Related Research Articles
In law, the expression trial de novo means a "new trial" by a different tribunal. A trial de novo is usually ordered by an appellate court when the original trial failed to make a determination in a manner dictated by law.

The Court of Cassation is one of the four courts of last resort in France. It has jurisdiction over all civil and criminal matters triable in the judicial system, and is the supreme court of appeal in these cases. It has jurisdiction to review the law, and to certify questions of law, to determine miscarriages of justice. The Court is located in the Palace of Justice in Paris.
An administrative law judge (ALJ) in the United States is a judge and trier of fact who both presides over trials and adjudicates claims or disputes involving administrative law.
The Employment Appeal Tribunal is a tribunal in England and Wales and Scotland, and is a superior court of record. Its primary role is to hear appeals from Employment Tribunals in England, Scotland and Wales. It also hears appeals from decisions of the Certification Officer and the Central Arbitration Committee and has original jurisdiction over certain industrial relations issues.

The Administrative Appeals Tribunal (AAT) is an Australian tribunal that conducts independent merits review of administrative decisions made under Commonwealth laws of the Australian Government. The AAT review decisions made by Australian Government ministers, departments and agencies, and in limited circumstances, decisions made by state government and non-government bodies. They also review decisions made under Norfolk Island laws. It is not a court and not part of the Australian court hierarchy; however, its decisions are subject to review by the Federal Court of Australia and the Federal Circuit Court of Australia. The AAT was established by the Administrative Appeals Tribunal Act 1975 and started operation in 1976.

The Oklahoma Employment Security Commission (OESC) is an independent agency of the state of Oklahoma responsible for providing employment services to the citizens of Oklahoma. The Commission is part of a national network of employment service agencies and is funded by money from the United States Department of Labor. The Commission is also responsible for administering the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 on behalf of the state.
Thomas v. Review Board of the Indiana Employment Security Division, 450 U.S. 707 (1981), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that Indiana's denial of unemployment compensation benefits to petitioner violated his First Amendment right to free exercise of religion, under Sherbert v. Verner (1963).

In California, the Employment Development Department (EDD) is a department of government that administers the Unemployment Insurance (UI), Disability Insurance (DI), and Paid Family Leave (PFL) programs. The department also provides employment service programs and collects the state's labor market information and employment data. The department is one of California's three major taxation agencies, alongside California Department of Tax and Fee Administration and the Franchise Tax Board; in addition to collecting unemployment insurance taxes, the Department administers the reporting, collection, and enforcement of the state's personal income taxes.

The New York State Department of Labor is the department of the New York state government that enforces labor law and administers unemployment benefits.
Iowa Workforce Development is a government agency in the American state of Iowa, responsible for overseeing workplace safety, workers' compensation, unemployment insurance and job training services. It was formed in May 1996.

The Wisconsin Department of Workforce Development (DWD) is an agency of the Wisconsin state government responsible for providing services to Wisconsin workers, employers, and job-seekers to meet Wisconsin's workforce needs. To effect its mission, the Department administers unemployment benefits and workers' compensation programs for the state of Wisconsin; ensures compliance with state laws on wages and discrimination; provides job resources, training, and employment assistance for job-seekers; and engages with employers to help them find and maintain adequate staffing for their businesses.

The 2020 United States Senate election in Arkansas was held on November 3, 2020, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Arkansas, concurrently with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.
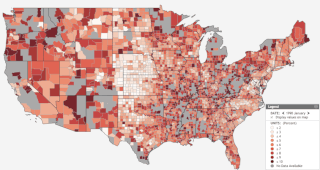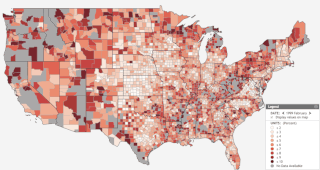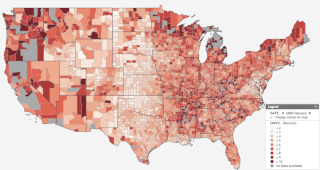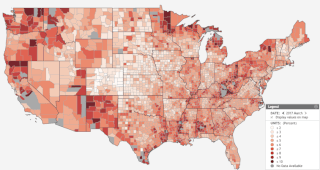
Unemployment insurance in the United States, colloquially referred to as unemployment benefits, refers to social insurance programs which replace a portion of wages for individuals during unemployment. The first unemployment insurance program in the U.S. was created in Wisconsin in 1932, and the federal Social Security Act of 1935 created programs nationwide that are administered by state governments. The constitutionality of the program was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1937.

