Related Research Articles

The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.
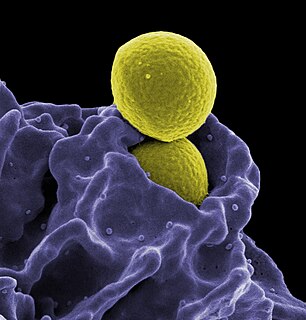
Immunology is a branch of medicine and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences.

A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface.
A cancer vaccine is a vaccine that either treats existing cancer or prevents development of cancer. Vaccines that treat existing cancer are known as therapeutic cancer vaccines or tumor antigen vaccines. Some of the vaccines are "autologous", being prepared from samples taken from the patient, and are specific to that patient.
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis.
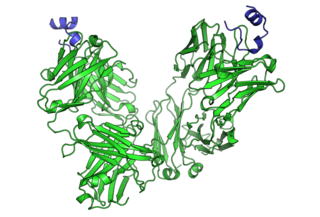
Cancer immunotherapy is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspeciality of oncology.

An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). APCs process antigens and present them to T-cells.
Cross-presentation is the ability of certain professional antigen-presenting cells (mostly dendritic cells) to take up, process and present extracellular antigens with MHC class I molecules to CD8 T cells (cytotoxic T cells). Cross-priming, the result of this process, describes the stimulation of naive cytotoxic CD8+ T cells into activated cytotoxic CD8+ T cells. This process is necessary for immunity against most tumors and against viruses that infect dendritic cells and sabotage their presentation of virus antigens. Cross presentation is also required for the induction of cytotoxic immunity by vaccination with protein antigens, for example, tumour vaccination.
In the human immune system, central tolerance is the process of eliminating any developing T or B lymphocytes that are reactive to self. Through elimination of autoreactive lymphocytes, tolerance ensures that the immune system does not attack self peptides. Lymphocyte maturation occurs in primary lymphoid organs such as the bone marrow and the thymus. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow and T cells mature in the thymus.

Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now bound to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), is transported to the surface of the cell, a process known as presentation, where it can be recognized by a T-cell receptor. If there has been an infection with viruses or bacteria, the cell will present an endogenous or exogenous peptide fragment derived from the antigen by MHC molecules. There are two types of MHC molecules which differ in the behaviour of the antigens: MHC class I molecules (MHC-I) bind peptides from the cell cytosol, while peptides generated in the endocytic vesicles after internalisation are bound to MHC class II (MHC-II). Cellular membranes separate these two cellular environments - intracellular and extracellular. Each T cell can only recognize tens to hundreds of copies of a unique sequence of a single peptide among thousands of other peptides presented on the same cell, because an MHC molecule in one cell can bind to quite a large range of peptides. Predicting which antigens will be presented to the immune system by a certain MHC/HLA type is difficult, but the technology involved is improving.
MHC-restricted antigen recognition, or MHC restriction, refers to the fact that a T cell can interact with a self-major histocompatibility complex molecule and a foreign peptide bound to it, but will only respond to the antigen when it is bound to a particular MHC molecule.

