A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; synthetic toxicants created by artificial processes are thus excluded. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived from the word toxic.
An antidote is a substance which can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek (φάρμακον) ἀντίδοτον (pharmakon) antidoton, "(medicine) given as a remedy". Antidotes for anticoagulants are sometimes referred to as reversal agents.

Atracidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders, commonly known as Australian funnel-web spiders or atracids. It has been included as a subfamily of the Hexathelidae, but is now recognized as a separate family. All members of the family are native to Australia. Atracidae consists of three genera: Atrax, Hadronyche, and Illawarra, comprising 35 species. Some members of the family produce venom, which is dangerous to humans, and bites by spiders of six of the species have caused severe injuries to victims. The bite of the Sydney funnel-web spider and northern tree funnel-web spider are potentially deadly, but no fatalities have occurred since the introduction of modern first-aid techniques and antivenom.
Apache Lucene is a free and open-source search engine software library, originally written completely in Java by Doug Cutting. It is supported by the Apache Software Foundation and is released under the Apache Software License.

Toxin or the Toxin symbiote is a fictional antihero and at times supervillain in the Marvel Comics universe. He is the third major symbiote of the Spider-Man series, the ninth known to have appeared in the comics outside of the Planet of the Symbiotes storyline, and the first symbiote that Spider-Man considers an ally, despite temporary alliances with Venom on numerous occasions. The first host of the Toxin symbiote is former NYPD police officer Patrick Mulligan. Toxin later bonded to Eddie Brock as his second host after Patrick Mulligan was killed.
Mega Morphs was a comic book limited series published by Marvel Comics in 2005. Mega Morphs is based on a series of action figures made by Toy Biz. The comics feature Spider-Man, Ghost Rider, Captain America, Hulk and Wolverine. The comic was drawn by Lou Kang and written by Sean McKeever.
A latrotoxin is a high-molecular mass neurotoxin found in the venom of spiders of the genus Latrodectus. Latrotoxins are the main active components of the venom and are responsible for the symptoms of latrodectism.

Delta atracotoxin is a low-molecular-weight neurotoxic polypeptide found in the venom of the Sydney funnel-web spider.
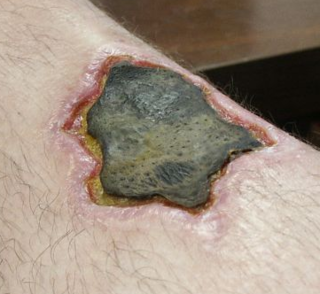
Loxoscelism is a condition occasionally produced by the bite of the recluse spiders. The area becomes dusky and a shallow open sore forms as the skin around the bite dies (necrosis). It is the only proven type of necrotic arachnidism in humans. While there is no known therapy effective for loxoscelism, there has been research on antibiotics, surgical timing, hyperbaric oxygen, potential antivenoms and vaccines. Because of the number of diseases that may mimic loxoscelism, it is frequently misdiagnosed by physicians.
Stromatoxin is a spider toxin that blocks certain delayed-rectifier and A-type voltage-gated potassium channels.
Phoneutria nigriventer toxin-3 is more commonly referred to as PhTx3.

Arachno-Bot is a printable spider robot built as an exploratory tool in environments that are too hazardous for humans. It gets its name because of its movement and look as a real spider. Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation in Stuttgart, Germany has developed Arachno by using a natural spider as the model for their robot, which they created through 3D printing.
ConoServer is a database of toxins that are expressed by the predatory sea snails in the family Conidae, the cone snails. These toxins are known as conotoxins or conopeptides. The toxins are of importance to medical research. A notable feature of these peptides is their high specificity and affinity towards human ion channels, receptors and transporters of the nervous system. This makes conopeptides an interesting resource for the physiological studies of neuroreceptors and promising drug leads.
The Savage Six is the name of two different fictional villain groups appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics.
Hanatoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the Grammostola spatulata tarantula. The toxin is mostly known for inhibiting the activation of voltage-gated potassium channels, most specifically Kv4.2 and Kv2.1, by raising its activation threshold.
Huwentoxins (HWTX) are a group of neurotoxic peptides found in the venom of the Chinese bird spider Haplopelma schmidti. The species was formerly known as Haplopelma huwenum, Ornithoctonus huwena and Selenocosmia huwena. While structural similarity can be found among several of these toxins, HWTX as a group possess high functional diversity.

Venom vs. Carnage is a comic book limited series written by Peter Milligan with art by Clayton Crain published by Marvel Comics. It has a total of four issues and has been reprinted in trade paperback form under the title Spider-Man: Venom vs. Carnage. It features the first appearance of the Toxin symbiote.
Oxotoxins, or oxytoxins, are a group of neurotoxins present in the venom of lynx spiders belonging to the genus Oxyopes, hence the name oxytoxin. They are disulfide-rich peptides. Only two types are so far reported from two different species, the larger oxytoxin 1 (OxyTx1) from Oxyopes kitabensis, and the smaller oxytoxin 2 (OxyTx2) from Oxyopes lineatus. OxyTx1, the first known oxytoxin, was discovered in 2002. It was found to enhance the lethal efficacy of the spider venom by acting together with oxyopinins. It is composed of 69 amino acid residue, which are cross-linked by five disulfide bridges. It is a large peptide having a molecular mass of 8059.2 Da; but shows the size of 9,109.4 Da due to the presence of disulfide bridges. It is a potent insecticide, but non-toxic to mice up to 1 μg/20-g mouse. It acts synergistically with oxyopinins of the same venom to increase the insecticidal effect.
Plectreurys tristis is a species of venomous spiders commonly known as primitive hunting spiders belonging to a family of plectreurid spiders. They produce a venom that contains a group of insecticidal peptides called plectoxins. They are found in western North America, Central America and Mexico.





