Related Research Articles
Year 651 (DCLI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 651 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Yazdegerd III was the last Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 632 to 651. His father was Shahriyar and his grandfather was Khosrow II.
The Battle of Callinicum took place on Easter Saturday, 19 April 531 AD, between an army of the Byzantine Empire under Belisarius and a Sasanian cavalry force commanded by Azarethes. After being defeated at the Battle of Dara, the Sasanians moved to invade Roman Syria in an attempt to turn the tide of the war. Belisarius' rapid response foiled the plan, and his troops pushed the Persians to the Syrian border through maneuvering before forcing a battle in which the Sasanians won a Pyrrhic victory.

The Muslim conquest of Persia, also called the Muslim conquest of Iran, the Arab conquest of Persia, or the Arab conquest of Iran, was a major military campaign undertaken by the Rashidun Caliphate between 632 and 654. As part of the early Muslim conquests, which had begun under Muhammad in 622, it led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire and the eventual decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been predominant throughout Persia as the nation's official religion. The persecution of Zoroastrians by the early Muslims during and after this conflict prompted many of them to flee eastward to India, where they were granted refuge by various kings.
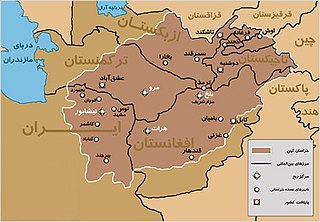
Greater Khorāsān, or Khorāsān is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau between West and Central Asia.
The Sasanian army was the primary military body of the Sasanian armed forces, serving alongside the Sasanian navy. The birth of the army dates back to the rise of Ardashir I, the founder of the Sasanian Empire, to the throne. Ardashir aimed at the revival of the Persian Empire, and to further this aim, he reformed the military by forming a standing army which was under his personal command and whose officers were separate from satraps, local princes and nobility. He restored the Achaemenid military organizations, retained the Parthian cavalry model, and employed new types of armour and siege warfare techniques. This was the beginning for a military system which served him and his successors for over 400 years, during which the Sasanian Empire was, along with the Roman Empire and later the East Roman Empire, one of the two superpowers of Late Antiquity in Western Eurasia. The Sasanian army protected Eranshahr from the East against the incursions of central Asiatic nomads like the Hephthalites and Turks, while in the west it was engaged in a recurrent struggle against the Roman Empire.

Spāhbed is a Middle Persian title meaning "army chief" used chiefly in the Sasanian Empire. Originally there was a single spāhbed, called the Ērān-spāhbed, who functioned as the generalissimo of the Sasanian army. From the time of Khosrow I on, the office was split in four, with a spāhbed for each of the cardinal directions. After the Muslim conquest of Persia, the spāhbed of the East managed to retain his authority over the inaccessible mountainous region of Tabaristan on the southern shore of the Caspian Sea, where the title, often in its Islamic form ispahbadh, survived as a regnal title until the Mongol conquests of the 13th century. An equivalent title of Persian origin, ispahsālār or sipahsālār, gained great currency across the Muslim world in the 10th–15th centuries.

The Battle of Nahavand, also spelled Nihavand or Nahawand, was fought in 642 between the Rashidun Muslim forces under caliph Umar and Sasanian Persian armies under King Yazdegerd III. Yazdegerd escaped to the Merv area, but was unable to raise another substantial army. It was a victory for the Rashidun Caliphate and the Persians consequently lost the surrounding cities including Spahan (Isfahan).

The Battle of the Bridge or the Battle of al-Jisr was a battle at the bank of the Euphrates river between Arabs led by Abu Ubaid al-Thaqafi, and the Persian Sasanian forces led by Bahman Jaduya. It is traditionally dated to the year 634, and was the only major Sassanian victory over the Rashidun Caliphate army.
Marzbān, or Marzpān were a class of margraves, warden of the marches, and by extension military commanders, in charge of border provinces of the Parthian Empire and mostly Sasanian Empire of Iran.

Juansher was the Mihranid prince of Caucasian Albania, ruling the principality from 637 to 669. He was the son and successor of Varaz Grigor.

The SasanianEmpire or Sassanid Empire, also known as the Second Persian Empire or Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th to 8th centuries. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651, making it the second longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty after the Arsacids of the Parthian Empire.

Chaghaniyan, known as al-Saghaniyan in Arabic sources, was a medieval region and principality located on the right bank of the Oxus River, to the south of Samarkand.

The Battle of Ullais was fought between the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Persian Empire in the middle of June 633 AD in Iraq, and is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Blood River since, as a result of the battle, there were enormous amounts of Persian Sasanian and Arab Christian casualties.

The Rashidun Caliphate was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his death in 632 CE. During its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in West Asia and Northeast Africa.
Abū ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿĀmir ibn Kurayz was a Rashidun politician and general, serving as governor of Basra from 647 to 656 AD during the reign of Rashidun Caliph Uthman ibn Affan. He was a cousin of the Caliph through his father. He is known for his administrative and military prowess including his successful campaigns of reconquest and pacification of former territories of the Sasanian Empire in what is now Iran and Afghanistan.
Farrukhzad was an Iranian aristocrat from the House of Ispahbudhan and the founder of the Bavand dynasty, ruling from 651 to 665. Originally a powerful servant of the Sasanian king Khosrow II, he, along with several other powerful aristocrats made a conspiracy against the latter and ended his tyrannical rule. They thereafter put Khosrow's son Kavadh II on the throne, whose rule lasted only a few months, before he was killed by a plague, being succeeded by his son Ardashir III, who was only after one year murdered by the rebellious former Sasanian army chief (spahbed) Shahrbaraz, who usurped the throne.

The Sasanian dynasty was the house that founded the Sasanian Empire of Iran, ruling this empire from 224 to 651 AD. It began with Ardashir I, who named the dynasty in honour of his predecessor, Sasan.

The Battle of Ray was fought between the Sasanians and the Rashidun Caliphate in 651. It was also part of the rivalry between the Ispahbudhan family and the Mihran family.

The Principality of Chaghaniyan, known in Arabic sources as al-Saghaniyan, was a part of the Hephthalite Confederation from the 5th to the 7th century CE. After this, it was ruled by a local, presumably Iranian dynasty, which governed the Chaghaniyan region from the late 7th-century to the early 8th-century CE. These rulers were known by their titles of “Chaghan Khudah”.
References
- ↑ Hogan, Linda; Lehrke, Dylan (2009). Religion and the Politics of Peace and Conflict (in Arabic). Wipf and Stock Publishers. p. 188. ISBN 9781630878238 . Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Harrel, John (2016). The Nisibis War: The Defence of the Roman East AD 337-363. Pen and Sword. p. 69. ISBN 9781473848337 . Retrieved 14 April 2018.