Related Research Articles

Attila, frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central and Eastern Europe.

The Ostrogoths were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great.
Year 454 (CDLIV) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aetius and Studius. The denomination 454 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians, were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity who are best known for their short-lived 5th-century kingdom upon the Roman frontier, near present-day Krems an der Donau in Austria. This kingdom, like those of the neighbouring Heruli and Scirii, first appears in records after the death of Attila in 453. The Rugii, Heruli, Scirii and others are believed to have moved into this region from distant homelands under pressure from the Huns, and become part of Attila's Hunnic empire which also moved and came to be based in this region. The Rugii were subsequently part of the alliance which defeated Attila's sons and the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Nedao in 454, giving their kingdom independence. In 469 they were part of a similar alliance who lost to the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Bolia, weakening their kingdom significantly.

The Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, also called the Battle of the Campus Mauriacus, Battle of Châlons, Battle of Troyes or the Battle of Maurica, took place on June 20, 451 AD, between a coalition, led by the Roman general Flavius Aetius and the Visigothic king Theodoric I, against the Huns and their vassals, commanded by their king, Attila. It proved to be one of the last major military operations of the Western Roman Empire, although Germanic foederati composed the majority of the coalition army. The exact strategic significance is disputed. Historians generally agree that the siege of Aurelianum was the decisive moment in the campaign and stopped the Huns' attempt to advance any further into Roman territory or establish vassals in Roman Gaul. However, the Huns successfully looted and pillaged much of Gaul and crippled the military capacity of the Romans and Visigoths. Attila died only two years later, in 453. After the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD, the coalition of the Huns and the incorporated Germanic vassals gradually disintegrated.

The Gepids were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals.

The Battle of Nedao was fought in Pannonia in 454 CE between the Huns and their former Germanic vassals. Nedao is believed to be a tributary of the Sava River.
Mundus or Mundo was a Barbarian commander of Gepid, Hun, and/or Gothic origins. He appears to have been the son of the Gepid king Giesmus. In the early 500s he commanded a group of bandits in Pannonia, eventually allying himself to the Ostrogothic king Theodoric the Great. After Theodoric's death in 526, Mundus entered Byzantine service under emperor Justinian I, fighting in the Balkans, defending Justinian during the Nika riots, and fighting in the first stage of the Gothic War, during which he died in 536.

Hlöðskviða, known in English as The Battle of the Goths and Huns and occasionally known by its German name Hunnenschlachtlied, is an Old Norse heroic poem found in Hervarar saga ok Heiðreks. Many attempts have been made to try to fit it with known history, but it is an epic poem, telescoping and fictionalising history to a large extent; some verifiable historical information from the time are place names, surviving in Old Norse forms from the period 750–850, but it was probably collected later in Västergötland.

The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
Ernak was the last known ruler of the Huns, and the third son of Attila. After Attila's death in AD 453, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in AD 454, and probably ruled simultaneously over Huns in dual kingship with his brother Dengizich, but in separate divisions in separate lands.
Dengizich, was a Hunnic ruler and son of Attila. After Attila's death in 453 AD, his empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in 454 AD, and probably ruled simultaneously over the Huns in dual kingship with his brother Ernak, but separate divisions in separate lands.
Valamir or Valamer was an Ostrogothic king in the former Roman province of Pannonia from AD 447 until his death. During his reign, he fought alongside the Huns against the Roman Empire and then, after Attila the Hun's death, fought against the Huns to consolidate his independent control over a large group of Goths.

Ellac was the oldest son of Attila (434–453) and Kreka. After Attila's death in 453 AD, his empire crumbled, and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He ruled briefly and died at the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD. Ellac was succeeded by his brothers, Dengizich and Ernak.

The Turcilingi were an obscure barbarian people, or possibly a clan or dynasty, who appear in historical sources relating to Middle Danubian peoples who were present in Italy during the reign of Romulus Augustulus (475–76). Their only known leader was Odoacer (Odovacar), but he was described as a ruler of several ethnic groups.

Balamber was ostensibly a chieftain of the Huns, mentioned by Jordanes in his Getica. Jordanes simply called him "king of the Huns" and writes the story of Balamber crushing the tribes of the Ostrogoths in the 370s; somewhere between 370 and more probably 376 AD.
The Battle of Bassianae took place between the Ostrogoths and the Huns in 468. Recovering from the defeat at Nedao in 454, the Hunnic leader Dengizich launched an invasion across the Danube with a large Hun force, but was defeated by the Ostrogothic king Valamir. Jordanes writes that in turn the Huns "for ever after" left the Goths in peace.
The Battle of Bolia took place in 468 between the Ostrogoths and a coalition of Germanic tribes in the Roman province of Pannonia. It was fought on the south side of the Danube near its confluence with the river Bolia, in present-day Hungary. The Ostrogoths won, achieving supremacy in Pannonia, but soon migrated south towards richer lands.
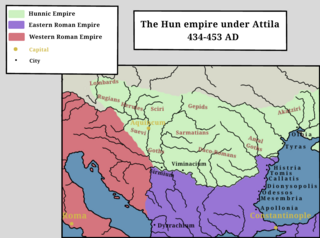
The history of the Huns spans the time from before their first secure recorded appearance in Europe around 370 AD to after the disintegration of their empire around 469. The Huns likely entered Western Asia shortly before 370, from Central Asia: they first conquered the Goths and the Alans, pushing a number of tribes to seek refuge within the Roman Empire. In the following years, the Huns conquered most of the Germanic and Scythian tribes outside of the borders of the Roman Empire. They also launched invasions of both the Asian provinces of Rome and the Sasanian Empire in 375. Under Uldin, the first Hunnic ruler named in contemporary sources, the Huns launched a first unsuccessful large-scale raid into the Eastern Roman Empire in Europe in 408. From the 420s, the Huns were led by the brothers Octar and Ruga, who both cooperated with and threatened the Romans. Upon Ruga's death in 435, his nephews Bleda and Attila became the new rulers of the Huns, and launched a successful raid into the Eastern Roman Empire before making peace and securing an annual tribute and trading raids under the Treaty of Margus. Attila appears to have killed his brother, and became sole ruler of the Huns in 445. He would go on to rule for the next eight years, launching a devastating raid on the Eastern Roman Empire in 447, followed by an invasion of Gaul in 451. Attila is traditionally held to have been defeated in Gaul at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, however some scholars hold the battle to have been a draw or Hunnic victory. The following year, the Huns invaded Italy and encountered no serious resistance before turning back.
Hunimund was a leader – variously described by Jordanes as dux and as rex – of a group of Suebi.
References
- ↑ Nic Fields, The Hun: Scourge of God AD 375-565, (Osprey, 2006), 16.
- ↑ Gudmund Schütte, Our Forefathers the Gothonic Nations vol. 2 (trans. 1933), p. 22.
- ↑ Mundo was called both a Gepid and a Hun, and was probably a descendant of both Attila and Ardaric; Mundo was the son of Giesmos, a son of Attila who had married a daughter of Ardaric's. (Kim 2013:p. 94).