage-Rumbaugh, a primatologist who has studied the bonobo throughout her life, Kanzi has exhibited advanced linguistic aptitude.

Research into great ape language has involved teaching chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas and orangutans to communicate with humans and each other using sign language, physical tokens, lexigrams, and imitative human speech. Some primatologists argue that the use of these communication methods indicate primate "language" ability, though this depends on one's definition of language. The cognitive tradeoff hypothesis suggests that human language skills evolved at the expense of the short-term and working memory capabilities potentially observed in other hominids.
Nyota, also known by the lexigram , is a bonobo. Nyota was born at the Language Research Center at Georgia State University. His mother was Panbanisha and his father was P-suke. With Panbanisha's death on November 6, 2012, Nyota became the sole surviving member of his immediate family.
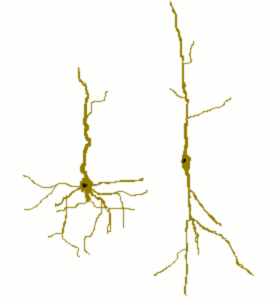
Von Economo neurons, also called spindle neurons, are a specific class of mammalian cortical neurons characterized by a large spindle-shaped soma gradually tapering into a single apical axon in one direction, with only a single dendrite facing opposite. Other cortical neurons tend to have many dendrites, and the bipolar-shaped morphology of von Economo neurons is unique here.

Emily Sue Savage-Rumbaugh is a psychologist and primatologist most known for her work with two bonobos, Kanzi and Panbanisha, investigating their linguistic and cognitive abilities using lexigrams and computer-based keyboards. Originally based at Georgia State University's Language Research Center in Atlanta, Georgia, she worked at the Iowa Primate Learning Sanctuary in Des Moines, Iowa from 2006 until her departure in November 2013. She currently sits on the Board of Directors of Bonobo Hope.
Sara Gruen is Canadian-American author. She is a 2007 recipient of the Alex Award for young adult literature.
William M. Fields, also known by the lexigram , is an American qualitative investigator studying language, culture, and tools in non-human primates. He is best known for his collaboration with Sue Savage-Rumbaugh beginning in 1997 at the Language Research Center of Georgia State University. There he co-reared Nyota , a baby bonobo, with Panbanisha , Kanzi and Savage-Rumbaugh . Fields and Savage-Rumbaugh are the only scientists in the world carrying out language research with bonobos.

Panbanisha, also known by the lexigram , was a female bonobo that featured in studies on great ape language by Professor Sue Savage-Rumbaugh. Her name is Swahili for "to cleave together for the purpose of contrast."
Human Ape is a 2008 National Geographic documentary film on the genetic and evolutionary origins of human behavior, and covers the genetic and behavioural similarities and differences between humans and other great apes. The award-winning independent production company Pioneer Productions of London was commissioned by National Geographic Channels International to produce Human Ape.

Rise of the Planet of the Apes is a 2011 American science fiction action film directed by Rupert Wyatt and written by the writing team of Rick Jaffa and Amanda Silver. It is a reboot of the Planet of the Apes film series and its the seventh installment overall and the first in the reboot series. The film stars James Franco, Freida Pinto, John Lithgow, Brian Cox, Tom Felton, and Andy Serkis. In the film, Caesar (Serkis), a chimpanzee genetically enhanced and raised by chemist Will Rodman (Franco), goes from living in captivity to eventually leading an ape uprising against humanity.

Two Roads Books is an imprint of John Murray Press now a division of Hachette.

Wake, also called WWW: Wake, is a 2009 novel written by Canadian novelist Robert J. Sawyer and the first book in his WWW Trilogy. It was first serialized in four parts in Analog Science Fiction and Fact from November 2008 to March 2009, was first published in book form on April 8, 2009, and was followed by Watch in 2010 and by Wonder in 2011. The novel details the spontaneous emergence of an intelligence on the World Wide Web, called Webmind, and its friendship with a blind teenager named Caitlin.

Eliot Schrefer is an American and British author of both adult and young adult fiction, and a two-time finalist for the National Book Award in Young People's Literature. Schrefer's first novel Glamorous Disasters was published by Simon & Schuster in 2006. He is most known for his young adult novels Endangered (2012) and Threatened (2014), which are survival stories featuring young people and great apes. He is currently on the faculty of the Creative Writing MFA Program at Fairleigh Dickinson University.

Isabel Behncke Izquierdo is a field ethologist who studies animal behaviour to understand other animals, as well as to understand humans and our place in nature. Originally from Chile, she is a primatologist, a pioneer adventurer-scientist and the first South American in following great apes in the wild. Behncke is currently director of the Centro de Estudios Públicos (CEP), and advisor to the Chilean government, working on long-term strategies in science, technology, innovation and knowledge as a member of the National Council of Science, Technology, Knowledge and Innovation for Development (CTCI), of the Ministry of Science, Technology, Knowledge and Innovation of Chile She is a board member of the PERC research institute, which is dedicated to promoting environmental conservation, Gruter Institute research fellow, researcher at the Social Complexity Research Center, Faculty of Government, Universidad del Desarrollo, and Member of the conservation area team at Estancia Cerro Guido in Chilean Patagonia.