Thy-1 or CD90 is a 25–37 kDa heavily N-glycosylated, glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored conserved cell surface protein with a single V-like immunoglobulin domain, originally discovered as a thymocyte antigen. Thy-1 can be used as a marker for a variety of stem cells and for the axonal processes of mature neurons. Structural study of Thy-1 led to the foundation of the Immunoglobulin superfamily, of which it is the smallest member, and led to some of the initial biochemical description and characterization of a vertebrate GPI anchor and also the first demonstration of tissue specific differential glycosylation.
Immunosenescence is the gradual deterioration of the immune system, brought on by natural age advancement. A 2020 review concluded that the adaptive immune system is affected more than the innate immune system. Immunosenescence involves both the host's capacity to respond to infections and the development of long-term immune memory. Age-associated immune deficiency is found in both long- and short-lived species as a function of their age relative to life expectancy rather than elapsed time. It has been studied in animal models including mice, marsupials and monkeys. Immunosenescence is a contributory factor to the increased frequency of morbidity and mortality among the elderly. Along with anergy and T-cell exhaustion, immunosenescence belongs among the major immune system dysfunctional states. However, while T-cell anergy is a reversible condition, as of 2020 no techniques for immunosenescence reversal had been developed.
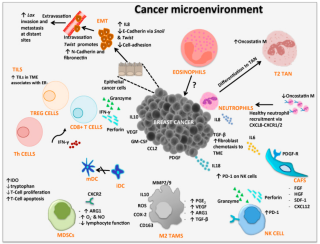
Cancer immunology is an interdisciplinary branch of biology that is concerned with understanding the role of the immune system in the progression and development of cancer; the most well known application is cancer immunotherapy, which utilises the immune system as a treatment for cancer. Cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting are based on protection against development of tumors in animal systems and (ii) identification of targets for immune recognition of human cancer.
Clonal deletion is the removal through apoptosis of B cells and T cells that have expressed receptors for self before developing into fully immunocompetent lymphocytes. This prevents recognition and destruction of self host cells, making it a type of negative selection or central tolerance. Central tolerance prevents B and T lymphocytes from reacting to self. Thus, clonal deletion can help protect individuals against autoimmunity. Clonal deletion is thought to be the most common type of negative selection. It is one method of immune tolerance.
Thymic involution is the shrinking (involution) of the thymus with age, resulting in changes in the architecture of the thymus and a decrease in tissue mass. Thymus involution is one of the major characteristics of vertebrate immunology, and occurs in almost all vertebrates, from birds, teleosts, amphibians to reptiles, though the thymi of a few species of sharks are known not to involute. This process is genetically regulated, with the nucleic material responsible being an example of a conserved sequence — one maintained through natural selection since it arose in a common ancestor of all species now exhibiting it, via a phenomenon known to bioinformaticists as an orthologic sequence homology.
Alfred Singer is an American immunologist who works at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), where he is the Chief of the Experimental Immunology Branch of the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Center for Cancer Research. He is best known for his work regarding lymphocyte development, particularly the differentiation of immature CD4+8+ thymocytes into mature T cells. Singer's work is foundational in the understanding of T cells and MHC-restricted antigen recognition.
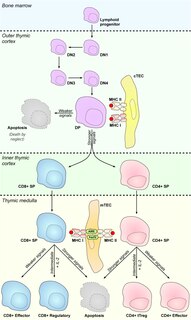
Medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) represent a unique stromal cell population of the thymus which plays an essential role in the establishment of central tolerance. Therefore, mTECs rank among cells relevant for the development of functional mammal immune system.
Antigen transfer in the thymus is the transmission of self-antigens between thymic antigen-presenting cells which contributes to the establishment of T cell central tolerance.
Dr. Misty R. Jenkins is an Australian scientist known for her research into lymphocytes and cancer treatment.
References
- ↑ American Men & Women of Science: Q-S - Page 12 (21 ed.). Thomson Gale. 2003. p. 121. ISBN 978-0787665234.
- ↑ "Arnold E. Reif". The Wellesley Townsman. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ↑ Reif A., Allen J. (1964). "The AKR thymic antigen and its distribution in leukemias and nervous tissue". J. Exp. Med. 120 (3): 413–433. doi:10.1084/jem.120.3.413. PMC 2137766 . PMID 14207060.
- ↑ "Cell surface antigen Thy-1 : immunology, neurology, and therapeutic applications / edited by Arnold E. Reif, Michael Schlesinger - Trove". trove.nla.gov.au. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ Reif A., Allen J. (1966). "Mouse Thymic Iso-antigens". Nature. 209 (5022): 521–523. doi:10.1038/209521b0. PMID 5919593.
- ↑ h-index
- ↑ "Immunity and cancer in man : an introduction / edited by Arnold E. Reif. - Trove". trove.nla.gov.au. Retrieved 2021-09-13.
- ↑ "Immunity to cancer / edited by Arnold E. Reif, Malcolm S. Mitchell - Trove". trove.nla.gov.au. Retrieved 2021-09-13.