
The Center for Nanoscale Materials is one of five Nanoscale Science Research Centers the United States Department of Energy sponsors. The Center is at Argonne National Laboratory location in Lemont, Illinois.
The hydrogen economy is the use of hydrogen as a fuel, particularly for electricity production and hydrogen vehicles; and using hydrogen for long term energy storage and for long distance transport of low-carbon energy.
Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel when burned with oxygen. It can be used in electrochemical cells or internal combustion engines to power vehicles or electric devices. It has begun to be used in commercial fuel cell vehicles such as passenger cars, and has been used in fuel cell buses for many years. It is also used as a fuel for the propulsion of spacecraft.

The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), located in Golden, Colorado, specializes in renewable energy and energy efficiency research and development. NREL is a government-owned, contractor-operated facility, and is funded through the United States Department of Energy. This arrangement allows a private entity to operate the lab on behalf of the federal government. NREL receives funding from Congress to be applied toward research and development projects. NREL also performs research on photovoltaics (PV) under the National Center for Photovoltaics. NREL has a number of PV research capabilities including research and development, testing, and deployment. NREL's campus houses several facilities dedicated to PV research.
In the 19th century, it was observed that the sunlight striking certain materials generates detectable electric current - the photoelectric effect. This discovery has laid the foundation of solar cells. Solar cells have gone on to be used in many applications. They have historically been used in situations where electrical power from the grid was unavailable.
Hybrid solar cells combine advantages of both organic and inorganic semiconductors. Hybrid photovoltaics have organic materials that consist of conjugated polymers that absorb light as the donor and transport holes. Inorganic materials in hybrid cells are used as the acceptor and electron transporter in the structure. The hybrid photovoltaic devices have a potential for not only low-cost by roll-to-roll processing but also for scalable solar power conversion.

Photovoltaic solar panels absorb sunlight as a source of energy to generate electricity. A photovoltaic (PV) module is a packaged, connected assembly of typically 6x10 photovoltaic solar cells. Photovoltaic modules constitute the photovoltaic array of a photovoltaic system that generates and supplies solar electricity in commercial and residential applications.
Nanochemistry is the combination of chemistry and nanoscience. Nanochemistry is associated with synthesis of building blocks which are dependent on size, surface, shape and defect properties. Nanochemistry is being used in chemical, materials and physical, science as well as engineering, biological and medical applications. Nanochemistry and other nanoscience fields have the same core concepts but the usages of those concepts are different.
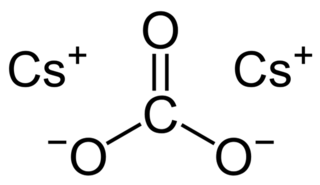
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid compound. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates like potassium and sodium carbonates, although it remains quite insoluble in other organic solvents such as toluene, p-xylene, and chlorobenzene. This compound is used in organic synthesis as a base. It also appears to have applications in energy conversion.
Over the past few decades, the fields of science and engineering have been seeking to develop new and improved types of energy technologies that have the capability of improving life all over the world. In order to make the next leap forward from the current generation of technology, scientists and engineers have been developing energy applications of nanotechnology. Nanotechnology, a new field in science, is any technology that contains components smaller than 100 nanometers. For scale, a single virus particle is about 100 nanometers in width.
The Waterloo Institute for Nanotechnology (WIN) is located at the University of Waterloo and is co-located with the Institute for Quantum Computing in the Mike and Ophelia Lazaridis Quantum-Nano Centre (QNC). WIN is currently headed by Dr. Sushanta Mitra. Its inaugural director was Arthur Carty.

Mark C. Hersam is a professor of Chemistry and Materials Science Engineering at Northwestern University (2000–present) who, according to the National Science Foundation, has made "major breakthrough[s]" in the field of nanotechnology. He is a 2014 recipient of the MacArthur "Genius" Award and a 1996 Marshall Scholar. He is also an Associate Editor of ACS Nano.
Sun-free photovoltaics is a photovoltaics technology which does not require sunlight to produce electricity. This technique was developed by research team at Massachusetts Institute of Technology Photovoltaic cells convert light to electricity most efficiently at specific wavelengths. The surface featured of Sun-free photovoltaics is engineered such that it converts heat energy into the specific wavelengths. This increases the efficiency of existing thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems.

A nanoscale plasmonic motor is a type of nanomotor, converting light energy to rotational motion at nanoscale. It is constructed from pieces of gold sheet in a gammadion shape, embedded within layers of silica. When irradiated with light from a laser, the gold pieces rotate. The functioning is explained by the quantum concept of the plasmon. This type of nanomotor is much smaller than other types, and its operation can be controlled by varying the frequency of the incident light.

The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE is an institute of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Located in Freiburg, Germany, The Institute performs applied scientific and engineering research and development for all areas of solar energy. Fraunhofer ISE has three external branches in Germany which carry out work on solar cell and semiconductor material development: the Laboratory and Service Center (LSC) in Gelsenkirchen, the Technology Center of Semiconductor Materials (THM) in Freiberg, and the Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics (CSP) in Halle. Since 2006, Prof. Dr. Eicke R. Weber is the director of Fraunhofer ISE. With over 1,100 employees, Fraunhofer ISE is the largest institute for applied solar energy research in Europe. The 2012 Operational Budget including investments is 74.3 million euro.
Quantum photoelectrochemistry is the investigation of the quantum mechanical nature of photoelectrochemistry, the subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems, typically through the application of quantum chemical calculations. Quantum photoelectrochemistry provides an expansion of quantum electrochemistry to processes involving also the interaction with light (photons). It therefore also includes essential elements of photochemistry. Key aspects of quantum photoelectrochemistry are calculations of optical excitations, photoinduced electron and energy transfer processes, excited state evolution, as well as interfacial charge separation and charge transport in nanoscale energy conversion systems.

Mercouri Kanatzidis is a Charles E. and Emma H. Morrison Professor of Chemistry and Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University and Senior Scientist at Argonne National Laboratory.
Juan Bisquert, is a physicist known for his contributions to materials and devices for sustainable energy production. He grew up in Dénia, and he is a professor at Jaume I University in Castellón de la Plana. His work on solar cells relates physical principles and modelling of electronic and ionic processes to the interpretation of measurement techniques for the photovoltaic operation. He is the author of more than 350 publications and three books.

Amanda Karen Petford-Long is a Professor of Materials Science and Distinguished Fellow at the Argonne National Laboratory. She is also a Professor of Materials Science at Northwestern University.











