
AIX is a series of proprietary Unix operating systems developed and sold by IBM for several of its computer platforms.

In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.

z/OS is a 64-bit operating system for IBM z/Architecture mainframes, introduced by IBM in October 2000. It derives from and is the successor to OS/390, which in turn was preceded by a string of MVS versions. Like OS/390, z/OS combines a number of formerly separate, related products, some of which are still optional. z/OS has the attributes of modern operating systems but also retains much of the older functionality that originated in the 1960s and is still in regular use—z/OS is designed for backward compatibility.

HCL Notes is a proprietary collaborative software platform for Unix (AIX), IBM i, Windows, Linux, and macOS, sold by HCLTech. The client application is called Notes while the server component is branded HCL Domino.
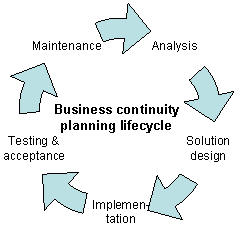
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.

Db2 is a family of data management products, including database servers, developed by IBM. It initially supported the relational model, but was extended to support object–relational features and non-relational structures like JSON and XML. The brand name was originally styled as DB2 until 2017, when it changed to its present form.

The software release life cycle is the process of developing, testing, and distributing a software product. It typically consists of several stages, such as pre-alpha, alpha, beta, and release candidate, before the final version, or "gold", is released to the public.
IBM i is an operating system developed by IBM for IBM Power Systems. It was originally released in 1988 as OS/400, as the sole operating system of the IBM AS/400 line of systems. It was renamed to i5/OS in 2004, before being renamed a second time to IBM i in 2008. It is an evolution of the System/38 CPF operating system, with compatibility layers for System/36 SSP and AIX applications. It inherits a number of distinctive features from the System/38 platform, including the Machine Interface which provides hardware independence, the implementation of object-based addressing on top of a single-level store, and the tight integration of a relational database into the operating system.
Key management refers to management of cryptographic keys in a cryptosystem. This includes dealing with the generation, exchange, storage, use, crypto-shredding (destruction) and replacement of keys. It includes cryptographic protocol design, key servers, user procedures, and other relevant protocols.

The IBM 4758 PCI Cryptographic Coprocessor is a secure cryptoprocessor implemented on a high-security, tamper resistant, programmable PCI expansion card. Specialized cryptographic electronics, microprocessor, memory, and random number generator housed within a tamper-responding environment provide a highly secure subsystem in which data processing and cryptography can be performed.
WebSphere Application Server (WAS) is a software product that performs the role of a web application server. More specifically, it is a software framework and middleware that hosts Java-based web applications. It is the flagship product within IBM's WebSphere software suite. It was initially created by Donald F. Ferguson, who later became CTO of Software for Dell. The first version was launched in 1998. This project was an offshoot from IBM HTTP Server team starting with the Domino Go web server.
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) is an online community that produces freely available articles, methodologies, documentation, tools, and technologies in the fields of IoT, system software and web application security. The OWASP provides free and open resources. It is led by a non-profit called The OWASP Foundation. The OWASP Top 10 - 2021 is the published result of recent research based on comprehensive data compiled from over 40 partner organizations.
Enterprise software, also known as enterprise application software (EAS), is computer software used to satisfy the needs of an organization rather than its individual users. Enterprise software is an integral part of a computer-based information system, handling a number of business operations, for example to enhance business and management reporting tasks, or support production operations and back office functions. Enterprise systems must process information at a relatively high speed.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.
4690 Operating System is a specially designed point of sale (POS) operating system, originally sold by IBM. In 2012, IBM sold its retail business, including this product, to Toshiba, which assumed support. 4690 is widely used by IBM and Toshiba retail customers to run retail systems which run their own applications and others.
The IBM 4764 Cryptographic Coprocessor is a secure cryptoprocessor that performs cryptographic operations used by application programs and by communications such as SSL private key transactions associated with SSL digital certificates.

Linoma Software was a developer of secure managed file transfer and IBM i software solutions. The company was acquired by HelpSystems in June 2016. Mid-sized companies, large enterprises and government entities use Linoma's software products to protect sensitive data and comply with data security regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA/HITECH, SOX, GLBA and state privacy laws. Linoma's software runs on a variety of platforms including Windows, Linux, UNIX, IBM i, AIX, Solaris, HP-UX and Mac OS X.
Trusteer is a Boston-based computer security division of IBM, responsible for a suite of security software. Founded by Mickey Boodaei and Rakesh K. Loonkar, in Israel in 2006, Trusteer was acquired in September 2013 by IBM for $1 billion.
Linux on IBM Z or Linux on zSystems is the collective term for the Linux operating system compiled to run on IBM mainframes, especially IBM Z / IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE servers. Similar terms which imply the same meaning are Linux/390, Linux/390x, etc. The three Linux distributions certified for usage on the IBM Z hardware platform are Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and Ubuntu.