The California Unemployment Insurance Appeals Board is a quasi-judicial administrative court in the U.S. state of California which hears appeals from determinations on unemployment insurance claims and taxes by the Employment Development Department. It is governed by a five-member Board, of which three are appointed by the Governor, one is appointed by the Speaker of the Assembly and one by the Senate President pro tempore. The Board was initially formed in 1943.

The Judiciary of the Netherlands is the system of courts which interprets and applies the law in the Netherlands.

Charles E. Moritz v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 469 F.2d 466 (1972), was a case before the United States Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit in which the Court held that discrimination on the basis of sex constitutes a violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the United States Constitution. Charles Moritz had claimed a tax deduction for the cost of a caregiver for his invalid mother and the Internal Revenue Service had denied the deduction. The law specifically allowed such a deduction, but only for women and formerly married men, which Moritz was not.

National Coalition for Men v. Selective Service System was a court case that was first decided in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas on February 22, 2019, declaring that requiring men but disallowing women to register for the draft for military service in the United States was unconstitutional. The ruling did not specify which actions the government needed to take to resolve the conflict with the constitution. That ruling was reversed by the Fifth Circuit. In June 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court declined to review the decision by the Court of Appeals.
Kim Hammer is a Missionary Baptist preacher and state legislator in Arkansas. He serves in the Arkansas Senate. He is a Republican. He hosts a weekly conservative talk radio show.

The writ of mandate is a type of extraordinary writ in the U.S. state of California. In California, certain writs are used by the superior courts, courts of appeal and the Supreme Court to command lower bodies, including both courts and administrative agencies, to do or not to do certain things. A writ of mandate may be granted by a court as an order to an inferior tribunal, corporation, board or person, both public and private. Unlike the federal court system, where interlocutory appeals may be taken on a permissive basis and mandamus are usually used to contest recusal decisions, the writ of mandate in California is not restricted to purely ministerial tasks, but can be used to correct any legal error by the trial court. Nonetheless, ordinary writ relief in the Court of Appeal is rarely granted.
References
- ↑ John Moritz (8 June 2017). "Court rules firing merits jobless aid". Arkansas Democrat-Gazette . Retrieved 5 October 2021.
overturned previous decisions by the Appeal Tribunal of the Department of Workforce Services
- 1 2 "Appealing a UI Determination". Arkansas Division of Workforce Services. Archived from the original on 19 February 2021. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
Reference: Ark. Code Annotated Section 11-10-523 through 11-10-530
- ↑ Clinton's Accuser Dismissed From State Job in Arkansas, Associated Press (January 30, 1992): "the appeal tribunal, which hears unemployment cases"
- ↑ Michael R. Wickline (28 August 2014). "Judges toss jobless benefits' denial". Arkansas Democrat-Gazette . Retrieved 5 October 2021.
During an Appeal Tribunal hearing in December 2013
- ↑ Mary Spencer McGowan (1989). "Unemployment Insurance Occasional Paper". UI Research Exchange. U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration. 89 (4): 113.
- ↑ "Arkansas Employment Security Division records, 1937-1992". Arkansas Digital Archives. Arkansas State Archives. Archived from the original on 26 November 2020. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
the Arkansas Employment Security Division [...] until 2005, when the division reorganized to become the Department of Workforce Services
- ↑ John Moritz (8 June 2017). "Court rules firing merits jobless aid". Arkansas Democrat-Gazette . Retrieved 5 October 2021.
overturned previous decisions by the Appeal Tribunal of the Department of Workforce Services
- ↑ Karen Ricketts, Transformation cabinet announced by Governor Hutchinson, KLRT-TV (May 22, 2019).
- ↑ Arkansas governor names cabinet leaders for reduced number of state agencies, Arkansas Democrat-Gazette (May 22, 2019).
- ↑ Tyler Hale, Childers to Head Division of Workforce Services, Arkansas Money and Politics (May 23, 2019).
- ↑ Benjamin Hardy (28 October 2020). "Thousands of unemployment claims remain locked by the state". Van Buren County Democrat. Arkansas Nonprofit News Network. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
tried to challenge the denial but has been told the appeals process is at a standstill due to a backlog at the Arkansas Appeal Tribunal
- ↑ "Arkansas Court Rules Facebook Comments Don't Justify Denial Of Unemployment Benefits". Southwest Times Record . 17 December 2015. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
The Arkansas Appeal Tribunal reversed that decision, but the state Board of Review reversed the Appeal Tribunal, only to have its decision reversed Wednesday by the Court of Appeals