The Three Kingdoms from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the Western Jin dynasty. The short-lived state of Yan on the Liaodong Peninsula, which lasted from 237 to 238, is sometimes considered as a "4th kingdom".

The Yellow Turban Rebellion, alternatively translated as the Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a peasant revolt during the late Eastern Han dynasty of ancient China. The uprising broke out in c. March 184 CE, during the reign of Emperor Ling. Although the main rebellion was suppressed by 185 CE, it took 21 years for full suppression of resistant areas and emerging rebellions by 205 CE. The weakening of the imperial court and the rising political influence of ultra-autonomous regional military-governors, who helped suppress the rebellion, eventually led to rampant warlord dominance and the resultant Three Kingdoms period.

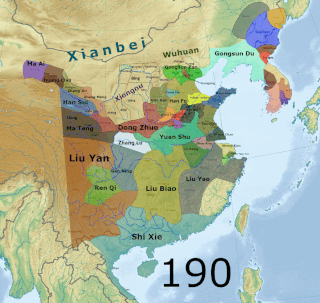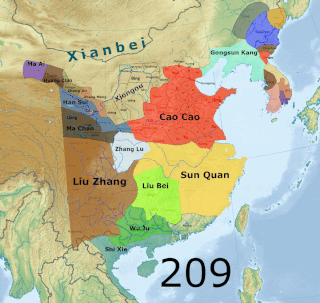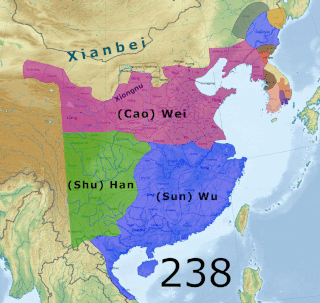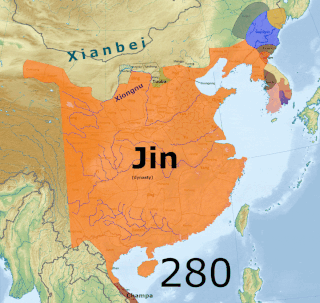
Sun Jian (155–191?), courtesy name Wentai, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He allied himself with Yuan Shu in 190 when warlords from eastern China formed a coalition to oust Dong Zhuo, a tyrannical warlord who held the puppet Emperor Xian in his power. Although he controlled neither many troops nor much land, Sun Jian's personal bravery and resourcefulness were feared by Dong Zhuo, who placed him among Yuan Shao, Yuan Shu and Liu Biao as the most influential men at that time. After the coalition disbanded in the next year, China fell into civil war. In 191, Sun Jian was killed in battle during an offensive campaign against Liu Biao.

Lü Bu, courtesy name Fengxian, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of Imperial China. Originally a subordinate of a minor warlord Ding Yuan, he betrayed and murdered Ding Yuan and defected to Dong Zhuo, the warlord who controlled the Han central government in the early 190s. In 192, he turned against Dong Zhuo and killed him after being instigated by Wang Yun and Shisun Rui, but was later defeated and driven away by Dong Zhuo's followers.
Liu Bian, also known as Emperor Shao of Han and the Prince of Hongnong, was the 13th emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He became emperor around the age of 13 upon the death of his father, Emperor Ling, and ruled briefly from 15 May to 28 September 189 before he was deposed, after which he became known as the "Prince of Hongnong". His emperor title, "Emperor Shao", was also used by other emperors who were in power for very short periods of time. In March 190, he was poisoned by Dong Zhuo, the warlord who deposed him and replaced him with his younger half-brother, Liu Xie.

Emperor Xian of Han, personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220.

Dong Zhuo, courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Originally from Liang Province, Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the eunuch faction by the court officials led by General-in-Chief He Jin.

Yuan Shao, courtesy name Benchu (本初), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other.

The military history of the Three Kingdoms period encompasses roughly a century's worth of prolonged warfare and disorder in Chinese history. After the assassination of General-in-chief He Jin in September 189, the administrative structures of the Han government became increasingly irrelevant. By the time of death of Cao Cao, the most successful warlord of North China, in 220, the Han empire was divided between the three rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu. Due to the ensuing turmoil, the competing powers of the Three Kingdoms era found no shortage of willing recruits for their armies, although press-ganging as well as forcible enlistment of prisoners from defeated armies still occurred. Following four centuries of rule under the Han dynasty, the Three Kingdoms brought about a new era of conflict in China that shifted institutions in favor of a more permanent and selective system of military recruitment. This ultimately included the creation of a hereditary military class as well as increasing reliance on non-Chinese cavalry forces and the end of universal conscription.

He Jin, courtesy name Suigao, was a Chinese military general and politician. He was the military Grand Marshal and regent of the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was an elder half-brother of Empress He, and a maternal uncle of Emperor Shao. In 189, he and his sister shared power as regents when the young Emperor Shao was put on the throne following Emperor Ling's death. During the time, the conflict between He Jin and the influential eunuch faction intensified. The eunuch faction lured He Jin into a trap in the imperial palace and assassinated him. While He Jin's subordinates, led by the warlord Yuan Shao, slaughtered the eunuch faction in revenge, the warlord Dong Zhuo took advantage of the power vacuum to enter the imperial capital Luoyang and seize control of the Han central government. Dong Zhuo's seizure of control and the subsequent breakdown of central command that followed brought forth the beginning of massive civil wars that lasted for nearly a century, during which time the Han dynasty came to an end and the Three Kingdoms period began in its place.
Empress He, personal name unknown, posthumously known as Empress Lingsi, was an empress of the Eastern Han dynasty. She was the second empress consort of Emperor Ling and the mother of Emperor Shao. After the death of Emperor Ling in 189, she became empress dowager when her young son, Liu Bian, became the new emperor. She was caught up in the conflict between her brother, General-in-Chief He Jin, and the eunuch faction, who were both vying for power in the Han imperial court. After He Jin's assassination and the elimination of the eunuch faction, the warlord Dong Zhuo took advantage of the power vacuum to lead his forces into the imperial capital and seize control of the Han central government. Dong Zhuo subsequently deposed Emperor Shao replaced him with Liu Xie and had Empress Dowager He poisoned to death.
The Ten Attendants, also known as the Ten Eunuchs, were a group of influential eunuch-officials in the imperial court of Emperor Ling in Eastern Han China. Although they are often referred to as a group of 10, there were actually 12 of them, and all held the position of zhong changshi in Emperor Ling's imperial court.
Bao Xin (152–192) was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China.

The end of the Han dynasty was the period of Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms era. During the end of the Han dynasty, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow Turban Rebellion (184–205). Meanwhile, the Han Empire's institutions were destroyed by the warlord Dong Zhuo and fractured into regional regimes ruled by various warlords, some of whom were nobles and officials of the Han imperial court. The warlord Cao Cao took control of Emperor Xian and his court in 196 and began gradually reunifying the empire. Cao Cao ostensibly operated under Emperor Xian's rule, though in reality the emperor was a hostage.

The Campaign against Dong Zhuo was a punitive expedition initiated by a coalition of regional officials and warlords against the warlord Dong Zhuo in 190 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. The members of the coalition claimed that Dong had the intention of usurping the throne by holding Emperor Xian hostage and by establishing a strong influence in the imperial court. They justified their campaign as to remove Dong from power. The campaign led to the evacuation of the capital Luoyang and the shifting of the imperial court to Chang'an. It was a prelude to the end of the Han dynasty and, subsequently, the Three Kingdoms period.
He Yong (d.c.191-192), courtesy name Boqiu, was a Chinese politician who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty. He was born in Nanyang and went to the Imperial University in Luoyang where he became known for being a well-connected talent spotter. Exiled to Runan during the Disasters of Partisan Prohibitions incidents in 169 until 184, he would then serve the Han court. Plotting against Dong Zhuo, he would be arrested on a separate matter and took his own life.
The campaign against Yuan Shu was a punitive expedition that took place between 197 and 199 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. The campaign was initiated by the Han government against warlord Yuan Shu after Yuan declared himself emperor of the new Zhong dynasty, an act perceived as treason against Emperor Xian, the nominal Han ruler. The campaign concluded with the defeat of Yuan Shu and collapse of his self-established Zhong dynasty.
The Liang Province rebellion from 184 to 189 started as an insurrection of the Qiang peoples against the Han dynasty in the western province of Liang in the second century AD in China, but the Lesser Yuezhi and sympathetic Han rebels soon joined the cause to wrestle control of the province away from central authority. This rebellion, which closely followed the Yellow Turban Rebellion, was part of a series of disturbances that led to the decline and ultimate downfall of the Han dynasty. Despite receiving relatively little attention in the hands of traditional historians, the rebellion nonetheless had lasting importance as it weakened Han Chinese power in the northwest and prepared that land for a number of non-Han-ruled states in the centuries to come.
Zhang Yang, courtesy name Zhishu, was a Chinese politician and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Originally from Yunzhong Commandery in the north, he eventually became the de facto ruler of Henei Commandery. A brave and lenient man, Zhang Yang would provide refuge for Emperor Xian of Han and be involved in court politics, eventually attaining the rank of Grand Marshal (大司馬). Seeking to help an old friend, he would be assassinated by a subordinate.
Ren Jun, courtesy name Boda, was a military officer serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Leaving his home, he was early follower and trusted aide, he would often oversee the supply lines and was entrusted with implementing the key tuntian farming system.









